File - 10th Grade Science ABHS
... Interpreting rocks formations The present Using Steno’s ideas, you can begin to describe the history of a rock formation. explains the past Another important idea, developed by Scottish geologist James Hutton (1726-97), is that the present explains the past. In other words, if you understand the geo ...
... Interpreting rocks formations The present Using Steno’s ideas, you can begin to describe the history of a rock formation. explains the past Another important idea, developed by Scottish geologist James Hutton (1726-97), is that the present explains the past. In other words, if you understand the geo ...
Earthquake, Volcano and Mountain Review Sheet
... a. Earthquake: a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault b. Fault: a fracture in Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rock move past each other i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform bo ...
... a. Earthquake: a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault b. Fault: a fracture in Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rock move past each other i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform bo ...
Earthquakes - thorntonso
... devising her system of classifying stars by their spectra, she cataloged over 10,000 stars within the next nine years. Her duties were expanded and she was put in charge of dozens of young women hired to do mathematical computations (as now done by computers). The type of star she discovered will be ...
... devising her system of classifying stars by their spectra, she cataloged over 10,000 stars within the next nine years. Her duties were expanded and she was put in charge of dozens of young women hired to do mathematical computations (as now done by computers). The type of star she discovered will be ...
GENERAL SCIENCE 1110L LAB LAB 9: Sea Floor Spreading
... The pattern of sea floor spreading can be observed by studying the magnetic field of the rock on the sea floor. At the mid-ocean ridge, magma rises up from the mantle below and cools. As it continues to cool, iron in the rock aligns itself with the magnetic field of the Earth, much like the needle i ...
... The pattern of sea floor spreading can be observed by studying the magnetic field of the rock on the sea floor. At the mid-ocean ridge, magma rises up from the mantle below and cools. As it continues to cool, iron in the rock aligns itself with the magnetic field of the Earth, much like the needle i ...
Quake moved Japan coast 8 feet, shifted Earth`s axis
... "At this point, we know that one GPS station moved (8 feet), and we have seen a map from GSI (Geospatial Information Authority) in Japan showing the pattern of shift over a large area is consistent with about that much shift of the land mass," said Kenneth Hudnut, a geophysicist with the U.S. Geolog ...
... "At this point, we know that one GPS station moved (8 feet), and we have seen a map from GSI (Geospatial Information Authority) in Japan showing the pattern of shift over a large area is consistent with about that much shift of the land mass," said Kenneth Hudnut, a geophysicist with the U.S. Geolog ...
File
... When two oceanic plates collide, one dips below the other Trenches curve due to earth’s spherical shape. ...
... When two oceanic plates collide, one dips below the other Trenches curve due to earth’s spherical shape. ...
ESVolcanoes - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸ Magma rises through the fractures and comes to the surface along long, narrow cracks called __________________________________. Most volcanic eruptions along the mid-ocean ridges go unnoticed. (Exception: _________________________________) Iceland is a part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that _____ ...
... ▸ Magma rises through the fractures and comes to the surface along long, narrow cracks called __________________________________. Most volcanic eruptions along the mid-ocean ridges go unnoticed. (Exception: _________________________________) Iceland is a part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that _____ ...
TODAY`S ANNOUNCEMENTS - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... The stress in the Earth’s crust has been relieved by large and small earthquakes, leaving a gap in the zone of most danger. Scientists are able to image where the tectonic plates are in contact, and there is a gap between them After a certain amount of time, movement on the San Andreas Fault may bec ...
... The stress in the Earth’s crust has been relieved by large and small earthquakes, leaving a gap in the zone of most danger. Scientists are able to image where the tectonic plates are in contact, and there is a gap between them After a certain amount of time, movement on the San Andreas Fault may bec ...
Urška Slivšek, 1.E GIMB PACIFIC NORTHWEST OVERDUE FOR A
... A fresh look at the quake history of the Pacific Northwest suggests a big quake may be right around the corner. By bringing together the data from the ocean and coastal marshes into a geophysical model that takes into account how the crust bows upwards between quakes, the researchers have confirmed ...
... A fresh look at the quake history of the Pacific Northwest suggests a big quake may be right around the corner. By bringing together the data from the ocean and coastal marshes into a geophysical model that takes into account how the crust bows upwards between quakes, the researchers have confirmed ...
Plate Tectonics - Cloudfront.net
... affect Earth’s surface at the plate boundaries and causes them to move. Plates move in 3 ways: 1. slide past each other 2. move apart (divergent) 3. collide (convergent) ...
... affect Earth’s surface at the plate boundaries and causes them to move. Plates move in 3 ways: 1. slide past each other 2. move apart (divergent) 3. collide (convergent) ...
THERMAL CONVECTION
... 2. Next, make a cube out of a piece of silly putty. The silly putty can be thought of as an elastic solid for short-duration stresses (if you roll it into a ball, it will bounce off the floor, similar to a rubber ball, if dropped), and a viscous fluid for longer time processes (note also the viscosi ...
... 2. Next, make a cube out of a piece of silly putty. The silly putty can be thought of as an elastic solid for short-duration stresses (if you roll it into a ball, it will bounce off the floor, similar to a rubber ball, if dropped), and a viscous fluid for longer time processes (note also the viscosi ...
Midterm Exam
... Because they float on the oceans Because they float on Earth’s liquid mantle Because of “trench-pull” and “ridge-push forces” ...
... Because they float on the oceans Because they float on Earth’s liquid mantle Because of “trench-pull” and “ridge-push forces” ...
Geography - Bure Valley School
... Composite volcanoes, sometimes known as strato volcanoes, are steep sided cones formed from layers of ash and [lava] flows. The eruptions from these volcanoes may be a pyroclastic flow rather than a flow of lava. A pyroclastic flow is a superheated mixture of hot steam, ash, rock and dust. A pyrocla ...
... Composite volcanoes, sometimes known as strato volcanoes, are steep sided cones formed from layers of ash and [lava] flows. The eruptions from these volcanoes may be a pyroclastic flow rather than a flow of lava. A pyroclastic flow is a superheated mixture of hot steam, ash, rock and dust. A pyrocla ...
Convection and the Mantle
... the surface, the warm soup spreads out and cools, becoming denser. Then gravity pulls this cooler, denser soup down to the bottom, where it is heated again and begins to rise. This flow that transfers heat within a fluid is called a convection current. The heating and cooling of the fluid, changes i ...
... the surface, the warm soup spreads out and cools, becoming denser. Then gravity pulls this cooler, denser soup down to the bottom, where it is heated again and begins to rise. This flow that transfers heat within a fluid is called a convection current. The heating and cooling of the fluid, changes i ...
mid-ocean ridges - River Mill Academy
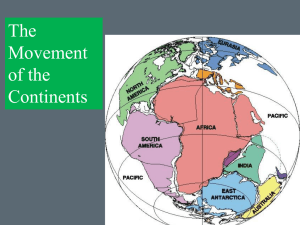
... present locations. Wegener’s theory was not taken seriously because no one could believe that things as large as continents could move and because Wegener could not propose a mechanism which could explain such motion. ...
... present locations. Wegener’s theory was not taken seriously because no one could believe that things as large as continents could move and because Wegener could not propose a mechanism which could explain such motion. ...
Schumann Resonance Frequencies Found Within
... there are monthly variations of the first mode (first harmonic) that range between 7.8 and 8.0 Hz. The duration variation in frequency shift, with a peak around 15 hr UT, has been attributed to either the meridian drift in global lightning activity or global alternation in the height of the ionosphe ...
... there are monthly variations of the first mode (first harmonic) that range between 7.8 and 8.0 Hz. The duration variation in frequency shift, with a peak around 15 hr UT, has been attributed to either the meridian drift in global lightning activity or global alternation in the height of the ionosphe ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.