Chapter 2: Pressure Distribution in a Fluid
... translation and/or rotation and there is no relative motion between particles; consequently, there are no strains or strain rates and the viscous term drops out of the N-S equation V 0 . ...
... translation and/or rotation and there is no relative motion between particles; consequently, there are no strains or strain rates and the viscous term drops out of the N-S equation V 0 . ...
SECTION 9 - RENAL FUNCTION AND HOMEOSTASIS
... The GFR measurement is significant because it reflects the net production of filtrate by the nephrons of the kidney. Since urea and other waste products in the plasma are filtered at the glomerulus and excreted in the urine, the efficiency of the kidneys in performing this function can be evaluated. ...
... The GFR measurement is significant because it reflects the net production of filtrate by the nephrons of the kidney. Since urea and other waste products in the plasma are filtered at the glomerulus and excreted in the urine, the efficiency of the kidneys in performing this function can be evaluated. ...
Chapter 1 Introduction 一、名词解释 1.Human Physiology Physiology
... 2. What is the walk-along theary of contraction? Walk-along theory is a generally accepted model for the way in which contraction occurs in the sarcomere of striated muscle, by the sliding of the thick filaments relative to the thin filaments. As soon as the actin filament becomes activated by the c ...
... 2. What is the walk-along theary of contraction? Walk-along theory is a generally accepted model for the way in which contraction occurs in the sarcomere of striated muscle, by the sliding of the thick filaments relative to the thin filaments. As soon as the actin filament becomes activated by the c ...
ME33: Fluid Flow Lecture 1: Information and Introduction
... Fluids in rigid – body motion In this section we obtain relations for the variation of pressure in fluids moving like a solid body with or without acceleration in the absence of any shear stresses (i.e., no motion between fluid layers relative to each other). ...
... Fluids in rigid – body motion In this section we obtain relations for the variation of pressure in fluids moving like a solid body with or without acceleration in the absence of any shear stresses (i.e., no motion between fluid layers relative to each other). ...
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST
... Why the difference? The intracellular compartment is separated from the extracellular compartment by cell membranes. This barrier is selectively permeable, and contains active sodiumpotassium pumps which maintain the concentration differences. Plasma and interstitial fluid compartments are separate ...
... Why the difference? The intracellular compartment is separated from the extracellular compartment by cell membranes. This barrier is selectively permeable, and contains active sodiumpotassium pumps which maintain the concentration differences. Plasma and interstitial fluid compartments are separate ...
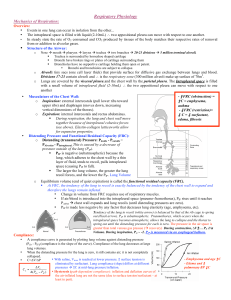
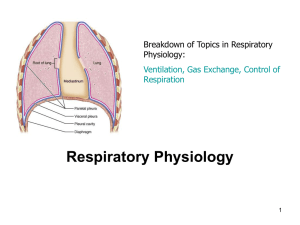
11 Respiratory physiology
... baroreceptors detecting blood pressure in the aortic arch and carotid sinus. • The respiratory system has chemoreceptors in those areas, too. They function to detect the O2, CO2, and pH levels of the blood. • The medulla oblongata also has chemoreceptors that monitor pH. This information is sent to ...
... baroreceptors detecting blood pressure in the aortic arch and carotid sinus. • The respiratory system has chemoreceptors in those areas, too. They function to detect the O2, CO2, and pH levels of the blood. • The medulla oblongata also has chemoreceptors that monitor pH. This information is sent to ...
Renal Physiology - e-safe
... The glomerulus is the filter unit of the nephron. It passively lets water, amino acids, sodium and other free ions pass through its membranes and into the tubule system, but not charged proteins, large proteins or cells. The unique basement membrane, which is at the interface of the capillaries and ...
... The glomerulus is the filter unit of the nephron. It passively lets water, amino acids, sodium and other free ions pass through its membranes and into the tubule system, but not charged proteins, large proteins or cells. The unique basement membrane, which is at the interface of the capillaries and ...
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... Volume changes: End-diastolic volume, End-systolic volume, Stroke volume and Cardiac output. Aortic pressure: Diastolic pressure 80 mmHg, Systolic pressure 120 mmHg, most of systole ventricular pressure higher than ...
... Volume changes: End-diastolic volume, End-systolic volume, Stroke volume and Cardiac output. Aortic pressure: Diastolic pressure 80 mmHg, Systolic pressure 120 mmHg, most of systole ventricular pressure higher than ...
1 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... Volume changes: End-diastolic volume, End-systolic volume, Stroke volume and Cardiac output. Aortic pressure: Diastolic pressure 80 mmHg, Systolic pressure 120 mmHg, most of systole ventricular pressure higher than ...
... Volume changes: End-diastolic volume, End-systolic volume, Stroke volume and Cardiac output. Aortic pressure: Diastolic pressure 80 mmHg, Systolic pressure 120 mmHg, most of systole ventricular pressure higher than ...
An immersed-shell method for modelling fluid–structure interactions
... However, when the structure moves in the fluid domain, re-meshing is necessary. This is the case, for example, for wind turbine rotors or floating wind turbines. In this context, the whole structure dynamically interacts with the surrounding wind and waves. Re-meshing is computationally expensive an ...
... However, when the structure moves in the fluid domain, re-meshing is necessary. This is the case, for example, for wind turbine rotors or floating wind turbines. In this context, the whole structure dynamically interacts with the surrounding wind and waves. Re-meshing is computationally expensive an ...