Quantization of Mechanical Motion
... Black body radiation: occurs in discrete portions with energy quantum E=ħω (M.Plank) ...
... Black body radiation: occurs in discrete portions with energy quantum E=ħω (M.Plank) ...
Science GHST Review
... Physical versus Chemical Changes Physical changes are when no new substances are formed (i.e. phase changes such as melting, freezing, boiling, condensation, evaporation, sublimation) Chemical changes occur when new substances are formed (i.e. rusting, foaming, burning) Whether physical change ...
... Physical versus Chemical Changes Physical changes are when no new substances are formed (i.e. phase changes such as melting, freezing, boiling, condensation, evaporation, sublimation) Chemical changes occur when new substances are formed (i.e. rusting, foaming, burning) Whether physical change ...
AP Physics Daily Problem #110
... The plates are spaced 3cm apart and are 6.0cm long. The bottom plate is held at ground potential. Neglect gravity e- ...
... The plates are spaced 3cm apart and are 6.0cm long. The bottom plate is held at ground potential. Neglect gravity e- ...
Take silver atoms with an electron that has a moment of µz = −g e(e
... If the electrons have two different kinds of spin directions, atoms with those electrons should have different total spins and then they should respond differently to magnetic fields. In the Stern-Gerlach experiment they send these atoms in the x direction between magnets one above the other, where ...
... If the electrons have two different kinds of spin directions, atoms with those electrons should have different total spins and then they should respond differently to magnetic fields. In the Stern-Gerlach experiment they send these atoms in the x direction between magnets one above the other, where ...
Solving the Helium Atom
... particle), one knows everything physics can predict. Wavefunctions are calculated by solving the Schrödinger equation, given below in one of its many forms: ...
... particle), one knows everything physics can predict. Wavefunctions are calculated by solving the Schrödinger equation, given below in one of its many forms: ...
What is the quantum state?
... • The information we have defines a probability distribution ρ over phase space. • ρ is not a physical property of the particle. The particle occupies a definite point in phase space and does not care what probabilities I have assigned to different states. ...
... • The information we have defines a probability distribution ρ over phase space. • ρ is not a physical property of the particle. The particle occupies a definite point in phase space and does not care what probabilities I have assigned to different states. ...
The world of Atoms - University of California, Irvine
... “I cannot but confess that I attach only a transitory importance to this interpretation. I still believe in the possibility of a model of reality - that is to say, of a theory which represents things themselves and not merely the probability of their occurrence. On the other hand, it seems to me cer ...
... “I cannot but confess that I attach only a transitory importance to this interpretation. I still believe in the possibility of a model of reality - that is to say, of a theory which represents things themselves and not merely the probability of their occurrence. On the other hand, it seems to me cer ...
7Copenhagen
... For what period of time is the uncertainty of the energy of an electron 5.0 x 10-19 J? Et > h/2 (5.0 x 10-19 J)t > h/2 t = 2.1 x 10-16 s ...
... For what period of time is the uncertainty of the energy of an electron 5.0 x 10-19 J? Et > h/2 (5.0 x 10-19 J)t > h/2 t = 2.1 x 10-16 s ...
PHE-01 (2007
... 5. (a) Calculate the gravitational force and the electrical force between two electrons 1.0 cm apart and compare them. ...
... 5. (a) Calculate the gravitational force and the electrical force between two electrons 1.0 cm apart and compare them. ...
January 2008
... Consider an ideal parallel plate diode in a vacuum tube. A constant potential difference, V0 > 0, is maintained between the cathode and the anode which are separated by a distance d. Electrons are assumed to be released from the cathode at zero potential with negligible velocity, but are accelerated ...
... Consider an ideal parallel plate diode in a vacuum tube. A constant potential difference, V0 > 0, is maintained between the cathode and the anode which are separated by a distance d. Electrons are assumed to be released from the cathode at zero potential with negligible velocity, but are accelerated ...
PHE-01 (2007)
... 5. (a) Calculate the gravitational force and the electrical force between two electrons 1.0 cm apart and compare them. ...
... 5. (a) Calculate the gravitational force and the electrical force between two electrons 1.0 cm apart and compare them. ...
Atomic Line Spectra: the Bohr model Line Spectra of Excited Atoms
... Because Because each each orbit orbit has has aa predicted radius, the predicted radius, the wavelength wavelength of of aa moving moving particle particle is is λλ == h/mv h/mv (v (v is is velocity). velocity). ...
... Because Because each each orbit orbit has has aa predicted radius, the predicted radius, the wavelength wavelength of of aa moving moving particle particle is is λλ == h/mv h/mv (v (v is is velocity). velocity). ...
Dynamics
... Momentum is defined be mass and velocity. • Derivative is force • Defines equations of motion ...
... Momentum is defined be mass and velocity. • Derivative is force • Defines equations of motion ...
Document
... The position of a particle traveling around a circular path of radius r at constant speed v can be given in three ways: 1. By the usual x and y coordinates . (For this discussion we will take the origin at the center of the circular path). The vector r = xi + yj is called the radius vector. 2. By th ...
... The position of a particle traveling around a circular path of radius r at constant speed v can be given in three ways: 1. By the usual x and y coordinates . (For this discussion we will take the origin at the center of the circular path). The vector r = xi + yj is called the radius vector. 2. By th ...
WBL6_Lecture_Ch27
... Light scattering off atomic electrons is called the Compton effect. The scattered light has a longer wavelength: ...
... Light scattering off atomic electrons is called the Compton effect. The scattered light has a longer wavelength: ...
quantum, relativistic and classical physics
... momentum S which occurs when an atom is placed in a magnetic field aligned along the z direction. In this connection explain the role of the quantum numbers m and ms and define how L and S are related to the corresponding quantum numbers and s. [7 marks] (ii) Briefly note the experimental observa ...
... momentum S which occurs when an atom is placed in a magnetic field aligned along the z direction. In this connection explain the role of the quantum numbers m and ms and define how L and S are related to the corresponding quantum numbers and s. [7 marks] (ii) Briefly note the experimental observa ...
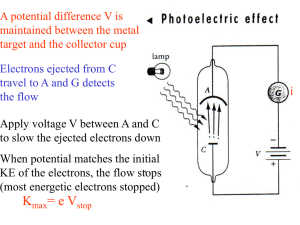
V stop f
... • Light strikes a sodium surface and causes photoelectric emission. If Vstop = 5.0 volts and the work function is 2.2 eV, what is the wavelength of the light? • Ephoton = hf = hc/ • Kmax = Ephoton - = hc/ - = e Vstop • = (hc)/(e Vstop + ) • h = 6.63x10-34 J.s = 6.63x10-34 /1.6x10-19 eV.s ...
... • Light strikes a sodium surface and causes photoelectric emission. If Vstop = 5.0 volts and the work function is 2.2 eV, what is the wavelength of the light? • Ephoton = hf = hc/ • Kmax = Ephoton - = hc/ - = e Vstop • = (hc)/(e Vstop + ) • h = 6.63x10-34 J.s = 6.63x10-34 /1.6x10-19 eV.s ...