ert146 lect on translational motion
... • We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. • As discussed in Chapter 16, when a body is subjected to general plane motion, it undergoes a combination of translation and rotation. • First, a coordinate system with its origi ...
... • We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. • As discussed in Chapter 16, when a body is subjected to general plane motion, it undergoes a combination of translation and rotation. • First, a coordinate system with its origi ...
SHM1simpleHarm
... A 2kg block is pulled a distance of 0.04 meters and then released, setting the system in motion. a. Find the spring constant. b. Find the period and frequency of oscillation. c. Calculate the maximum velocity attained. d. Calculate the maximum acceleration. e. Determine the total energy in the syste ...
... A 2kg block is pulled a distance of 0.04 meters and then released, setting the system in motion. a. Find the spring constant. b. Find the period and frequency of oscillation. c. Calculate the maximum velocity attained. d. Calculate the maximum acceleration. e. Determine the total energy in the syste ...
StudyGuideForcesAP2016
... Force is the same; acceleration depends on the mass; more mass is less acceleration according to Newton’s 2nd Law (F=ma) Coefficient of static friction: Increase incline until the box just starts to slip. Solve for the force of gravity parallel to the incline at that angle. This is equal to static f ...
... Force is the same; acceleration depends on the mass; more mass is less acceleration according to Newton’s 2nd Law (F=ma) Coefficient of static friction: Increase incline until the box just starts to slip. Solve for the force of gravity parallel to the incline at that angle. This is equal to static f ...
FORCES VOCABULARY
... 6. Terminal Velocity: The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity. 7. Projectile motion: The curved path of an object in free fall after it is given an initial forward velocity. 8. Inertia: The tendency of an object to resist a change in its ...
... 6. Terminal Velocity: The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity. 7. Projectile motion: The curved path of an object in free fall after it is given an initial forward velocity. 8. Inertia: The tendency of an object to resist a change in its ...
Chapter 3—Forces
... Section 3: Newton’s Third Law Describes action/reaction pairs When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second one exerts a force on the first that is equal in size and opposite in direction OR: “to every action force there is an equal opposite reaction force” ...
... Section 3: Newton’s Third Law Describes action/reaction pairs When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second one exerts a force on the first that is equal in size and opposite in direction OR: “to every action force there is an equal opposite reaction force” ...
Chapter 4, Part III
... A mover is trying to lift a piano (slowly) up to a second-story apartment. He uses a rope looped over 2 pulleys. What force must he exert on the rope to slowly lift the piano’s mg = 2000-N weight? mg = 2000 N Free Body Diagram ...
... A mover is trying to lift a piano (slowly) up to a second-story apartment. He uses a rope looped over 2 pulleys. What force must he exert on the rope to slowly lift the piano’s mg = 2000-N weight? mg = 2000 N Free Body Diagram ...
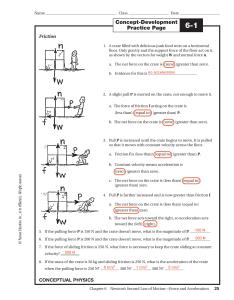
Concept-Development Practice Page
... Bronco skydives and parachutes from a stationary helicopter. Various stages of fall are shown in positions (a) through (f). Using Newton’s second law, ...
... Bronco skydives and parachutes from a stationary helicopter. Various stages of fall are shown in positions (a) through (f). Using Newton’s second law, ...
Exam Review Packet - Mrs. Hale`s Physics Website at Huron High
... v. Understand the conditions necessary for ‘free fall’ problems and the special consequences of this type of problem (Ex: vy=0 at the top of an object’s path) c. Vectors: i. Know which quantities are vectors and which are scalars ii. Know how to break a vector into its two perpendicular components a ...
... v. Understand the conditions necessary for ‘free fall’ problems and the special consequences of this type of problem (Ex: vy=0 at the top of an object’s path) c. Vectors: i. Know which quantities are vectors and which are scalars ii. Know how to break a vector into its two perpendicular components a ...
1 - alcdsb
... a constant speed of 75.0 km/h. At exactly the same time, a bus leaves Scalar and heads for Vector. The bus travels at a constant speed of 85.0 km/h. a) Where do the two vehicles meet on the highway that connects the two places? b) How much time (in min) passes before they meet? ...
... a constant speed of 75.0 km/h. At exactly the same time, a bus leaves Scalar and heads for Vector. The bus travels at a constant speed of 85.0 km/h. a) Where do the two vehicles meet on the highway that connects the two places? b) How much time (in min) passes before they meet? ...