Vector Calculus in Three Dimensions
... Example 4.4. Our goal is to move a mass through the force field f = ( y, −x, 1 ) T T starting from the initial point ( 1, 0, 1 ) and moving vertically to the final point ( 1, 0, 2 π ) . T Question: does it require more work to move in a straight line x(t) = ( 1, 0, t ) or along T the spiral helix x( ...
... Example 4.4. Our goal is to move a mass through the force field f = ( y, −x, 1 ) T T starting from the initial point ( 1, 0, 1 ) and moving vertically to the final point ( 1, 0, 2 π ) . T Question: does it require more work to move in a straight line x(t) = ( 1, 0, t ) or along T the spiral helix x( ...
Multizone Air Flow Modelling (COMIS) - IEA-EBC
... flow characteristics are well understood, and it is driven by fans with known pressure-flow characteristics. Techniques and calculation methods have been developed for the design and sizing of such systems. Much more difficult is the prediction of the general movement of air both within and between ...
... flow characteristics are well understood, and it is driven by fans with known pressure-flow characteristics. Techniques and calculation methods have been developed for the design and sizing of such systems. Much more difficult is the prediction of the general movement of air both within and between ...
Natural convection in a mushy layer
... /3 is usually positive since p*la*T is typically much larger than unity. The combining in this way of the effects of temperature and composition on the density is valid once the strong coupling expressed by (2.6) is accepted. Note that this denies the possibility of any form of double-diffusive conv ...
... /3 is usually positive since p*la*T is typically much larger than unity. The combining in this way of the effects of temperature and composition on the density is valid once the strong coupling expressed by (2.6) is accepted. Note that this denies the possibility of any form of double-diffusive conv ...
NON-EQUILIBRIUM THERMODYNAMICS:
... = A d/ T, which is always positive for spontaneous processes as d and A always have the same sign (as, clearly, d > 0 implies forward reaction and d < 0 implies backward reaction). If A = 0, the system is at equilibrium and so d = 0. The rate of entropy production per unit time is diS/dt = Av/ ...
... = A d/ T, which is always positive for spontaneous processes as d and A always have the same sign (as, clearly, d > 0 implies forward reaction and d < 0 implies backward reaction). If A = 0, the system is at equilibrium and so d = 0. The rate of entropy production per unit time is diS/dt = Av/ ...
INDENTATION PRESSURE OF A SMOOTH CIRCULAR PUNCH*
... may be concentrated or distributed but it is assumed that over the contact area there is a uniformly distributed normal pressure. According to the Drucker-Prager-Greenberg theorem an upper bound on this indentation pressure, p, may be obtained by constructing a kinematically admissible velocity fiel ...
... may be concentrated or distributed but it is assumed that over the contact area there is a uniformly distributed normal pressure. According to the Drucker-Prager-Greenberg theorem an upper bound on this indentation pressure, p, may be obtained by constructing a kinematically admissible velocity fiel ...
Animation principles
... which can be found here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hY8jpD8zU4Y. Transformation between defined key frames can be applied to any animating object parameters: position, shape, velocity, color, lighting settings (light intensity, beam size, light color, and the texture cast by the light). Supposin ...
... which can be found here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hY8jpD8zU4Y. Transformation between defined key frames can be applied to any animating object parameters: position, shape, velocity, color, lighting settings (light intensity, beam size, light color, and the texture cast by the light). Supposin ...
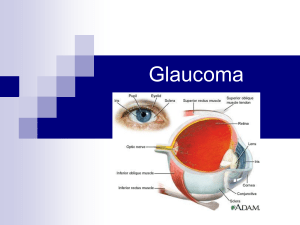
Characteristic pattern to loss of visual field
... Most cases involve increased fluid pressure, known as intraocular pressure (IOP) But increased IOP may not necessarily be cause, 20% have normal tension glaucoma Gradual loss of vision, can progress to blindness if untreated ...
... Most cases involve increased fluid pressure, known as intraocular pressure (IOP) But increased IOP may not necessarily be cause, 20% have normal tension glaucoma Gradual loss of vision, can progress to blindness if untreated ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.