Weathering and Erosion
... What are landforms? • The natural shapes or features on the Earth’s surface are called landforms. • Many different types of landforms can be found on the Earth. ...
... What are landforms? • The natural shapes or features on the Earth’s surface are called landforms. • Many different types of landforms can be found on the Earth. ...
Chapter 8
... – Convergent plate boundarieswhen plates move toward one another and collide • Oceanic plates + continental plate • 2 continental plates meet ...
... – Convergent plate boundarieswhen plates move toward one another and collide • Oceanic plates + continental plate • 2 continental plates meet ...
the geosphere - Blinklearning
... The geosphere is the solid layer of the Earth, which, in turn, is divided in three layers that are separated by areas known as discontinuities. The deeper a layer is the more density and temperature it presents. The crust · Continental crust: it forms the continental platform, continents and is comp ...
... The geosphere is the solid layer of the Earth, which, in turn, is divided in three layers that are separated by areas known as discontinuities. The deeper a layer is the more density and temperature it presents. The crust · Continental crust: it forms the continental platform, continents and is comp ...
ch01 - earthjay science
... Many radioactive elements can be used as geologic clocks. Each radioactive element decays at its own nearly constant rate. The rate of decay also know as the half-life can be measured. Once this rate is known, geologists can determine the length of time over which decay has been occurring by measuri ...
... Many radioactive elements can be used as geologic clocks. Each radioactive element decays at its own nearly constant rate. The rate of decay also know as the half-life can be measured. Once this rate is known, geologists can determine the length of time over which decay has been occurring by measuri ...
Inquiry 15.1 - Using a Simple Model of Plate
... 8) Can plates ever move without forming new land? If so, when? ____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 9) How do you think colliding plates on the earth cause earthquakes? ___________________________ ...
... 8) Can plates ever move without forming new land? If so, when? ____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 9) How do you think colliding plates on the earth cause earthquakes? ___________________________ ...
Earthquakes
... Alaska has more large earthquakes than the rest of the united states. Scientists first need to know where the faults are and how they behave in order to understand the risk that different areas of the US face. The trans-Alaska pipeline transports about 17% of the nation’s crude oil. Fault systems ca ...
... Alaska has more large earthquakes than the rest of the united states. Scientists first need to know where the faults are and how they behave in order to understand the risk that different areas of the US face. The trans-Alaska pipeline transports about 17% of the nation’s crude oil. Fault systems ca ...
The Atmosphere
... acid (HCl), which was the source of the chloride in sea salt (mostly NaCl). • The volatiles were probably released early in the Earth's history, when it melted and segregated into the core, mantle, and crust. This segregation occurred because of differences in density, the crust being the "lightest" ...
... acid (HCl), which was the source of the chloride in sea salt (mostly NaCl). • The volatiles were probably released early in the Earth's history, when it melted and segregated into the core, mantle, and crust. This segregation occurred because of differences in density, the crust being the "lightest" ...
Lecture 7. Marine Sediments
... First major scientific expedition Globe-encircling voyage Chemical, physical, and biological measurements and collections Disproved Edward Forbes “azoic theory” by collecting sea life from waters as deep as 9000 m ...
... First major scientific expedition Globe-encircling voyage Chemical, physical, and biological measurements and collections Disproved Edward Forbes “azoic theory” by collecting sea life from waters as deep as 9000 m ...
Next Question
... When all the grains of a rock are large and easy to see, we say the rock has a _______ _______ texture. Coarse grained ...
... When all the grains of a rock are large and easy to see, we say the rock has a _______ _______ texture. Coarse grained ...
Chapter 15 Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources “It`s A
... up the surface of the earth. Geological processes that occur on the surface of the earth include erosion and weathering. Tectonic plates have rearranged the earth’s continents and ocean basins over millions of years like pieces of a gigantic jigsaw puzzle. The plates have three types of boundaries. ...
... up the surface of the earth. Geological processes that occur on the surface of the earth include erosion and weathering. Tectonic plates have rearranged the earth’s continents and ocean basins over millions of years like pieces of a gigantic jigsaw puzzle. The plates have three types of boundaries. ...
MS Science - Verona School District
... • When rocks move along a fault, they release energy that travels as vibrations on and in Earth called seismic waves. • These waves originate where rocks first move along the fault, at a location inside Earth called the focus. ...
... • When rocks move along a fault, they release energy that travels as vibrations on and in Earth called seismic waves. • These waves originate where rocks first move along the fault, at a location inside Earth called the focus. ...
Document
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the crust of the Earth is composed of moving plates. These plates move along the lithosphere (Earth’s crust and upper mantle) and the asthenosphere (the plastic-like layer beneath the lithosphere). This theory also says that these plates are always in motion ...
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the crust of the Earth is composed of moving plates. These plates move along the lithosphere (Earth’s crust and upper mantle) and the asthenosphere (the plastic-like layer beneath the lithosphere). This theory also says that these plates are always in motion ...
INTRODUCTION
... 1. Earth’s mantle plays an important role in plate tectonics. Why is the mantle so important to this process? A. Earthquakes occur constantly in the mantle, which causes the plates to move. B. The mantle is made up entirely of liquid rock, on which Earth’s crustal plates can float. C. Heavy metals i ...
... 1. Earth’s mantle plays an important role in plate tectonics. Why is the mantle so important to this process? A. Earthquakes occur constantly in the mantle, which causes the plates to move. B. The mantle is made up entirely of liquid rock, on which Earth’s crustal plates can float. C. Heavy metals i ...
6-8 Plate Tectonics Activity
... Divergent boundaries are found when tectonic plates are moving away from each other. As two plates slide apart, new crust fills in and a rift is created. Many times small volcanoes and earthquakes occur as plates move apart. When two oceanic plate slide apart, seafloor spreading occurs and new ocean ...
... Divergent boundaries are found when tectonic plates are moving away from each other. As two plates slide apart, new crust fills in and a rift is created. Many times small volcanoes and earthquakes occur as plates move apart. When two oceanic plate slide apart, seafloor spreading occurs and new ocean ...
view this article in PDF format.
... placed halfway between adjacent sites of unlike polarity (Figure 2). The local paleomagnetic column is correlated with the GMPTS (Figure 2). Because of the binary nature of polarity zones (normal or reversed), it is essential that the local column be independently calibrated with either an isotopic ...
... placed halfway between adjacent sites of unlike polarity (Figure 2). The local paleomagnetic column is correlated with the GMPTS (Figure 2). Because of the binary nature of polarity zones (normal or reversed), it is essential that the local column be independently calibrated with either an isotopic ...
Earth`s crust is made up of moving plates.
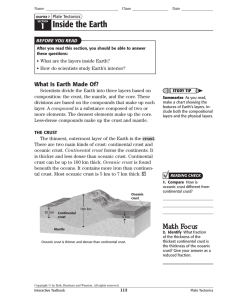
... Then you would travel for 22 h through the outer core, a dense, hot region that is made up mostly of liquid iron and some nickel. The pressure is very high. Like the mantle, the material in the outer core flows. Finally, on the last part of your journey to Earth’s centre, you would travel for 12.5 ...
... Then you would travel for 22 h through the outer core, a dense, hot region that is made up mostly of liquid iron and some nickel. The pressure is very high. Like the mantle, the material in the outer core flows. Finally, on the last part of your journey to Earth’s centre, you would travel for 12.5 ...
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics
... As scientists learned more about sea-floor spreading and magnetic reversals, they formed a theory to explain how continents move. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into many pieces—tectonic plates—that move slowly over the asthenosphere. Tectonic plates move ver ...
... As scientists learned more about sea-floor spreading and magnetic reversals, they formed a theory to explain how continents move. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into many pieces—tectonic plates—that move slowly over the asthenosphere. Tectonic plates move ver ...
Volcanism in Response to Plate Flexure
... An old and cold lithospheric plate behaves elastically and may be flexed because of loading by an ocean island or seamount or by subduction-related plate flexure (21). In the area between sites A and B, the bathymetric high (or outer rise) is aligned parallel to the Japan Trench. The Pacific Plate f ...
... An old and cold lithospheric plate behaves elastically and may be flexed because of loading by an ocean island or seamount or by subduction-related plate flexure (21). In the area between sites A and B, the bathymetric high (or outer rise) is aligned parallel to the Japan Trench. The Pacific Plate f ...
d45 plate boundaries ppt
... • The map on p D42 shows the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes on Earth. • Many of the most active volcanoes are on the edges of the Pacific Ocean, the “Ring of Fire”. • The theory of plate tectonics helps explain this • CHALLENGE QUESTION: How does plate tectonics explain the locations of eart ...
... • The map on p D42 shows the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes on Earth. • Many of the most active volcanoes are on the edges of the Pacific Ocean, the “Ring of Fire”. • The theory of plate tectonics helps explain this • CHALLENGE QUESTION: How does plate tectonics explain the locations of eart ...
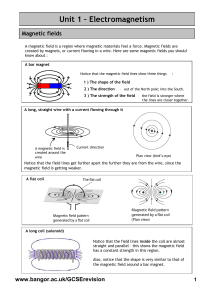
Unit 1 – Electromagnetism
... The mechanisms and processes involved when earthquakes occur are extremely complex. However some of the characteristics of earthquakes can be explained: ...
... The mechanisms and processes involved when earthquakes occur are extremely complex. However some of the characteristics of earthquakes can be explained: ...
Chapter 1, Section 1: What is a Mineral? Pages 4 to 7
... 5. One reason that weathering is so important is because it breaks rock down into fragments or, ______________________________, from which sedimentary rocks are made. 6. Define erosion. _______________________________________________________________________________ 7. Define deposition. ____________ ...
... 5. One reason that weathering is so important is because it breaks rock down into fragments or, ______________________________, from which sedimentary rocks are made. 6. Define erosion. _______________________________________________________________________________ 7. Define deposition. ____________ ...
The Sandbox Experiment - Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
... resistance to sliding (Ff in the diagram). However, because gravity cannot pull the can through the glass plate, there are actually two forces involved: the force pushing the can directly against the glass (the normal force, Fn) and that part of gravity which pulls the can down the slope (the tangen ...
... resistance to sliding (Ff in the diagram). However, because gravity cannot pull the can through the glass plate, there are actually two forces involved: the force pushing the can directly against the glass (the normal force, Fn) and that part of gravity which pulls the can down the slope (the tangen ...
Causes of Volcanic Eruptions
... Boundaries Most volcanic activity on Earth occurs at mid-ocean ridges. The next slide shows how magma forms at divergent boundaries such as those found along midocean ridges. ...
... Boundaries Most volcanic activity on Earth occurs at mid-ocean ridges. The next slide shows how magma forms at divergent boundaries such as those found along midocean ridges. ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.