Chapter 3
... The theory that pieces of the lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection Plate Tectonics currents in the mantle A break in Earth’ crust along which rocks move Fault A deep valley that forms where two plates move apart Rift Valley Key Idea: Convection currents in the mantle are the forc ...
... The theory that pieces of the lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection Plate Tectonics currents in the mantle A break in Earth’ crust along which rocks move Fault A deep valley that forms where two plates move apart Rift Valley Key Idea: Convection currents in the mantle are the forc ...
INSTRUCTIONAL OVERVIEW Teacher_Susan Steele____ Class
... SC-07-2.3.1 Students will make inferences and predictions related to changes in the Earth’s surface or atmosphere based on data/evidence. The Earth’s processes we see today, including erosion, movement of lithosphere plates and changes in atmospheric composition, are predictable and similar to those ...
... SC-07-2.3.1 Students will make inferences and predictions related to changes in the Earth’s surface or atmosphere based on data/evidence. The Earth’s processes we see today, including erosion, movement of lithosphere plates and changes in atmospheric composition, are predictable and similar to those ...
WASL Review Homework #3
... d. You may look at a variety of sources for answers but do not copy from other students or plagiarize. e. Neatness counts! f. Label all drawings and tables. Include titles on drawings and tables. g. Include units with numbers throughout the assignment. h. Be thorough and give explanations! ...
... d. You may look at a variety of sources for answers but do not copy from other students or plagiarize. e. Neatness counts! f. Label all drawings and tables. Include titles on drawings and tables. g. Include units with numbers throughout the assignment. h. Be thorough and give explanations! ...
Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection
... What does a volcano tell us about what is happening in the Earth’s Interior? -The Earth releases tremendous amounts of energy from its Inner and Outer Cores in a controlled manner by way of tectonic processes. - These processes create changes to existing land and produce new land formation. -Volcano ...
... What does a volcano tell us about what is happening in the Earth’s Interior? -The Earth releases tremendous amounts of energy from its Inner and Outer Cores in a controlled manner by way of tectonic processes. - These processes create changes to existing land and produce new land formation. -Volcano ...
Welcome to the Segment One Final Review
... Centrosphere: Center of the Earth. Inner and outer core – both iron. Outer core is liquid, inner core is ...
... Centrosphere: Center of the Earth. Inner and outer core – both iron. Outer core is liquid, inner core is ...
Plate Tectonics Continued
... Pangaea. As we travel through history, the continents move apart and new oceanic crust is formed between the continents. The earth’s magnetic polarity is reversing throughout history as well. Magnetite in the rock will orient with the earth’s polarity until the rock hardens. Show magnetite’s orienta ...
... Pangaea. As we travel through history, the continents move apart and new oceanic crust is formed between the continents. The earth’s magnetic polarity is reversing throughout history as well. Magnetite in the rock will orient with the earth’s polarity until the rock hardens. Show magnetite’s orienta ...
Instructions: Earth`s Layers Questions
... The seismometers showed scientists that that earthquakes, volcanoes, and other active geologic features for the most part aligned along distinct belts around the world, and those belts defined the edges of tectonic plates. This supported the theory of plate tectonics, which suggests that the surface ...
... The seismometers showed scientists that that earthquakes, volcanoes, and other active geologic features for the most part aligned along distinct belts around the world, and those belts defined the edges of tectonic plates. This supported the theory of plate tectonics, which suggests that the surface ...
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name
... The seismometers showed scientists that that earthquakes, volcanoes, and other active geologic features for the most part aligned along distinct belts around the world, and those belts defined the edges of tectonic plates. This supported the theory of plate tectonics, which suggests that the surface ...
... The seismometers showed scientists that that earthquakes, volcanoes, and other active geologic features for the most part aligned along distinct belts around the world, and those belts defined the edges of tectonic plates. This supported the theory of plate tectonics, which suggests that the surface ...
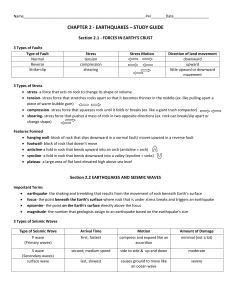
CHAPTER 2 - EARTHQUAKES – STUDY GUIDE
... hanging wall- block of rock that slips downward in a normal fault/ moves upward in a reverse fault footwall- block of rock that doesn’t move anticline-a fold in rock that bends upward into an arch (anticline = arch) syncline- a fold in rock that bends downward into a valley (syncline = sinks ...
... hanging wall- block of rock that slips downward in a normal fault/ moves upward in a reverse fault footwall- block of rock that doesn’t move anticline-a fold in rock that bends upward into an arch (anticline = arch) syncline- a fold in rock that bends downward into a valley (syncline = sinks ...
Plates are large rigid slabs on Earth`s surface. Interact at boundaries
... not appear below this depth either. The lower mantle convection heats the upper mantle, but there doesn’t seem to be mixing between the two zones. There is a sharp seismic boundary between the two. The core is of different composition than the mantle. The core is metallic, and the outer core i ...
... not appear below this depth either. The lower mantle convection heats the upper mantle, but there doesn’t seem to be mixing between the two zones. There is a sharp seismic boundary between the two. The core is of different composition than the mantle. The core is metallic, and the outer core i ...
revised_midterm_guide
... melting have had in determining the Earth’s overall composition and internal structure) isostasy (give evidence that isostasy occurs) how paleomagnetism is recorded in rocks and how it was crucial in developing the "seafloor spreading" concept how the evidence for seafloor spreading and contin ...
... melting have had in determining the Earth’s overall composition and internal structure) isostasy (give evidence that isostasy occurs) how paleomagnetism is recorded in rocks and how it was crucial in developing the "seafloor spreading" concept how the evidence for seafloor spreading and contin ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide
... 41 – 44. Identify the features labeled in figure 7-1. Ch 8: Earthquakes 45. A zone of weakness or a break in Earth’s crust is known as what? 46. Where do most present-day faults occur? 47. A tectonic plate boundary where colliding plates slide past each other (such as the San Andreas fault in Califo ...
... 41 – 44. Identify the features labeled in figure 7-1. Ch 8: Earthquakes 45. A zone of weakness or a break in Earth’s crust is known as what? 46. Where do most present-day faults occur? 47. A tectonic plate boundary where colliding plates slide past each other (such as the San Andreas fault in Califo ...
Earth’s Structure
... below the earth’s surface, the P waves slow down, and the S waves disappear. • This indicates that there is a liquid section that begins 2,900 Km beneath the earth’s surface. ...
... below the earth’s surface, the P waves slow down, and the S waves disappear. • This indicates that there is a liquid section that begins 2,900 Km beneath the earth’s surface. ...
Earth Structure
... TASK 1 EARTH’S STRUCTURE The earth has a layered structure of crust (two main types), mantle, outer and inner core, each layer having a distinctive thickness, composition, density and physical state. Write notes using your textbooks (ES 1, ES 2 and ES 3) about each layer in the earth. TASK 2 EVIDENC ...
... TASK 1 EARTH’S STRUCTURE The earth has a layered structure of crust (two main types), mantle, outer and inner core, each layer having a distinctive thickness, composition, density and physical state. Write notes using your textbooks (ES 1, ES 2 and ES 3) about each layer in the earth. TASK 2 EVIDENC ...
Why do volcanoes erupt?
... Magma is a mixture of molten or semi-molten rock, solid rock and gases formed from the partial melting of the crust and/or mantle. Most of the world’s 550 active volcanoes on Earth are located along the margins of adjacent plates. When two plates collide at a destructive plate boundary, subduction w ...
... Magma is a mixture of molten or semi-molten rock, solid rock and gases formed from the partial melting of the crust and/or mantle. Most of the world’s 550 active volcanoes on Earth are located along the margins of adjacent plates. When two plates collide at a destructive plate boundary, subduction w ...
Quiz Analysis Unit 4: Plate Tectonics
... 5.2.7 Describe how scientists have inferred the structure of inner Earth 5.2.8 Describe how convection provides the mechanism to cause plate movement ...
... 5.2.7 Describe how scientists have inferred the structure of inner Earth 5.2.8 Describe how convection provides the mechanism to cause plate movement ...
MovingPlates
... They release small particles. Certain heavy elements in the core, like Uranium, decay in such a way that they actually give off radiation. Gamma rays given off by decaying heavy elements in the core heat it up, like a flame heats a pot of soup. ...
... They release small particles. Certain heavy elements in the core, like Uranium, decay in such a way that they actually give off radiation. Gamma rays given off by decaying heavy elements in the core heat it up, like a flame heats a pot of soup. ...
the thin and solid outermost layer of Earth above the mantle
... Bubble in the correct answer on your scantron. 1. Continental Drift is a. the hypothesis that a single large landmass broke up into smaller landmasses to form the continents, which then drifted to their present locations; the movement of continents b. the theory that explains how large pieces of Ear ...
... Bubble in the correct answer on your scantron. 1. Continental Drift is a. the hypothesis that a single large landmass broke up into smaller landmasses to form the continents, which then drifted to their present locations; the movement of continents b. the theory that explains how large pieces of Ear ...
Catastrophic Events
... The Mediterranean-Himalayan Belt of earthquake and volcanic activity extends from west of Indonesia through the Himalayas in Asia and the Mediterranean region. Earthquake waves help scientists to construct hypotheses about the structure of the earth’s interior. The earth has layers, including a crus ...
... The Mediterranean-Himalayan Belt of earthquake and volcanic activity extends from west of Indonesia through the Himalayas in Asia and the Mediterranean region. Earthquake waves help scientists to construct hypotheses about the structure of the earth’s interior. The earth has layers, including a crus ...
Plate Tectonics
... between Eismitte and West camp. It had been buried (by Villumsen) with great care and a pair of skis marked the grave site. Wegener had been fifty years of age and a heavy smoker and it was believed that he had died of heart failure brought on by overexertion. His body was reburied in the same spot ...
... between Eismitte and West camp. It had been buried (by Villumsen) with great care and a pair of skis marked the grave site. Wegener had been fifty years of age and a heavy smoker and it was believed that he had died of heart failure brought on by overexertion. His body was reburied in the same spot ...
earth jeopardy
... 10-The atmosphere surrounding Earth helps to maintain the various climates found around the world and keeps Earth from becoming extremely cold all over. How does the atmosphere help to keep Earth insulated and warm? a) The atmosphere creates heat as Earth moves through space, helping to insulate Ea ...
... 10-The atmosphere surrounding Earth helps to maintain the various climates found around the world and keeps Earth from becoming extremely cold all over. How does the atmosphere help to keep Earth insulated and warm? a) The atmosphere creates heat as Earth moves through space, helping to insulate Ea ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.