Econ 2101 Macroeconomic Theory
... a complex market system with no one in charge would work to coordinate all economic activity. This idea became known as Capitalism. - Traditionalism - Centralized Planning - Capitalism and Free Markets ...
... a complex market system with no one in charge would work to coordinate all economic activity. This idea became known as Capitalism. - Traditionalism - Centralized Planning - Capitalism and Free Markets ...
Chapter 4, Section 5
... exchange of goods and services among a group of people • The way people choose to produce and exchange goods is called as economic system – Traditional Economy - trade without money, or “barter” – Command Economy – production determined by government, who also owns the means of production, and does ...
... exchange of goods and services among a group of people • The way people choose to produce and exchange goods is called as economic system – Traditional Economy - trade without money, or “barter” – Command Economy – production determined by government, who also owns the means of production, and does ...
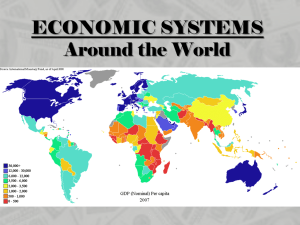
ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
... Production & distribution are governed by supply & demand Most resources owned by private citizens Free enterprise (competition between companies) Individuals & businesses make decisions, not gov’t ...
... Production & distribution are governed by supply & demand Most resources owned by private citizens Free enterprise (competition between companies) Individuals & businesses make decisions, not gov’t ...
Geographical distribution of investments from three leading
... - British domination on seas – Central States cut off from supplies – self-sufficiency & autarky, statesponsored robbery on conquered lands - British dependence on overseas routes – reason for unlimited submarine warfare - rising prices of imports due to surging transport cost - decline of world tra ...
... - British domination on seas – Central States cut off from supplies – self-sufficiency & autarky, statesponsored robbery on conquered lands - British dependence on overseas routes – reason for unlimited submarine warfare - rising prices of imports due to surging transport cost - decline of world tra ...
Name - Midway ISD
... 4. What is the profit motive, and who has it? 5. Capitalism thrives on ___________________. Why? 6. Why is the role of the consumer important in our economy? 7. The role of the government is to act as ________________, ______________, _______________________, and __________________of national goals. ...
... 4. What is the profit motive, and who has it? 5. Capitalism thrives on ___________________. Why? 6. Why is the role of the consumer important in our economy? 7. The role of the government is to act as ________________, ______________, _______________________, and __________________of national goals. ...
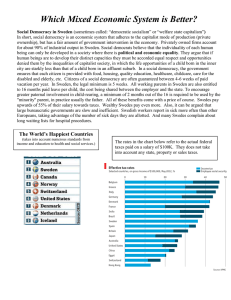
3. Sweden and Canada economics - Social Studies 30-1
... • Probably the closest Canada has come to a pure market system was during the 1920s. – During that decade governments followed Adam Smith's advice, and left the privately owned economy alone. – Because government did little, taxes were low. – Then came the "crash of '29" followed by the Great Depre ...
... • Probably the closest Canada has come to a pure market system was during the 1920s. – During that decade governments followed Adam Smith's advice, and left the privately owned economy alone. – Because government did little, taxes were low. – Then came the "crash of '29" followed by the Great Depre ...
6. Sweden and Canada economics - socialstudies30
... • Probably the closest Canada has come to a pure market system was during the 1920s. – During that decade governments followed Adam Smith's advice, and left the privately owned economy alone. – Because government did little, taxes were low. – Then came the "crash of '29" followed by the Great Depre ...
... • Probably the closest Canada has come to a pure market system was during the 1920s. – During that decade governments followed Adam Smith's advice, and left the privately owned economy alone. – Because government did little, taxes were low. – Then came the "crash of '29" followed by the Great Depre ...
02. economic systems - Development of e
... labour, land and capital. Firms buy these inputs at prices set in the markets. In the output markets, the enterprises sell out the goods and services to the consumers or households. ii) Types of Economy An economy might be designed to depend exclusively either on the market or on government to make ...
... labour, land and capital. Firms buy these inputs at prices set in the markets. In the output markets, the enterprises sell out the goods and services to the consumers or households. ii) Types of Economy An economy might be designed to depend exclusively either on the market or on government to make ...
to LecWk2-2_WWPostwarEcon - b
... When a nation’s internal price structure fails to keep track w/international mkt, the only way to adjust accordingly is through deflation Lowers the cost of all commodities (including wages); hits farmers esp. hard Long cycles of unemployment à underconsumption/underinvestment, crises In an interna ...
... When a nation’s internal price structure fails to keep track w/international mkt, the only way to adjust accordingly is through deflation Lowers the cost of all commodities (including wages); hits farmers esp. hard Long cycles of unemployment à underconsumption/underinvestment, crises In an interna ...
Africa and the Second World War.
... and Democratic ideologies of Britain, ,France and USA. The 2 ideologies were irreconcilable and led to war e.g. Mussolini fascist leader of Italy stated “ The struggle bet the 2 words can permit no compromise, it is either we or they”. Fascism started in Italy and was developed by Mussolini & establ ...
... and Democratic ideologies of Britain, ,France and USA. The 2 ideologies were irreconcilable and led to war e.g. Mussolini fascist leader of Italy stated “ The struggle bet the 2 words can permit no compromise, it is either we or they”. Fascism started in Italy and was developed by Mussolini & establ ...
mixed economy
... The United States is said to have a mixed economy because privately owned businesses and government both play important roles. American capitalism emphasizes private ownership. Private businesses produce most goods and services, and almost two-thirds of the nation's total economic output goes to ind ...
... The United States is said to have a mixed economy because privately owned businesses and government both play important roles. American capitalism emphasizes private ownership. Private businesses produce most goods and services, and almost two-thirds of the nation's total economic output goes to ind ...
The Great Crash
... cities desiring the right to vote, which only further intensified race relations ...
... cities desiring the right to vote, which only further intensified race relations ...
MUSSOLINI`S ECONOMIC POLICIES
... it was hands off period when taxes were cut exports increased and state spending cut. Living standards for all classes rose. However this was true across the world. ...
... it was hands off period when taxes were cut exports increased and state spending cut. Living standards for all classes rose. However this was true across the world. ...
Here
... available services based upon set values and principles. • County governments to have reliable sources of revenue to enable them to govern and deliver services effectively • Consultation and cooperation with national government. ...
... available services based upon set values and principles. • County governments to have reliable sources of revenue to enable them to govern and deliver services effectively • Consultation and cooperation with national government. ...
Greek Crisis
... So what is ordoliberalism? In his book Austerity, the History of a Dangerous Idea, Mark Blyth refers to ordoliberalism as the German twin of neoliberalism.[7] This is true, but the two are fraternal, not identical twins, as they differ in fundamental ways. Unlike for classical liberals in the Anglo- ...
... So what is ordoliberalism? In his book Austerity, the History of a Dangerous Idea, Mark Blyth refers to ordoliberalism as the German twin of neoliberalism.[7] This is true, but the two are fraternal, not identical twins, as they differ in fundamental ways. Unlike for classical liberals in the Anglo- ...
Slide 1
... prices to pay for higher wages, and so on. Which may lead to hyperinflation. • However, Deflation can occur, like when an economy produces more goods than people want, it has to lower prices and cut production. The us tries to maintain a slow but steady rate of economic growth. ...
... prices to pay for higher wages, and so on. Which may lead to hyperinflation. • However, Deflation can occur, like when an economy produces more goods than people want, it has to lower prices and cut production. The us tries to maintain a slow but steady rate of economic growth. ...
Economic Myths and Reform Realities for Germany
... retirement provisions give little incentive to work after reaching retirement age, as working income is partially deducted from the pension, and unemployment insurance needs to be paid. The government is planning changes. They need to come soon. Germany can also boost its female labor force, especia ...
... retirement provisions give little incentive to work after reaching retirement age, as working income is partially deducted from the pension, and unemployment insurance needs to be paid. The government is planning changes. They need to come soon. Germany can also boost its female labor force, especia ...
Ch. 10
... compare and contrast different theories and models of economic development and the relationship between LDCs and relatively developed countries. ...
... compare and contrast different theories and models of economic development and the relationship between LDCs and relatively developed countries. ...
GHSGT_Review_-_Economics
... unlimited wants exceed limited productive resources Trade-offs – alternatives that must be given up when one choice is made over another Opportunity cost – the next best alternative given up when individuals, businesses and governments confront scarcity by making choices ...
... unlimited wants exceed limited productive resources Trade-offs – alternatives that must be given up when one choice is made over another Opportunity cost – the next best alternative given up when individuals, businesses and governments confront scarcity by making choices ...
American Federation of Labor A union established
... The change from man-made to machine-made production, usually at a larger scale for consumption by a home market and for foreign markets. Knights of Labor A union formed by Uriah Stephens and later led by Terence Powderly, it had almost 700,000 members by 1886, composed of both skilled and unskilled ...
... The change from man-made to machine-made production, usually at a larger scale for consumption by a home market and for foreign markets. Knights of Labor A union formed by Uriah Stephens and later led by Terence Powderly, it had almost 700,000 members by 1886, composed of both skilled and unskilled ...
Word
... What is the federal deficit? What were the effects of the Great Depression on government economic policy? What economic policy was the New Deal based on? Define a tariff. What is the role of the Office of Management and Budget? Define a trade surplus. What is the largest free trade zone in t ...
... What is the federal deficit? What were the effects of the Great Depression on government economic policy? What economic policy was the New Deal based on? Define a tariff. What is the role of the Office of Management and Budget? Define a trade surplus. What is the largest free trade zone in t ...
Slide 1
... e.g., international convention for an automated system (expert software) to make financial policy changes as economic conditions change, conducted initially in larger economic countries Single global currency Artificial life—as computers were a key element in the information economy, so too artifici ...
... e.g., international convention for an automated system (expert software) to make financial policy changes as economic conditions change, conducted initially in larger economic countries Single global currency Artificial life—as computers were a key element in the information economy, so too artifici ...
Innovation Policy vs. Industrial Policy
... industrial policy means the infusion of goaloriented, strategic thinking into public economic policy…In more abstract terms, industrial policy is the logical outgrowth of the changing concept of comparative advantage.” --Chalmers Johnson, The Industrial Policy Debate, 1984 ...
... industrial policy means the infusion of goaloriented, strategic thinking into public economic policy…In more abstract terms, industrial policy is the logical outgrowth of the changing concept of comparative advantage.” --Chalmers Johnson, The Industrial Policy Debate, 1984 ...