Chapter 6 practice questions
... 31) A 3.0 kg pendulum bob on a string 2.0 m long is released with a velocity of 2.0 m/s when the support string makes an angle of 45 degrees with the vertical. What is the tension in the string at the highest point of its motion? a) 12.5 N b) 17.8 N c) 21.4 N d) 28.9 N e) 31.6 N Ans: b 32) A 3.0 kg ...
... 31) A 3.0 kg pendulum bob on a string 2.0 m long is released with a velocity of 2.0 m/s when the support string makes an angle of 45 degrees with the vertical. What is the tension in the string at the highest point of its motion? a) 12.5 N b) 17.8 N c) 21.4 N d) 28.9 N e) 31.6 N Ans: b 32) A 3.0 kg ...
Ch 08) Rotational Motion
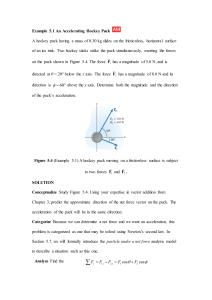
... velocity of the carousel, and (b) the linear velocity of a child (Fig. 8–7a) located 2.5 m from the center, point P in Fig. 8–7b. APPROACH The angular acceleration a is constant, so we can use a = ¢v兾¢ t (Eq. 8–3a) to solve for v after a time t = 8.0 s. With this v , we determine the linear velocity ...
... velocity of the carousel, and (b) the linear velocity of a child (Fig. 8–7a) located 2.5 m from the center, point P in Fig. 8–7b. APPROACH The angular acceleration a is constant, so we can use a = ¢v兾¢ t (Eq. 8–3a) to solve for v after a time t = 8.0 s. With this v , we determine the linear velocity ...
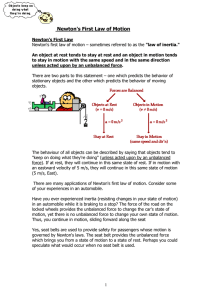
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Inertia and Mass This is the natural tendency of objects to resist changes in their state of motion. This tendency to resist changes in their state of motion is described as inertia. Inertia is the resistance an object has to a change in its state of motion. Galileo, the premier scientist of the se ...
... Inertia and Mass This is the natural tendency of objects to resist changes in their state of motion. This tendency to resist changes in their state of motion is described as inertia. Inertia is the resistance an object has to a change in its state of motion. Galileo, the premier scientist of the se ...
1-2 The Nature of Physics Physics is an experimental
... motion, all other components of instantaneous velocity are zero, and in this case we will often call v simply the instantaneous velocity. The The terms" velocity" and" speed" are used the interchangeably in everyday language, but they have distinct definitions in physics. We use the term speed to de ...
... motion, all other components of instantaneous velocity are zero, and in this case we will often call v simply the instantaneous velocity. The The terms" velocity" and" speed" are used the interchangeably in everyday language, but they have distinct definitions in physics. We use the term speed to de ...
TEKS 8.7 A
... the rock is pushing very hard on the rock underneath it. Meanwhile, the rock underneath is pushing back up with exactly the same force and in the opposite direction, so the forces, even though they are very large, are balanced out. If the ...
... the rock is pushing very hard on the rock underneath it. Meanwhile, the rock underneath is pushing back up with exactly the same force and in the opposite direction, so the forces, even though they are very large, are balanced out. If the ...
Rotational Motion and Astrophysics_tcm4-726390
... Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned. Any enquiries regarding this document/publication should be sent to us at ...
... Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned. Any enquiries regarding this document/publication should be sent to us at ...