Lecture 4
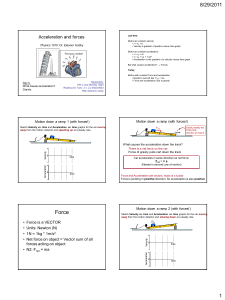
... • Velocity is gradient of position versus time graph Motion at constant acceleration: • v = v0 + at • x = x0 + v0t + ½ at2 • Acceleration is the gradient of a velocity versus time graph But what causes acceleration? Forces ...
... • Velocity is gradient of position versus time graph Motion at constant acceleration: • v = v0 + at • x = x0 + v0t + ½ at2 • Acceleration is the gradient of a velocity versus time graph But what causes acceleration? Forces ...
Ch 08-151
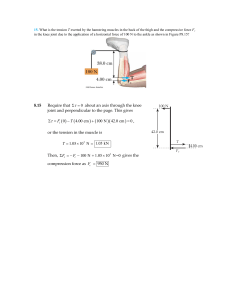
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
... pulley is a uniform solid cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg and an outer radius of 0.0300 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cord does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley. The b ...
For Physics - Career Point Kota
... Two pulses in a stretched string whose centres are initially 8 cm apart are moving towards each other as shown in the figure. The speed of each pulse is 2 cm/s. After 2 second the total energy of the pulses will be – 2 cm/s 2 cm/s 8 cm ...
... Two pulses in a stretched string whose centres are initially 8 cm apart are moving towards each other as shown in the figure. The speed of each pulse is 2 cm/s. After 2 second the total energy of the pulses will be – 2 cm/s 2 cm/s 8 cm ...
25 years of ionospheric modification with space shuttle oms
... at a speed of 3 km/s. The OMS nozzle can be pointed in the ram, wake or out-of-plane relative to the Space Shuttle orbit. The vector addition of the exhaust velocity and the orbit velocity provides possible injections speeds of between 4.7 and 10.7 km/s. When the exhaust impacts the ionosphere, neut ...
... at a speed of 3 km/s. The OMS nozzle can be pointed in the ram, wake or out-of-plane relative to the Space Shuttle orbit. The vector addition of the exhaust velocity and the orbit velocity provides possible injections speeds of between 4.7 and 10.7 km/s. When the exhaust impacts the ionosphere, neut ...
Multiple Choice Conceptual Questions
... with considerable momentum. If it rolls at the same speed but has twice as much mass, its momentum is (a) zero (b) doubled (c) quadrupled (d) unchanged 3) A moving object on which no forces are acting will continue to move with constant (a) acceleration (b) impulse (c) momentum (d) all of these (e) ...
... with considerable momentum. If it rolls at the same speed but has twice as much mass, its momentum is (a) zero (b) doubled (c) quadrupled (d) unchanged 3) A moving object on which no forces are acting will continue to move with constant (a) acceleration (b) impulse (c) momentum (d) all of these (e) ...
Impulse and Momentum
... and the base of the swing has a mass of 153 g. Assume that the swing and bird are originally at rest and that the bird takes off horizontally at 2.00 m/s. If the base can swing freely (without friction) around the pivot, how high will the base of the swing rise above its original level? How many obj ...
... and the base of the swing has a mass of 153 g. Assume that the swing and bird are originally at rest and that the bird takes off horizontally at 2.00 m/s. If the base can swing freely (without friction) around the pivot, how high will the base of the swing rise above its original level? How many obj ...
June 10
... Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the spaces provided on the Answer Booklet. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. ...
... Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the spaces provided on the Answer Booklet. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. ...
chapter4MakingSenseU..
... • F=ΔP/Δt= (calculus) dP/dt where t is time. • F=mΔV/Δt=mA=(calculus) m dV/dt • Rotational momentum of a spinning or orbiting object is known as angular momentum=radial distance x mass x velocity = r mV; L =r×P= r×mV. ...
... • F=ΔP/Δt= (calculus) dP/dt where t is time. • F=mΔV/Δt=mA=(calculus) m dV/dt • Rotational momentum of a spinning or orbiting object is known as angular momentum=radial distance x mass x velocity = r mV; L =r×P= r×mV. ...