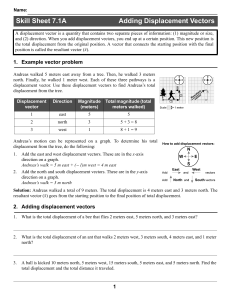
Skill Sheet 7.1A Adding Displacement Vectors
... An object is thrown off a cliff with a horizontal speed of 10 m/sec and some unknown initial vertical velocity. After 3 seconds the object hits the ground which is 30 meters below the cliff. Find the initial vertical velocity and the total horizontal distance traveled by the object. a. What do you k ...
... An object is thrown off a cliff with a horizontal speed of 10 m/sec and some unknown initial vertical velocity. After 3 seconds the object hits the ground which is 30 meters below the cliff. Find the initial vertical velocity and the total horizontal distance traveled by the object. a. What do you k ...
Rotational Kinematics
... Make the following conversions 1 revolution to radians 60 degrees to radians 4.5 revolutions to radians 48 degrees to radians ...
... Make the following conversions 1 revolution to radians 60 degrees to radians 4.5 revolutions to radians 48 degrees to radians ...
1 Simple harmonic motion related to circular motion
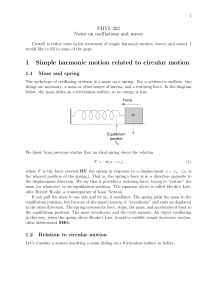
... the distance between nuclei. It is a strange funcr tion indeed. We sketch the function at right. At the equilibrium point ro , the potential energy is a minimum and the force is zero. The force increases for displacements (r − ro ), away from the equilibrium point. The function itself is not quadrat ...
... the distance between nuclei. It is a strange funcr tion indeed. We sketch the function at right. At the equilibrium point ro , the potential energy is a minimum and the force is zero. The force increases for displacements (r − ro ), away from the equilibrium point. The function itself is not quadrat ...
Ch 6 ppt
... Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. • Newton’s third law of motion can be simply stated as follows: All forces act in pairs. ...
... Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. • Newton’s third law of motion can be simply stated as follows: All forces act in pairs. ...
Energy - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • As the KE increases, the PE decreases • As the diver hits the bucket, all PE has been transferred to KE • Work produces energy • Energy changes throughout the dive • At the top of the platform, all GPE and no KE • The diver always possesses 10,000 J of energy (energy is conserved) • Inverse relati ...
... • As the KE increases, the PE decreases • As the diver hits the bucket, all PE has been transferred to KE • Work produces energy • Energy changes throughout the dive • At the top of the platform, all GPE and no KE • The diver always possesses 10,000 J of energy (energy is conserved) • Inverse relati ...
PRE-LAB FOR CONSERVATION OF ENERGY
... falling masses—Is the sum of the calculated kinetic and potential energies exactly the same number as the object falls? Can we apply similar concepts to systems involving forces other than gravitational forces such as systems with spring forces? What about frictional forces? In this lab, you will be ...
... falling masses—Is the sum of the calculated kinetic and potential energies exactly the same number as the object falls? Can we apply similar concepts to systems involving forces other than gravitational forces such as systems with spring forces? What about frictional forces? In this lab, you will be ...
Problems on Friction
... Problem 1: A dockworker loading crates on a ship finds that a 20-kg crate, initially at rest on a horizontal surface, requires a 75-N horizontal force to set it in motion. However, after the crate is in motion, a horizontal force of 60 N is required to keep it moving with a constant speed. Find the ...
... Problem 1: A dockworker loading crates on a ship finds that a 20-kg crate, initially at rest on a horizontal surface, requires a 75-N horizontal force to set it in motion. However, after the crate is in motion, a horizontal force of 60 N is required to keep it moving with a constant speed. Find the ...
Energy - Urbana School District #116
... The thermal energy that is converted from other forms due to friction, air resistance, drag, etc. is often referred to as “waste heat” because it represents energy “robbed from the system.” In real life some of the potential energy the orangutan had in the last example would have been converted to w ...
... The thermal energy that is converted from other forms due to friction, air resistance, drag, etc. is often referred to as “waste heat” because it represents energy “robbed from the system.” In real life some of the potential energy the orangutan had in the last example would have been converted to w ...
Chapter 2
... If b>2mω0, the medium is highly viscous. x The system does not oscillate but simply returns to its equilibrium position. overdamped ...
... If b>2mω0, the medium is highly viscous. x The system does not oscillate but simply returns to its equilibrium position. overdamped ...
Acceleration,
... • Greater acceleration requires greater centripetal force. • A more massive object requires a greater centripetal force to have the same circular speed as a less massive object. • No matter what the mass of an object is, if it moves in a circle, its force and acceleration are directed toward the cen ...
... • Greater acceleration requires greater centripetal force. • A more massive object requires a greater centripetal force to have the same circular speed as a less massive object. • No matter what the mass of an object is, if it moves in a circle, its force and acceleration are directed toward the cen ...
The Modern Galileo Experiment
... to begin data collection. Within the limits of the spring, move the Force Sensor and slowly stretch the spring about 50 cm over several seconds. Hold the sensor still until data collection stops. Do not get any closer than 40 cm to the Motion Detector 16. Examine the graphs. Identify when you starte ...
... to begin data collection. Within the limits of the spring, move the Force Sensor and slowly stretch the spring about 50 cm over several seconds. Hold the sensor still until data collection stops. Do not get any closer than 40 cm to the Motion Detector 16. Examine the graphs. Identify when you starte ...
Instructor`s Guide
... Assuming we can think of a nucleus as a sphere, we find the volume from V = (4/3)πr3 = (4/3) π[8.68 x 10-15m]3 = 2.739 x 10-42 m3 Dividing the mass by the volume, the result is r = [3.952 x 10-25 kg] / [2.739 x 10-42 m3] = 1.443 x 1017 kg/m3. ...
... Assuming we can think of a nucleus as a sphere, we find the volume from V = (4/3)πr3 = (4/3) π[8.68 x 10-15m]3 = 2.739 x 10-42 m3 Dividing the mass by the volume, the result is r = [3.952 x 10-25 kg] / [2.739 x 10-42 m3] = 1.443 x 1017 kg/m3. ...
Phys_21_N7_WORK_and_ENERGY
... to begin data collection. Within the limits of the spring, move the Force Sensor and slowly stretch the spring about 50 cm over several seconds. Hold the sensor still until data collection stops. Do not get any closer than 40 cm to the Motion Detector 16. Examine the graphs. Identify when you starte ...
... to begin data collection. Within the limits of the spring, move the Force Sensor and slowly stretch the spring about 50 cm over several seconds. Hold the sensor still until data collection stops. Do not get any closer than 40 cm to the Motion Detector 16. Examine the graphs. Identify when you starte ...
Work Forms of Energy Conservation of Energy Gravitational
... The thermal energy that is converted from other forms due to friction, air resistance, drag, etc. is often referred to as “waste heat” because it represents energy “robbed from the system.” In real life some of the potential energy the orangutan had in the last example would have been converted to w ...
... The thermal energy that is converted from other forms due to friction, air resistance, drag, etc. is often referred to as “waste heat” because it represents energy “robbed from the system.” In real life some of the potential energy the orangutan had in the last example would have been converted to w ...
energy transformations
... “Energy Transformations” examines the conversion of energy from one form to another. Work is defined, and changes from gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy, and the reverse, are calculated. Since graphing can aid understanding of motion, a distance-versus-time graph is produced and analy ...
... “Energy Transformations” examines the conversion of energy from one form to another. Work is defined, and changes from gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy, and the reverse, are calculated. Since graphing can aid understanding of motion, a distance-versus-time graph is produced and analy ...
SolutionsExIIF05
... 41. Assume that you are riding in a windowless room on a perfectly smooth surface. cYou can't feel any motion.) Imagine that you have a collection of objects and measuring devices in the room. Which of the following experiments could prove that the room is moving horizontally at a constant velocity? ...
... 41. Assume that you are riding in a windowless room on a perfectly smooth surface. cYou can't feel any motion.) Imagine that you have a collection of objects and measuring devices in the room. Which of the following experiments could prove that the room is moving horizontally at a constant velocity? ...
Horizontally Launched Projectiles (notes
... (Horizontal and Vertical Displacement) The previous diagrams, tables, and discussion pertain to how the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity vector change with time during the course of projectile's trajectory. Now we will investigate the manner in which the horizontal and vertical com ...
... (Horizontal and Vertical Displacement) The previous diagrams, tables, and discussion pertain to how the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity vector change with time during the course of projectile's trajectory. Now we will investigate the manner in which the horizontal and vertical com ...
Our Dynamic Universe notes
... B – Ball reaches maximum velocity C - Ball rebounds off the ground. D – Ball reaches maximum height after rebound When a velocity-time/acceleration-time graph falls below the x-axis, this can indicate that the object is slowing down OR that a change in direction has taken place. In both cases the ma ...
... B – Ball reaches maximum velocity C - Ball rebounds off the ground. D – Ball reaches maximum height after rebound When a velocity-time/acceleration-time graph falls below the x-axis, this can indicate that the object is slowing down OR that a change in direction has taken place. In both cases the ma ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.