Work and kinetic energy
... Work and kinetic energy • Work W= F||d =Fd cosθ • Kinetic energy (KE) is defined to be KE=½mv2 • Units of both are in Joules ...
... Work and kinetic energy • Work W= F||d =Fd cosθ • Kinetic energy (KE) is defined to be KE=½mv2 • Units of both are in Joules ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy
... • The energy of a moving object due to the object’s motion – The KE of any moving object depends on its mass and velocity ...
... • The energy of a moving object due to the object’s motion – The KE of any moving object depends on its mass and velocity ...
motion - Images
... • Speed is the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel the distance • Formula: Speed = distance ÷ time (S=D/T) • SI Unit: meters per second (m/s) • Ex. In the 100m dash the fastest runner finished in 10s. S= 100m/10s= 10m/s • 3 Types of Speed – Average speed is found by dividing the to ...
... • Speed is the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel the distance • Formula: Speed = distance ÷ time (S=D/T) • SI Unit: meters per second (m/s) • Ex. In the 100m dash the fastest runner finished in 10s. S= 100m/10s= 10m/s • 3 Types of Speed – Average speed is found by dividing the to ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... Vibrating System is Constant KE + PE = constant If the maximum amplitude of the motion is x0 then the energy at any point x is given by: ½ mv2 + ½ kx2 = ½ kx02 From this we can solve for velocity: │v│= √ [(x02 –x2)(k/m)] From Hooke’s law, F = -kx and F =ma, therefore a = -(k/m) x ...
... Vibrating System is Constant KE + PE = constant If the maximum amplitude of the motion is x0 then the energy at any point x is given by: ½ mv2 + ½ kx2 = ½ kx02 From this we can solve for velocity: │v│= √ [(x02 –x2)(k/m)] From Hooke’s law, F = -kx and F =ma, therefore a = -(k/m) x ...
Relativity, Inertia, and Equivalence Principle
... frame) Any accelerating system is non-inertial, there would be break in symmetry (a “special” direction would be established) If motion in one dimension is not acceleration, then we can consider an inertial frame along that direction – consider plane flying at constant speed… you could do experiment ...
... frame) Any accelerating system is non-inertial, there would be break in symmetry (a “special” direction would be established) If motion in one dimension is not acceleration, then we can consider an inertial frame along that direction – consider plane flying at constant speed… you could do experiment ...
Final exam
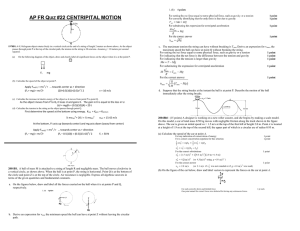
... Q2) A 5-kg block is released from rest at the top of the track shown in Figure 7.17. The track is 6-m high and smooth except for the portion AB whose length is 4 m, where µk = 0.4. At the end of the track the block hits a spring of force constant 600 N/m. What is the maximum compression of the sprin ...
... Q2) A 5-kg block is released from rest at the top of the track shown in Figure 7.17. The track is 6-m high and smooth except for the portion AB whose length is 4 m, where µk = 0.4. At the end of the track the block hits a spring of force constant 600 N/m. What is the maximum compression of the sprin ...
Ch6Lecture1
... is done only horizontally b) If you push on a wall that doesn’t move have you done any work? 2m ...
... is done only horizontally b) If you push on a wall that doesn’t move have you done any work? 2m ...
Conceptual Physics
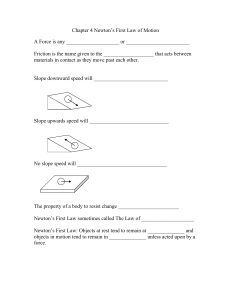
... A Force is any ____________________ or ________________________ Friction is the name given to the ___________________ that acts between materials in contact as they move past each other. ...
... A Force is any ____________________ or ________________________ Friction is the name given to the ___________________ that acts between materials in contact as they move past each other. ...
Chapter6
... In classical mechanics the trajectory of a particle moving under the influence of a force can be completely determined from the initial position and velocity. The total energy of a many particle system must be found from the positions and velocities of the particles as the sum of the kinetic and pot ...
... In classical mechanics the trajectory of a particle moving under the influence of a force can be completely determined from the initial position and velocity. The total energy of a many particle system must be found from the positions and velocities of the particles as the sum of the kinetic and pot ...
Mid Term Pre assessment
... 3. A loaf of bread weighs 1,362 g. The weight in kilograms is a. 1.362 kg. b. 1,362 kg. c. 0.1362 kg. d. 0.01362 kg. ...
... 3. A loaf of bread weighs 1,362 g. The weight in kilograms is a. 1.362 kg. b. 1,362 kg. c. 0.1362 kg. d. 0.01362 kg. ...
CPS Physics Final Study Guide site
... a. moving with a constant speed forward, away from the origin b. moving with a constant speed towards the origin c. not moving d. speeding up 26. If a distance vs. time graph has an increasing curve, it is showing: a. An object that is at rest. b. An object that is moving at a constant rate. c. An o ...
... a. moving with a constant speed forward, away from the origin b. moving with a constant speed towards the origin c. not moving d. speeding up 26. If a distance vs. time graph has an increasing curve, it is showing: a. An object that is at rest. b. An object that is moving at a constant rate. c. An o ...
Laws/Definitions/Formulae
... Period of a satellite : the period T of a satellite describing an orbit of radius d about a celestial body of mass M is given by T2 = 4π2d3/GM. Hookes Law: For a range of stresses, provided the elastic limit is not exceeded, the strain produced is proportional to the stress applied and independent o ...
... Period of a satellite : the period T of a satellite describing an orbit of radius d about a celestial body of mass M is given by T2 = 4π2d3/GM. Hookes Law: For a range of stresses, provided the elastic limit is not exceeded, the strain produced is proportional to the stress applied and independent o ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.