Document
... 12.3.2. An object, which is considered a rigid body, is in equilibrium. Which one of the following statements is false when determining the forces and torques acting on the object? a) The linear acceleration or the angular acceleration of the object may not be equal to zero. b) The location of the ...
... 12.3.2. An object, which is considered a rigid body, is in equilibrium. Which one of the following statements is false when determining the forces and torques acting on the object? a) The linear acceleration or the angular acceleration of the object may not be equal to zero. b) The location of the ...
Curriculum Map - Weld RE
... A2. Draw velocity vectors A3. Determine the resultant vector A4, Determine the components of vectors. A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B ...
... A2. Draw velocity vectors A3. Determine the resultant vector A4, Determine the components of vectors. A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B ...
Slide 1
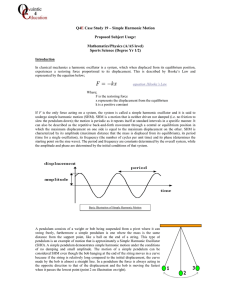
... playground swing longer or shorter when you stand rather than sit? When you stand, the pendulum is effectively shorter, because the center of mass of the pendulum (you) is raised and closer to the pivot. So period is less – it takes a shorter time. ...
... playground swing longer or shorter when you stand rather than sit? When you stand, the pendulum is effectively shorter, because the center of mass of the pendulum (you) is raised and closer to the pivot. So period is less – it takes a shorter time. ...
BilaksPhysiks
... 2. Which of the following choices correctly describes the x-component of the proton’s motion? A: The proton is accelerating in the xdirection (ax>0) B: There is no motion in the x-direction. C: The x-component of the proton’s velocity vx is constant. ...
... 2. Which of the following choices correctly describes the x-component of the proton’s motion? A: The proton is accelerating in the xdirection (ax>0) B: There is no motion in the x-direction. C: The x-component of the proton’s velocity vx is constant. ...
College Physics (Etkina) Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics 2.1
... acceleration. The magnitude of the force that the cart exerts on the horse A) is zero newtons. B) equal to the magnitude of . C) less than the magnitude of . D) greater than the magnitude of . E) cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the horse. Answer: B Var: 1 24) An object of weight W i ...
... acceleration. The magnitude of the force that the cart exerts on the horse A) is zero newtons. B) equal to the magnitude of . C) less than the magnitude of . D) greater than the magnitude of . E) cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the horse. Answer: B Var: 1 24) An object of weight W i ...