Phy 201: General Physics I
... The resistance of a rigid body to changes in its state of rotational motion ( ω ) is called the moment of inertia (or ...
... The resistance of a rigid body to changes in its state of rotational motion ( ω ) is called the moment of inertia (or ...
document
... described at the right could be experiencing a horizontal motion as described below. Noah Formula objects, arguing that the object could not have any horizontal motion if there are only vertical forces acting upon it. Noah claims that the object must be at rest, perhaps on a table or floor. After al ...
... described at the right could be experiencing a horizontal motion as described below. Noah Formula objects, arguing that the object could not have any horizontal motion if there are only vertical forces acting upon it. Noah claims that the object must be at rest, perhaps on a table or floor. After al ...
File
... Momentum, however, can be transferred from one object to another. The law of conservation of momentum states that if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t ...
... Momentum, however, can be transferred from one object to another. The law of conservation of momentum states that if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t ...
5.1 Circular Motion - leo physics website
... Rotor is quite often found in amusement park for visitors to enjoy with. A rotor is a hollow cylindrical room that can be set to rotate about the central vertical axis. A person enters the rotor and stand against the wall. The rotor gradually increases its rotating speed up to a preset one and the f ...
... Rotor is quite often found in amusement park for visitors to enjoy with. A rotor is a hollow cylindrical room that can be set to rotate about the central vertical axis. A person enters the rotor and stand against the wall. The rotor gradually increases its rotating speed up to a preset one and the f ...
what happens when an object changes direction
... a)Let’s turn the question around and ask if we apply a force can we cause a change in direction. Do an experiment with a ball such as a basketball or ball that is tightly blown up used on playgrounds. Roll the ball down a hall, an open space in the classroom or outside on a smooth, flat area. If you ...
... a)Let’s turn the question around and ask if we apply a force can we cause a change in direction. Do an experiment with a ball such as a basketball or ball that is tightly blown up used on playgrounds. Roll the ball down a hall, an open space in the classroom or outside on a smooth, flat area. If you ...
Document
... • An object in uniform circular motion moves at ____________ speed. Its velocity is ___________ to the circle and its acceleration is directed toward the ___________ of the circle. The object experiences ____________ which is directed in the same direction as the acceleration, toward the _________ o ...
... • An object in uniform circular motion moves at ____________ speed. Its velocity is ___________ to the circle and its acceleration is directed toward the ___________ of the circle. The object experiences ____________ which is directed in the same direction as the acceleration, toward the _________ o ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
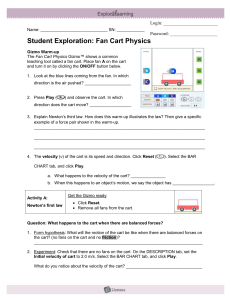
... 3. Explain Newton’s third law. How does this warm-up illustrates the law? Then give a specific example of a force pair shown in the warm-up. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
... 3. Explain Newton’s third law. How does this warm-up illustrates the law? Then give a specific example of a force pair shown in the warm-up. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
1 PHYS1100 Practice problem set, Chapter 4: 4, 8, 14, 17, 19, 23, 40
... PHYS1100 Practice problem set, Chapter 4: 4, 8, 14, 17, 19, 23, 40, 46, 50 ...
... PHYS1100 Practice problem set, Chapter 4: 4, 8, 14, 17, 19, 23, 40, 46, 50 ...
+ Rotational motion about its CM
... and two identical bullets hit into it symmetrically. The angular velocity of system will ________ A. increase; B. decrease; C. remain constant Solution: Total angular momentum of the system is conserved ...
... and two identical bullets hit into it symmetrically. The angular velocity of system will ________ A. increase; B. decrease; C. remain constant Solution: Total angular momentum of the system is conserved ...