bush medicine plants factsheet
... companies in Germany and morphine, cocaine and nicotine. Switzerland. treatment and is now known to have Alkaloids in native plants do not seem properties similar to quinine, the anti-malarial Soft corkwood is poisonous to have been important as traditional drug extracted from South American trees. ...
... companies in Germany and morphine, cocaine and nicotine. Switzerland. treatment and is now known to have Alkaloids in native plants do not seem properties similar to quinine, the anti-malarial Soft corkwood is poisonous to have been important as traditional drug extracted from South American trees. ...
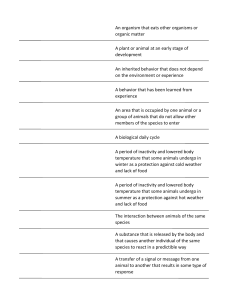
An organism that eats other organisms or organic matter A plant or
... An organism that eats other organisms or organic matter A plant or animal at an early stage of development An inherited behavior that does not depend on the environment or experience A behavior that has been learned from experience An area that is occupied by one animal or a group of animals that do ...
... An organism that eats other organisms or organic matter A plant or animal at an early stage of development An inherited behavior that does not depend on the environment or experience A behavior that has been learned from experience An area that is occupied by one animal or a group of animals that do ...
What Our Common Native Critters Eat
... Raptors (hawks, owls and eagles) are carnivores and eat either birds, small mammals or fish. Scavengers such as vultures, crows and ravens eat mostly carrion, but are also adept at finding human garbage. All of the above diets are the common textbook lists given for these animals, edited somewhat fo ...
... Raptors (hawks, owls and eagles) are carnivores and eat either birds, small mammals or fish. Scavengers such as vultures, crows and ravens eat mostly carrion, but are also adept at finding human garbage. All of the above diets are the common textbook lists given for these animals, edited somewhat fo ...
adaptation - Cloudfront.net
... High altitudes-more red blood cells for oxygen Deep water-flexible rib cages ...
... High altitudes-more red blood cells for oxygen Deep water-flexible rib cages ...
Luke - ayalabme3
... plants in the world. Such as roses, dandelions, and lots more. There is so many plants in the world I can’t believe it ! ...
... plants in the world. Such as roses, dandelions, and lots more. There is so many plants in the world I can’t believe it ! ...
Zoopharmacognosy

Zoopharmacognosy is a behaviour in which non-human animals apparently self-medicate by selecting and ingesting or topically applying plants, soils, insects, and psychoactive drugs to treat or prevent disease.The term derives from roots zoo (""animal""), pharma (""drug""), and gnosy (""knowing"") and was proposed in 1993. The term gained popularity from academic works and in a book by Cindy Engel called Wild Health: How Animals Keep Themselves Well and What We Can Learn from Them.A well-known example of zoopharmacognosy occurs when dogs eat grass to induce vomiting. However, the behaviour is more diverse than this. Animals ingest non-foods such as clay, charcoal and even toxic plants, apparently to prevent parasitic infestation or poisoning. Self-medication in wild animals remains a controversial subject because evidence is mostly circumstantial or anecdotal, however, there are many purported examples. The methods by which animals self-medicate vary, but can be classified according to function as prophylactic (preventative, before infection or poisoning) or therapeutic (after infection, to combat the pathogen or poisoning).