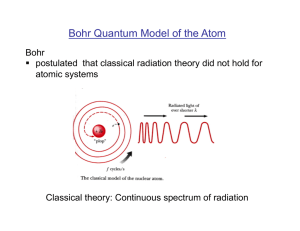
Bohr Quantum Model of the Atom
... § postulated that the electron orbital momentum is quantized Justification of Bohr’s postulates: comparison with experimental observations! ...
... § postulated that the electron orbital momentum is quantized Justification of Bohr’s postulates: comparison with experimental observations! ...
Sem 2 Course Review
... What are some similarities and differences between mechanical and light waves? How can we apply the mathematical equations used for mechanical waves to electromagnetic waves? Why is it important to make observations and record data to help understand and explain the universe around us? How d ...
... What are some similarities and differences between mechanical and light waves? How can we apply the mathematical equations used for mechanical waves to electromagnetic waves? Why is it important to make observations and record data to help understand and explain the universe around us? How d ...
Elementary Quantum Mechanics
... energy and momentum of the particle as in (1.1.1) and (1.1.3). This hypothesis was supported experimentally in 1927, when Davisson and Germer, by scattering electrons of known momentum on a nickel crystal, found that the electrons emerged in precisely the directions where one would expect to find in ...
... energy and momentum of the particle as in (1.1.1) and (1.1.3). This hypothesis was supported experimentally in 1927, when Davisson and Germer, by scattering electrons of known momentum on a nickel crystal, found that the electrons emerged in precisely the directions where one would expect to find in ...
The Lorentz Force and the Radiation Pressure of Light
... and the time average is hSi = Re(E × B∗ )/8π. S points in the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave and in units with c = 1 can be regarded interchangeably as power per unit area, energy per unit volume (or pressure) or momentum flux. If the freshman argument is correct, then the part ...
... and the time average is hSi = Re(E × B∗ )/8π. S points in the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave and in units with c = 1 can be regarded interchangeably as power per unit area, energy per unit volume (or pressure) or momentum flux. If the freshman argument is correct, then the part ...
Document
... a) Describe the motion of the mass. b) At what position does the particle has maximum and minimum kinetic energy? c) Plot the position versus time for the particle. d) What is the expression for the force as a function of position? ...
... a) Describe the motion of the mass. b) At what position does the particle has maximum and minimum kinetic energy? c) Plot the position versus time for the particle. d) What is the expression for the force as a function of position? ...
Equations of motion Worksheet.
... 1. A landing module is falling towards the Moon’s surface at a steady speed of 500 ms−1. At a height of 62.5 m, a small object becomes detached from the landing module and accelerates down with the acceleration of 1.60 ms−2. At what speed does the object hit the surface of the moon? ...
... 1. A landing module is falling towards the Moon’s surface at a steady speed of 500 ms−1. At a height of 62.5 m, a small object becomes detached from the landing module and accelerates down with the acceleration of 1.60 ms−2. At what speed does the object hit the surface of the moon? ...
6 Lecture 6: Momentum and variable
... namely, it states that the rate of change of the total momentum P of the system is equal to the external force. Eq. (116) is a general formulation of Newtonian dynamics. Momentum conservation of an isolated system can of course be obtained in the special case of a vanishing external force. Clearly, ...
... namely, it states that the rate of change of the total momentum P of the system is equal to the external force. Eq. (116) is a general formulation of Newtonian dynamics. Momentum conservation of an isolated system can of course be obtained in the special case of a vanishing external force. Clearly, ...
lecture2 - WordPress.com
... F t dt dx F t dt dt x F t dt dt dt m 0 m 0 0 m 0 ...
... F t dt dx F t dt dt x F t dt dt dt m 0 m 0 0 m 0 ...
Chapter 7 Atomic Structure and Periodicity Study Guide
... (2) frequency (ν)- a number of waves (cycles) per sec that pass a give point in space, measured in Hertz (which is cycles per sec = 1/sec = sec-1) ...
... (2) frequency (ν)- a number of waves (cycles) per sec that pass a give point in space, measured in Hertz (which is cycles per sec = 1/sec = sec-1) ...
Lecture - ChemWeb (UCC)
... Each energy level is degenerate. There are (2 J + 1) levels with the same energy. There is a second quantum number mJ which has integer values between – J and + J , that is (2 J + 1) values all with the same energy determined by J. 2 quantum numbers as there are 2 separate rotational axes/motions. F ...
... Each energy level is degenerate. There are (2 J + 1) levels with the same energy. There is a second quantum number mJ which has integer values between – J and + J , that is (2 J + 1) values all with the same energy determined by J. 2 quantum numbers as there are 2 separate rotational axes/motions. F ...
Physics Review for the Year Notes
... RESULTANT-- the vector which forms the diagonal of the parallelogram drawn with two vectors as sides. It can be solved graphically or by trigonometry. EQUILIBRANT-- the vector which is equal and opposite to the resultant. ACCELERATION -- a change in velocity with respect to time. a = v/t. It contain ...
... RESULTANT-- the vector which forms the diagonal of the parallelogram drawn with two vectors as sides. It can be solved graphically or by trigonometry. EQUILIBRANT-- the vector which is equal and opposite to the resultant. ACCELERATION -- a change in velocity with respect to time. a = v/t. It contain ...