O 2
... Figure 17.3 Solubilities of oxygen and carbon dioxide in water. The beakers at left depict the initial conditions in which water has just been exposed to air that has a partial pressure of gas of 100 mmHg; the breakers at right show the conditions after equilibration, when the gas has dissolved in t ...
... Figure 17.3 Solubilities of oxygen and carbon dioxide in water. The beakers at left depict the initial conditions in which water has just been exposed to air that has a partial pressure of gas of 100 mmHg; the breakers at right show the conditions after equilibration, when the gas has dissolved in t ...
D - VCOMcc
... C. Increased by a factor of four. D. Increased by a factor of sixteen. E. Remained the same. 26. Which of the following is normally associated with an increase in venous return to the heart? A. Acute large arterial dilation. B. Decreased mean systemic filling pressure. C. Increased blood volume. D. ...
... C. Increased by a factor of four. D. Increased by a factor of sixteen. E. Remained the same. 26. Which of the following is normally associated with an increase in venous return to the heart? A. Acute large arterial dilation. B. Decreased mean systemic filling pressure. C. Increased blood volume. D. ...
ExercisePhys Lesson2-1
... being used for fuel at different intensities during steadystate exercise. At rest, the average RER is 0.75, meaning that the body is burning approximately 85% fat and 15% carbohydrate. As intensity increases, so does RER, meaning a larger percentage of carbohydrate is being burned and a lesser p ...
... being used for fuel at different intensities during steadystate exercise. At rest, the average RER is 0.75, meaning that the body is burning approximately 85% fat and 15% carbohydrate. As intensity increases, so does RER, meaning a larger percentage of carbohydrate is being burned and a lesser p ...
Respiratory Physiology
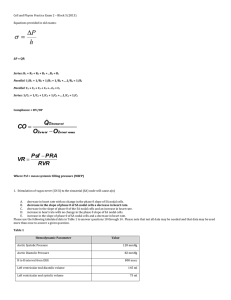
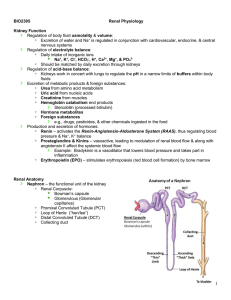
... Body fluids are measured in milliosmoles (mOsm) The kidneys keep the solute load of body fluids constant at about 300 mOsm This is accomplished by the Countercurrent Mechanism Countercurrent Mechanism Countercurrent Exchange System – the anatomical arrangement of vessels so that flow in one vessel i ...
... Body fluids are measured in milliosmoles (mOsm) The kidneys keep the solute load of body fluids constant at about 300 mOsm This is accomplished by the Countercurrent Mechanism Countercurrent Mechanism Countercurrent Exchange System – the anatomical arrangement of vessels so that flow in one vessel i ...
GFR - ISpatula
... of both kidneys per minute. • The volume of fluid filtered daily through all the corpuscles of both kidneys per day = 180 L • Hence, GFR= 180 L/24hours * (1000 ml/ L)*(1hour/60 min)= 125 ml/min (Males) • For 125ml/min; renal plasma flow = 625ml/min FF * PF=GFR, PF= 125/(20%)=625 ml/min • 55% of bloo ...
... of both kidneys per minute. • The volume of fluid filtered daily through all the corpuscles of both kidneys per day = 180 L • Hence, GFR= 180 L/24hours * (1000 ml/ L)*(1hour/60 min)= 125 ml/min (Males) • For 125ml/min; renal plasma flow = 625ml/min FF * PF=GFR, PF= 125/(20%)=625 ml/min • 55% of bloo ...
3 - USNA
... Notice in the last equality that we integrate over a density field to find the mass since we are dealing with continuous fluid mediums instead of discrete mass objects. We now have all the contributions necessary to consider the dynamics of an incompressible fluid in a non- rotating frame. Recall fr ...
... Notice in the last equality that we integrate over a density field to find the mass since we are dealing with continuous fluid mediums instead of discrete mass objects. We now have all the contributions necessary to consider the dynamics of an incompressible fluid in a non- rotating frame. Recall fr ...