Newton`s Laws Practice Problems
... Two giant iron spheres (much too heavy to lift) are suspended from a 15.0 m chain. The spheres appear identical but one is actually solid while the other is hollow. Design an experiment which will allow you to identify which is which. Identify whether or not your test uses the concepts of comparativ ...
... Two giant iron spheres (much too heavy to lift) are suspended from a 15.0 m chain. The spheres appear identical but one is actually solid while the other is hollow. Design an experiment which will allow you to identify which is which. Identify whether or not your test uses the concepts of comparativ ...
Newton Activities Handout
... applications of Newton’s Three Laws are a triumph of the theoretical approach (yes, triumph). They provided the groundwork for physics for the next two centuries and remain the basis for most of modern engineering. These laws are so simple that one can easily be deceived by how revolutionary they we ...
... applications of Newton’s Three Laws are a triumph of the theoretical approach (yes, triumph). They provided the groundwork for physics for the next two centuries and remain the basis for most of modern engineering. These laws are so simple that one can easily be deceived by how revolutionary they we ...
Circular
... the track. If R is the reaction acting on the ball bearing at the highest point A of the loop, which of A small object P of mass 0.3 kg is attached to one end of a light, rigid rod of length 0.5 m, which is free to rotate about the other end O as shown. The object is swung to rotate in a vertical ci ...
... the track. If R is the reaction acting on the ball bearing at the highest point A of the loop, which of A small object P of mass 0.3 kg is attached to one end of a light, rigid rod of length 0.5 m, which is free to rotate about the other end O as shown. The object is swung to rotate in a vertical ci ...
Electric Circuits
... In which situations is a person doing work on an object? a) A school crossing guard raises a stop sign that weighs 10 N. b) A student walks 1 m/s while wearing a backpack that weighs 15 N. c) A man exerts a 350 N force on a rope attached to a house. d) A worker holds a box 1 m off the floor. e) A ma ...
... In which situations is a person doing work on an object? a) A school crossing guard raises a stop sign that weighs 10 N. b) A student walks 1 m/s while wearing a backpack that weighs 15 N. c) A man exerts a 350 N force on a rope attached to a house. d) A worker holds a box 1 m off the floor. e) A ma ...
Lecture 18
... Procedure of analysis (17.5) Problems involving the kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion can be solved using the following procedure. 1. Establish the x-y inertial coordinate system. Draw both the free body diagram and kinetic diagram for the body. 2. Specify the direction and s ...
... Procedure of analysis (17.5) Problems involving the kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion can be solved using the following procedure. 1. Establish the x-y inertial coordinate system. Draw both the free body diagram and kinetic diagram for the body. 2. Specify the direction and s ...
Some Facts about the Motion?
... It is the total force or net force ftable 2 N (to the left) that determines an object’s acceleration. Fnet 10 N 2 N If there is more than one 8 N (to the right) vector acting on an object, the forces are added together as F 8N vectors, taking into account a net m 5 kg their directions. ...
... It is the total force or net force ftable 2 N (to the left) that determines an object’s acceleration. Fnet 10 N 2 N If there is more than one 8 N (to the right) vector acting on an object, the forces are added together as F 8N vectors, taking into account a net m 5 kg their directions. ...
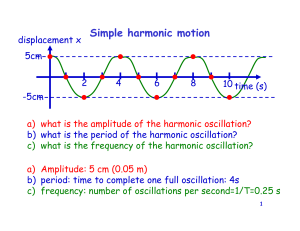
ProblemsOscillations
... constant of 19.6 N/m oscillates on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the spring is compressed by 0.04 and then released determine: a) the maximum speed of the object b) the speed of the object when the spring is compressed by 0.015 m c) when it is stretched by 0.015 m d) for what value of x does ...
... constant of 19.6 N/m oscillates on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the spring is compressed by 0.04 and then released determine: a) the maximum speed of the object b) the speed of the object when the spring is compressed by 0.015 m c) when it is stretched by 0.015 m d) for what value of x does ...
1 Experiment 3 NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... Force is the quantitiy that changes the movement of an object. It is an vector and has the same direction with acceleration. The unit of the force in SI unit system is Newton (N). 1 N is the force that gives 1m/s2 acceleration to an object with 1 kg mass. The unit of force in CGS unit system is Dyn. ...
... Force is the quantitiy that changes the movement of an object. It is an vector and has the same direction with acceleration. The unit of the force in SI unit system is Newton (N). 1 N is the force that gives 1m/s2 acceleration to an object with 1 kg mass. The unit of force in CGS unit system is Dyn. ...
What did the boy cat say to the girl cat on
... •(putter vs. feather) •The greater the mass of the object, the less it will be accelerated by a given force •(golf ball vs. ping pong ball) ...
... •(putter vs. feather) •The greater the mass of the object, the less it will be accelerated by a given force •(golf ball vs. ping pong ball) ...
Falling Objects and Gravity
... Summary 1. Acceleration due to gravity “g” near the earth’s surface is CONSTANT (i.e., NOT varying with TIME) and has a value of 9.8 m/s2. 2. An object in free fall will INCREASE its VELOCITY UNIFORMLY with time. (v = g t) 3. The distance fallen in a unit of time will INCREASE RAPIDLY with time as ...
... Summary 1. Acceleration due to gravity “g” near the earth’s surface is CONSTANT (i.e., NOT varying with TIME) and has a value of 9.8 m/s2. 2. An object in free fall will INCREASE its VELOCITY UNIFORMLY with time. (v = g t) 3. The distance fallen in a unit of time will INCREASE RAPIDLY with time as ...
PHYS 1405 Sample Questions (1-4)
... As done in class, add the vectors in the force diagram shown below. Is the NetForce zero or non-zero? _____________ If the NetForce is not zero, draw the arrow representing its size and direction and label it “NetForce”. ...
... As done in class, add the vectors in the force diagram shown below. Is the NetForce zero or non-zero? _____________ If the NetForce is not zero, draw the arrow representing its size and direction and label it “NetForce”. ...
Unit 8 Student Notes
... A tossed stone, a cannonball, or any object projected by any means that continues in motion is called a projectile. A thrown stone falls beneath the straight line it would follow with no gravity. The stone curves as it falls. Interestingly, this familiar curve is the result of two kinds of motion oc ...
... A tossed stone, a cannonball, or any object projected by any means that continues in motion is called a projectile. A thrown stone falls beneath the straight line it would follow with no gravity. The stone curves as it falls. Interestingly, this familiar curve is the result of two kinds of motion oc ...
AP C UNIT 4 - student handout
... Example 3: A ladder having a uniform density and a mass, m, rests against a frictionless vertical wall at an angle of 60◦ . The lower end rests on a flat surface where the coefficient of static friction is µs = 0.40. A student with a mass M = 2m attempts to climb the ladder. What fraction of the lengt ...
... Example 3: A ladder having a uniform density and a mass, m, rests against a frictionless vertical wall at an angle of 60◦ . The lower end rests on a flat surface where the coefficient of static friction is µs = 0.40. A student with a mass M = 2m attempts to climb the ladder. What fraction of the lengt ...
Chapter 5a
... - Forces are often measured by determining the ___________________ of a calibrated spring. - ______________ are vectors!! Remember vector addition. - To calculate ________ force on an object you must use vector addition. ...
... - Forces are often measured by determining the ___________________ of a calibrated spring. - ______________ are vectors!! Remember vector addition. - To calculate ________ force on an object you must use vector addition. ...