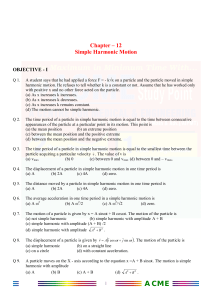
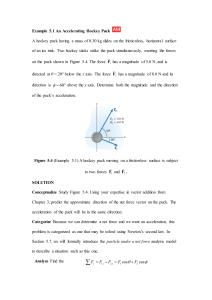
Physics 231 Topic 3: Forces & Laws of Motion
... because its mass is largest c) the normal force on the green crate is largest because its size is largest d) the gravitational force acting on each of the crates is the same e) all of the above ...
... because its mass is largest c) the normal force on the green crate is largest because its size is largest d) the gravitational force acting on each of the crates is the same e) all of the above ...
Seesaws 9 Balanced Seesaw
... A body at rest tends to remain at rest A body that’s rotating tends to keep rotating ...
... A body at rest tends to remain at rest A body that’s rotating tends to keep rotating ...
Chap8
... Describing Rotational Motion Angular Velocity If the velocity changes over a time interval, the average velocity is not equal to the instantaneous velocity at any given instant. Similarly, the angular velocity calculated in this way is actually the average angular velocity over a time interval, t. I ...
... Describing Rotational Motion Angular Velocity If the velocity changes over a time interval, the average velocity is not equal to the instantaneous velocity at any given instant. Similarly, the angular velocity calculated in this way is actually the average angular velocity over a time interval, t. I ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... the Figure. The rod is released from rest in the horizontal position. What is (A) its angular speed when it reaches the lowest point ? (B) its initial angular acceleration ? (C) initial linear acceleration of its free end ? L m ...
... the Figure. The rod is released from rest in the horizontal position. What is (A) its angular speed when it reaches the lowest point ? (B) its initial angular acceleration ? (C) initial linear acceleration of its free end ? L m ...
Chapter 3 - Houston ISD
... The origin of the The metric unit of force, the newton, relates force and motion. One newton equals newton 1 kilogram multiplied by 1 meter per second squared. This means that a force of one newton causes a 1-kilogram mass to have an acceleration of 1 m/sec2. In talking about force, “newton” is easi ...
... The origin of the The metric unit of force, the newton, relates force and motion. One newton equals newton 1 kilogram multiplied by 1 meter per second squared. This means that a force of one newton causes a 1-kilogram mass to have an acceleration of 1 m/sec2. In talking about force, “newton” is easi ...
I L - IBPhysicsLund
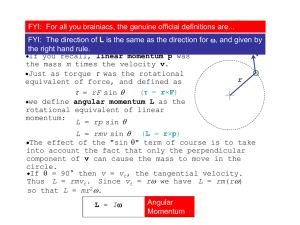
... of L–is the same as the direction for , and given by the right hand rule. v If you recall, linear momentum p was the mass m times the velocity v. Just as torque was the rotational r equivalent of force, and defined as ( = rF) = rF sin we define angular momentum L as the rotational equiva ...
... of L–is the same as the direction for , and given by the right hand rule. v If you recall, linear momentum p was the mass m times the velocity v. Just as torque was the rotational r equivalent of force, and defined as ( = rF) = rF sin we define angular momentum L as the rotational equiva ...
Physics 2010 Summer 2011 REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... Driving along a country road you stop at a stop sign. There is another stop sign 1 km down the road. The speed limit is 40 mph. Your car’s maximum acceleration is 3 m/s2 and the maximum deceleration is 4 m/s 2. (a) (b) ...
... Driving along a country road you stop at a stop sign. There is another stop sign 1 km down the road. The speed limit is 40 mph. Your car’s maximum acceleration is 3 m/s2 and the maximum deceleration is 4 m/s 2. (a) (b) ...
Friction
... between objects that are sliding with respect to one another. • Once enough force has been applied to the object to overcome static friction and get the object to move, the friction changes to sliding (or kinetic) friction. • Sliding (kinetic) friction is less than static friction. • If the componen ...
... between objects that are sliding with respect to one another. • Once enough force has been applied to the object to overcome static friction and get the object to move, the friction changes to sliding (or kinetic) friction. • Sliding (kinetic) friction is less than static friction. • If the componen ...
Wells Problem Workbook Pack
... Just look at the y axis and read off the axis what the velocity is, include a direction with the answer. - Displacement at a certain time (implies from when you started until that time), Find the areas between the motion line and the x axis for each section from start to the point in question. If yo ...
... Just look at the y axis and read off the axis what the velocity is, include a direction with the answer. - Displacement at a certain time (implies from when you started until that time), Find the areas between the motion line and the x axis for each section from start to the point in question. If yo ...
FREE Sample Here
... Q2.5 According to Newton’s first law, the only way the velocity of an object can change is if there is a net force on the object. A car changes speed and/or direction when its tires experience a force exerted by the road. If the road is too slippery, the tires can no longer apply these forces and th ...
... Q2.5 According to Newton’s first law, the only way the velocity of an object can change is if there is a net force on the object. A car changes speed and/or direction when its tires experience a force exerted by the road. If the road is too slippery, the tires can no longer apply these forces and th ...
8. Rotatory Motion
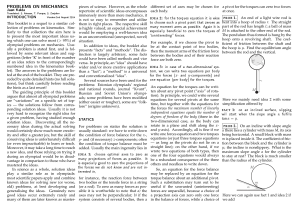
... A rod of length l is held vertically stationary with its lower end located at a point ‘p’, on the horizontal plane. When the rod is released to topple about ‘P’, the velocity of the upper end of the rod with which it hits the ground is : ...
... A rod of length l is held vertically stationary with its lower end located at a point ‘p’, on the horizontal plane. When the rod is released to topple about ‘P’, the velocity of the upper end of the rod with which it hits the ground is : ...
PROBLEMS ON MECHANICS
... ing string or rod undergoes a virtual This allows us to write down the conlengthening of ∆x, then T = (∆Π − dition of torque balance for the hanging portion of the rope (as we know the ho∑i δ⃗xi · ⃗Fi )/∆x. rizontal coordinate of its centre of mass). The method can also be used for find- The next pr ...
... ing string or rod undergoes a virtual This allows us to write down the conlengthening of ∆x, then T = (∆Π − dition of torque balance for the hanging portion of the rope (as we know the ho∑i δ⃗xi · ⃗Fi )/∆x. rizontal coordinate of its centre of mass). The method can also be used for find- The next pr ...
Ch#7 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q#3: A car accelerates from zero to 30 m/s in 1.5 s. Assuming the same average power is delivered by the car, how long does it take to accelerate it from zero to 60 m/s. (Ignore friction). (Ans: 6.0 s) ...
... Q#3: A car accelerates from zero to 30 m/s in 1.5 s. Assuming the same average power is delivered by the car, how long does it take to accelerate it from zero to 60 m/s. (Ignore friction). (Ans: 6.0 s) ...