Chapter 6: Force and Motion II
... coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.15. (a) What is the minimum magnitude of the force F, parallel to the plane that will prevent the sled from slipping down the plane? (b) What is the minimum magnitude F that will start the sled moving up the plane? (c) What value of F is required to move the sled ...
... coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.15. (a) What is the minimum magnitude of the force F, parallel to the plane that will prevent the sled from slipping down the plane? (b) What is the minimum magnitude F that will start the sled moving up the plane? (c) What value of F is required to move the sled ...
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING Course Specifications: (PHYS 201)
... The first part is classical physics which contains Newtonian relativity, Maxwell,s equations, Michelson-Morley experiment and Einstein,s special theory of relativity. The second part is the old quantum theory e.g. black body radiation , photoelectric effect, Compton effect, Bohr’s theory. The third ...
... The first part is classical physics which contains Newtonian relativity, Maxwell,s equations, Michelson-Morley experiment and Einstein,s special theory of relativity. The second part is the old quantum theory e.g. black body radiation , photoelectric effect, Compton effect, Bohr’s theory. The third ...
Chapter 3
... science, simply because it made Schrödinger look for a way of deriving a wave equation to be associated with a given physical system. De Broglie, in developing and applying his matter-wave conjecture, had employed 'geometrical' or 'pictorial' methods. He proposed no way to write down a wave equation ...
... science, simply because it made Schrödinger look for a way of deriving a wave equation to be associated with a given physical system. De Broglie, in developing and applying his matter-wave conjecture, had employed 'geometrical' or 'pictorial' methods. He proposed no way to write down a wave equation ...
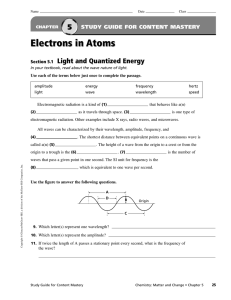
Electrons in Atoms
... electromagnetic radiation. Other examples include X rays, radio waves, and microwaves. All waves can be characterized by their wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and . The shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave is ...
... electromagnetic radiation. Other examples include X rays, radio waves, and microwaves. All waves can be characterized by their wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and . The shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave is ...
On the Planck Scale Potential Associated with Particles
... Searle in 1897 derived the relativistic electromagnetic energy of a moving charge spheroid shell [3]. Then in 1904, Lorentz [4] computed the electromagnetic momentum associated with a moving charge spheroid shell. However, the electromagnetic energy and the momentum expressions they obtained were ne ...
... Searle in 1897 derived the relativistic electromagnetic energy of a moving charge spheroid shell [3]. Then in 1904, Lorentz [4] computed the electromagnetic momentum associated with a moving charge spheroid shell. However, the electromagnetic energy and the momentum expressions they obtained were ne ...
Document
... 7. A car, initially at rest , travels 20 m in 4 s along a straight line with constant acceleration. The acceleration of the car (in m/s2) is: 8. An object is thrown straight up from ground level with a speed of 50 m/s. If g = 10 m/s 2 its distance above ground level 1.0 sec later is: 9 - 12 A ball i ...
... 7. A car, initially at rest , travels 20 m in 4 s along a straight line with constant acceleration. The acceleration of the car (in m/s2) is: 8. An object is thrown straight up from ground level with a speed of 50 m/s. If g = 10 m/s 2 its distance above ground level 1.0 sec later is: 9 - 12 A ball i ...
Heisenberg, Matrix Mechanics, and the Uncertainty Principle Genesis
... misleading or even wrong. This is indeed the main message of the revolutionary advances in the physical sciences in the 20th century. The discovery of quantum mechanics is the centre-piece of that revolution. By the end of the 19th century, the edifice of physics seemed to be on a firm foundation. T ...
... misleading or even wrong. This is indeed the main message of the revolutionary advances in the physical sciences in the 20th century. The discovery of quantum mechanics is the centre-piece of that revolution. By the end of the 19th century, the edifice of physics seemed to be on a firm foundation. T ...
“SUPERPOSITION” “interference term”
... In quantum mechanics, if state 1 → state 1’ and state 2 → 2’, then superposition of 1 and 2 → superposition of 1’ and 2’ . ...
... In quantum mechanics, if state 1 → state 1’ and state 2 → 2’, then superposition of 1 and 2 → superposition of 1’ and 2’ . ...
66 - Narod.ru
... In one of his early works of 1925 to 1926, Erwin Schrödinger, critical of the Bose-Einstein statistics formulation, wondered, "Why not start with the wave representation of the gas particles, and then impose on such ‘waves’ the quantization conditions ‘à la the Debye model’"? After that followed his ...
... In one of his early works of 1925 to 1926, Erwin Schrödinger, critical of the Bose-Einstein statistics formulation, wondered, "Why not start with the wave representation of the gas particles, and then impose on such ‘waves’ the quantization conditions ‘à la the Debye model’"? After that followed his ...
Chemistry - Isotopes
... The field of spectroscopy is based on the fact that electrons do NOT absorb/emit all energies, but instead absorb/emit certain, specific, (and unique) energies of EM radiation. Neils ___________ interpreted the definite energies given off by electrons as an indication that atomic electrons exist at ...
... The field of spectroscopy is based on the fact that electrons do NOT absorb/emit all energies, but instead absorb/emit certain, specific, (and unique) energies of EM radiation. Neils ___________ interpreted the definite energies given off by electrons as an indication that atomic electrons exist at ...
Class XI-Physics 2016-17
... b) There are 26 questions in all. Questions from 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each, questions from 6 to 10 carry two marks each, questions from 11 to 22 carry three marks each, question 23 carries 4 marks and questions from 24 to 26 carry five marks each. c) There is no overall choice. However an internal ch ...
... b) There are 26 questions in all. Questions from 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each, questions from 6 to 10 carry two marks each, questions from 11 to 22 carry three marks each, question 23 carries 4 marks and questions from 24 to 26 carry five marks each. c) There is no overall choice. However an internal ch ...
fiitjee aieee class room program
... (1) Linear momentum of a system of particles is zero. (2) Kinetic energy of system of particles is zero. (A) A does not imply B and B does not imply A. (B) A implies B but B does not imply A (C) A does not imply B but b implies A’ (D) A implies B and B implies A. ...
... (1) Linear momentum of a system of particles is zero. (2) Kinetic energy of system of particles is zero. (A) A does not imply B and B does not imply A. (B) A implies B but B does not imply A (C) A does not imply B but b implies A’ (D) A implies B and B implies A. ...
Summer Holidays Home Work
... velocity. How can we calculate uniform velocity from it. iii) From a velocity time graph, how can we find a) acceleration of a body b) Displacement of a body 4. Numerical Problemsi) The velocity of a car is 18 m/s, express this velocity in km/h. ii) An electric engine has a velocity of 120 km/h. How ...
... velocity. How can we calculate uniform velocity from it. iii) From a velocity time graph, how can we find a) acceleration of a body b) Displacement of a body 4. Numerical Problemsi) The velocity of a car is 18 m/s, express this velocity in km/h. ii) An electric engine has a velocity of 120 km/h. How ...
The Quantum Mechanics of a Particle in a Box - Philsci
... 3. The Newtonian ‘Force’ Acting on a Particle in a Box. In Newtonian physics, there are two ways of writing down an expression for the force acting on a particle. The first ‘definition’ is via Newton’s second law, F = m.a, or equivalently, F dp dt , where p is the particle’s momentum, m is the mas ...
... 3. The Newtonian ‘Force’ Acting on a Particle in a Box. In Newtonian physics, there are two ways of writing down an expression for the force acting on a particle. The first ‘definition’ is via Newton’s second law, F = m.a, or equivalently, F dp dt , where p is the particle’s momentum, m is the mas ...