Centripetal Force and Acceleration
... Centripetal Force Example Problem A beetle standing on the edge of an antique 12 inch vinyl record is whirling around at 33.33 rotations per minute. Compute the magnitude of the creature’s centripetal acceleration. ...
... Centripetal Force Example Problem A beetle standing on the edge of an antique 12 inch vinyl record is whirling around at 33.33 rotations per minute. Compute the magnitude of the creature’s centripetal acceleration. ...
ODU-Mechanics-Questions
... 10. A ball is dropped from a height and bounces up and down on a horizontal surface. Which velocity-time graph represents the motion of the ball from the moment it is released? ...
... 10. A ball is dropped from a height and bounces up and down on a horizontal surface. Which velocity-time graph represents the motion of the ball from the moment it is released? ...
Slide 1 - Phy 2048-0002
... body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and direction. Principle of superposition: when two or more forces act on a body, the net force can be obtained by adding the individual forces vectorially. Inertial reference frame: where Newton’s laws hold. ...
... body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and direction. Principle of superposition: when two or more forces act on a body, the net force can be obtained by adding the individual forces vectorially. Inertial reference frame: where Newton’s laws hold. ...
Part 1 - Mechanics and Thermodynamics
... equivalent in terms of accuracy. They have 1 m and 100 m absolute errors respectively. The often used term relative error is the ratio of the absolute error over the nominal value. The smaller is the relative error the higher the accuracy of the measurement. When making operations with physical quan ...
... equivalent in terms of accuracy. They have 1 m and 100 m absolute errors respectively. The often used term relative error is the ratio of the absolute error over the nominal value. The smaller is the relative error the higher the accuracy of the measurement. When making operations with physical quan ...
Biology Course Map - Georgia Standards
... a. Scientific investigators control the conditions of their experiments in order to produce valuable data. b. Scientific researchers are expected to critically assess the quality of data including possible sources of bias in their investigations’ hypotheses, observations, data analyses, and interpre ...
... a. Scientific investigators control the conditions of their experiments in order to produce valuable data. b. Scientific researchers are expected to critically assess the quality of data including possible sources of bias in their investigations’ hypotheses, observations, data analyses, and interpre ...
Chapter 2
... method, i.e. Newton-Euler Formulation. The motion of a rigid body can be decomposed into the translational motion with respect to an arbitrary point fixed to the rigid body, and the rotational motion of the rigid body about that point. The dynamic equations of a rigid body can also be represented by ...
... method, i.e. Newton-Euler Formulation. The motion of a rigid body can be decomposed into the translational motion with respect to an arbitrary point fixed to the rigid body, and the rotational motion of the rigid body about that point. The dynamic equations of a rigid body can also be represented by ...
TEKS 5 - Pearson School
... Aristotle The ancient Greek scientist and philosopher Aristotle (384 B.C.E.–322 B.C.E.) made many scientific discoveries through careful observation and logical reasoning. He was not always correct. Aristotle incorrectly proposed that force is required to keep an object moving at constant speed. Thi ...
... Aristotle The ancient Greek scientist and philosopher Aristotle (384 B.C.E.–322 B.C.E.) made many scientific discoveries through careful observation and logical reasoning. He was not always correct. Aristotle incorrectly proposed that force is required to keep an object moving at constant speed. Thi ...
Chapter 1
... •Newton’s third law is universal, it works whether the object is stationary or moving. •The two forces are exerted on two different objects. They do not cancel directly. (cf. Two forces exerted on the same object may cancel each other.) ...
... •Newton’s third law is universal, it works whether the object is stationary or moving. •The two forces are exerted on two different objects. They do not cancel directly. (cf. Two forces exerted on the same object may cancel each other.) ...
Physics Syllabus, Grade 9
... same direction then in the opposite direction Model with: Change the direction of the scale of the Human line. Go Left to right. What does that do to the lines on the graphs? Shift it over 1 m. Add one m and start there. The point is that the data is relative to the instrument. We already know that ...
... same direction then in the opposite direction Model with: Change the direction of the scale of the Human line. Go Left to right. What does that do to the lines on the graphs? Shift it over 1 m. Add one m and start there. The point is that the data is relative to the instrument. We already know that ...
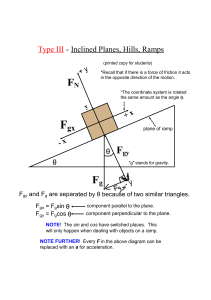
Type III Inclined Planes, Hills, Ramps
... *Recall that if there is a force of friction it acts in the opposite direction of the motion. *The coordinate system is rotated the same amount as the angle θ. ...
... *Recall that if there is a force of friction it acts in the opposite direction of the motion. *The coordinate system is rotated the same amount as the angle θ. ...
9.hamilton11e_ppt_11
... Horizontal velocity projects the object some distance from the release point © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved. ...
... Horizontal velocity projects the object some distance from the release point © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved. ...
EOC - Physics (What you need to know)
... areas) is measured in volts. The symbol is (v). Electric current is the flow of electrons through a conductor o is measured in amperes or amps. The symbol is (a). Resistance happens when the electrons flowing through the wire continually run into things in the wire and bounce around. o is measur ...
... areas) is measured in volts. The symbol is (v). Electric current is the flow of electrons through a conductor o is measured in amperes or amps. The symbol is (a). Resistance happens when the electrons flowing through the wire continually run into things in the wire and bounce around. o is measur ...
ΣF = ma
... actions. By producing a certain combination of muscle actions, we ultimately push against the ground which pushes back against the body with an equal and opposite force. This is explained by Newton's 3rd law of motion which states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Purpos ...
... actions. By producing a certain combination of muscle actions, we ultimately push against the ground which pushes back against the body with an equal and opposite force. This is explained by Newton's 3rd law of motion which states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Purpos ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.