Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
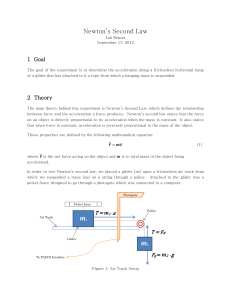
... Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s first law states that an object does not accelerate unless a net force is applied to the object. But how much will an object accelerate when there is a net force? The larger the force the larger the acceleration. Therefore acceleration is directly proportional to mass. ...
... Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s first law states that an object does not accelerate unless a net force is applied to the object. But how much will an object accelerate when there is a net force? The larger the force the larger the acceleration. Therefore acceleration is directly proportional to mass. ...
AP Sample Questions
... A block of mass m is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table placed on a laboratory on the surface of the Earth. An identical block is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table placed on the surface of the Moon. Let F be the net force necessary to give the Earth-bound block an acceleration of a ...
... A block of mass m is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table placed on a laboratory on the surface of the Earth. An identical block is at rest on a frictionless horizontal table placed on the surface of the Moon. Let F be the net force necessary to give the Earth-bound block an acceleration of a ...
Name of Model - Northwest ISD Moodle
... b. Draw a force diagram (side view) for a rollercoaster traveling over the top of a hill. Should the forces perpendicular to the track be balanced? If the forces are unbalanced, explain why there is a net force and the direction of the net force. The forces perpendicular to each car are not balanced ...
... b. Draw a force diagram (side view) for a rollercoaster traveling over the top of a hill. Should the forces perpendicular to the track be balanced? If the forces are unbalanced, explain why there is a net force and the direction of the net force. The forces perpendicular to each car are not balanced ...
Chapter 2 Lessons 1 - 3 slides
... A juggler throws a ball up in the air with an initial speed of 5ms-1 from a height of 1.2m. Assuming that g is 10ms-2, find the maximum height that the ball reaches above the ground and the time it takes to reach this height. Find the time taken for the ball to hit the ground if the juggler fails t ...
... A juggler throws a ball up in the air with an initial speed of 5ms-1 from a height of 1.2m. Assuming that g is 10ms-2, find the maximum height that the ball reaches above the ground and the time it takes to reach this height. Find the time taken for the ball to hit the ground if the juggler fails t ...
Circular Motion
... be a force acting on it. ● This agrees with Newton’s Second Law, that a net force results in acceleration. ○ If there were no forces involved, the object should be moving at a constant speed in a straight line (Newton's First Law), which it isn’t. ● Since the acceleration points to the centre, the f ...
... be a force acting on it. ● This agrees with Newton’s Second Law, that a net force results in acceleration. ○ If there were no forces involved, the object should be moving at a constant speed in a straight line (Newton's First Law), which it isn’t. ● Since the acceleration points to the centre, the f ...
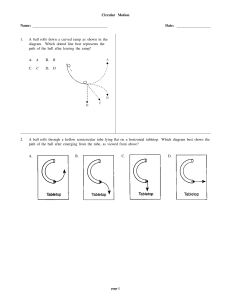
Circular Motion Name: Date: 1. A ball rolls down a curved ramp as
... If object O is moving in a uniform circular motion around point P at constant speed, which vector shown represents a centripetal force? A. ...
... If object O is moving in a uniform circular motion around point P at constant speed, which vector shown represents a centripetal force? A. ...
Circular & Satellite Motion
... 2. An imaginary line from the sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. Thus the planets move fastest when closest to the sun, ...
... 2. An imaginary line from the sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals. Thus the planets move fastest when closest to the sun, ...
How many laws did Newton create?
... 2. Which law explains why we need to wear seatbelts? 3. Which law says that force is equal to mass times acceleration (F=MA)? 4. Which law explains how rockets are launched into space? 5. Which law says that heavier objects require more force than lighter objects to move or accelerate them (Throwing ...
... 2. Which law explains why we need to wear seatbelts? 3. Which law says that force is equal to mass times acceleration (F=MA)? 4. Which law explains how rockets are launched into space? 5. Which law says that heavier objects require more force than lighter objects to move or accelerate them (Throwing ...
Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s first law states that an object does not accelerate unless a net force is applied to the object. But how much will an object accelerate when there is a net force? The larger the force the larger the acceleration. Therefore acceleration is directly proportional to mass. ...
... Newton’s Second Law: Newton’s first law states that an object does not accelerate unless a net force is applied to the object. But how much will an object accelerate when there is a net force? The larger the force the larger the acceleration. Therefore acceleration is directly proportional to mass. ...
Physics 50 Sample Midterm Exam #1
... A projectile is fired at time t = 0.0s, from point 0 at the edge of a cliff, with initial velocity components of v0x = 80 m/s and v0y = 600 m/s The projectile rises, then falls into the sea at point P, as shown in the figure. The time of flight of the projectile is 150.0 s. We want to determine the ...
... A projectile is fired at time t = 0.0s, from point 0 at the edge of a cliff, with initial velocity components of v0x = 80 m/s and v0y = 600 m/s The projectile rises, then falls into the sea at point P, as shown in the figure. The time of flight of the projectile is 150.0 s. We want to determine the ...
33333.3 N How much force is needed to keep a 1000 g ball moving
... velocity of 20 m/s around a turn of radius 12 m? ...
... velocity of 20 m/s around a turn of radius 12 m? ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Newton’s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...