No Slide Title
... the velocity the object will follow a uniform circular path. The direction of the velocity changes while the magnitude of the velocity remains constant. The acceleration is called the centripetal acceleration which means “center-seeking” and always points toward the center of the circular path. The ...
... the velocity the object will follow a uniform circular path. The direction of the velocity changes while the magnitude of the velocity remains constant. The acceleration is called the centripetal acceleration which means “center-seeking” and always points toward the center of the circular path. The ...
Rotation Lecture Notes B
... There is a common misconception that an object moving in a circle has an outward force acting on it, a socalled centrifugal (center-fleeing) force. Consider for example a person swinging a ball on the end of a string. If you have ever done this yourself, you know that you feel a force pulling outwar ...
... There is a common misconception that an object moving in a circle has an outward force acting on it, a socalled centrifugal (center-fleeing) force. Consider for example a person swinging a ball on the end of a string. If you have ever done this yourself, you know that you feel a force pulling outwar ...
Newton`s Laws
... There are TWO conditions here and one constraint. Condition #1 – The object CAN move but must be at a CONSTANT SPEED Condition #2 – The object is at REST Constraint #3 – As long as the forces are BALANCED!!!!! And if all the forces are balanced the SUM of all the forces is ZERO. ...
... There are TWO conditions here and one constraint. Condition #1 – The object CAN move but must be at a CONSTANT SPEED Condition #2 – The object is at REST Constraint #3 – As long as the forces are BALANCED!!!!! And if all the forces are balanced the SUM of all the forces is ZERO. ...
AP Sample Questions
... A block of mass m is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table placed on a laboratory on the surface of the Earth. An identical block is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table placed on the surface of the Moon. Let F be the net force necessary to give the Earth-bound block an acceleration of a ...
... A block of mass m is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table placed on a laboratory on the surface of the Earth. An identical block is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table placed on the surface of the Moon. Let F be the net force necessary to give the Earth-bound block an acceleration of a ...
Chapters One and Two - elementaryscienceteachers
... Acceleration refers to the rate at which velocity changes…a change in velocity over time. ...
... Acceleration refers to the rate at which velocity changes…a change in velocity over time. ...
ysics P2 Graded Task Bungee Jumping with equations
... Draw a velocity time graph of the jumpers fall using the information in the box above. Calculate the momentum of the jumper when they are at 20m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the jumper at this velocity. The bungee cord stretches as he falls. Name the energy stored in the cord. ...
... Draw a velocity time graph of the jumpers fall using the information in the box above. Calculate the momentum of the jumper when they are at 20m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the jumper at this velocity. The bungee cord stretches as he falls. Name the energy stored in the cord. ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... 2) The hang-time of a basketball player who jumps a vertical distance of 2 ft is about 2/3 second. What will the hang-time be if the player reaches the same height while jumping 4 ft horizontally? a) less than 2/3 s b) greater than 2/3 s c) equal to 2/3 s ...
... 2) The hang-time of a basketball player who jumps a vertical distance of 2 ft is about 2/3 second. What will the hang-time be if the player reaches the same height while jumping 4 ft horizontally? a) less than 2/3 s b) greater than 2/3 s c) equal to 2/3 s ...
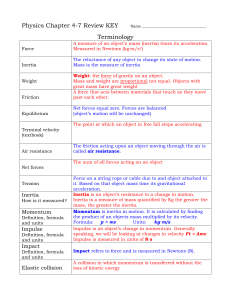
Study guide for Chapter 2 Test: Forces
... The top speed an object reaches when being pulled downward by gravity. It occurs when gravity and air resistance (fluid friction) equal each other. When terminal velocity is reached, acceleration is at zero. Inertia ...
... The top speed an object reaches when being pulled downward by gravity. It occurs when gravity and air resistance (fluid friction) equal each other. When terminal velocity is reached, acceleration is at zero. Inertia ...
Document
... free-hanging 10.0-lb weight, what is the force exerted by the floor on the 15.0-lb block? (c) If we replace the 10.0-lb weight in part (b) with a 20.0-lb weight, what is the force exerted by the floor on the 15.0-lb block? ANSWER: (a) 15.0 lb up (b) 5.00 lb up (c) 0 2. The distance between two telep ...
... free-hanging 10.0-lb weight, what is the force exerted by the floor on the 15.0-lb block? (c) If we replace the 10.0-lb weight in part (b) with a 20.0-lb weight, what is the force exerted by the floor on the 15.0-lb block? ANSWER: (a) 15.0 lb up (b) 5.00 lb up (c) 0 2. The distance between two telep ...