2AngDyn - TuHS Physics
... 1.2 m from the center of a merry-go-round that is a uniform cylinder with a mass of 240 kg and a radius of 1.5 m. What is its total moment of inertia? The total moment of inertia will just be the total of the parts: Children – use mr2 (assume they are points) MGR – use 1/2mr2 (solid cylinder) I = 3( ...
... 1.2 m from the center of a merry-go-round that is a uniform cylinder with a mass of 240 kg and a radius of 1.5 m. What is its total moment of inertia? The total moment of inertia will just be the total of the parts: Children – use mr2 (assume they are points) MGR – use 1/2mr2 (solid cylinder) I = 3( ...
Calculation of an Atomically Modulated Friction Force in Atomic-Force Microscopy.
... observed for moderate applied loads in the absence of wear and plastic deformations. For a multiatom «tip» which is commensurate with the substrate, the tip-substrate potential is proportional to the number of tip atoms at the interface, n, and so is the critical value Cerlt for nonzero friction. In ...
... observed for moderate applied loads in the absence of wear and plastic deformations. For a multiatom «tip» which is commensurate with the substrate, the tip-substrate potential is proportional to the number of tip atoms at the interface, n, and so is the critical value Cerlt for nonzero friction. In ...
Interim Assessment Sample Question
... Why does it take so much force to stop a fully loaded train or truck as opposed to a small car? Why do satellites in circular orbit maintain the same speed at all times? How does a seat belt keep a passenger from being injured in a car ...
... Why does it take so much force to stop a fully loaded train or truck as opposed to a small car? Why do satellites in circular orbit maintain the same speed at all times? How does a seat belt keep a passenger from being injured in a car ...
The Pendulum Introduction
... Supplementary Exercise Generate a fractal, chaotic attractor The motions of nonlinear dynamical systems such as the damped, driven pendulum can be aperiodic for some parameter ranges. For example, for the case A = 1.5, k = 0.5, φ = 0.66667 the pendulum motion is aperiodic and chaotic. The motion of ...
... Supplementary Exercise Generate a fractal, chaotic attractor The motions of nonlinear dynamical systems such as the damped, driven pendulum can be aperiodic for some parameter ranges. For example, for the case A = 1.5, k = 0.5, φ = 0.66667 the pendulum motion is aperiodic and chaotic. The motion of ...
PSE 3e Chapter 8 EOC Conceptual Questions Larry Smith
... between the forward direction (parallel to the track) and the center of the circle. 8.7. (a) The plane is in dynamic equilibrium, so the net force on the plane is zero. (b) The vertical forces cancel, and so do the horizontal forces, so the net force is zero. The plane is traveling in the positive x ...
... between the forward direction (parallel to the track) and the center of the circle. 8.7. (a) The plane is in dynamic equilibrium, so the net force on the plane is zero. (b) The vertical forces cancel, and so do the horizontal forces, so the net force is zero. The plane is traveling in the positive x ...
laws of motion
... to verify or refute theories. Science meant measurement of quantities and a search for mathematical relations between them. Not undeservedly, many regard Galileo as the father of modern science. ...
... to verify or refute theories. Science meant measurement of quantities and a search for mathematical relations between them. Not undeservedly, many regard Galileo as the father of modern science. ...
(1 Of 2) Air Track TEACHER
... where ‘F’ is the force involved in distorting the object, ‘k’ is the spring constant of the object (measured in Newtons per meter), and ‘x’ is the net displacement of the object, measured from its equilibrium point. A negative sign exists in this equation to show that the direction of the force is a ...
... where ‘F’ is the force involved in distorting the object, ‘k’ is the spring constant of the object (measured in Newtons per meter), and ‘x’ is the net displacement of the object, measured from its equilibrium point. A negative sign exists in this equation to show that the direction of the force is a ...
Using Newton`s Laws
... showing that a horizontal surface exerts a force that just balances the skier’s weight. At the other extreme, consider u = 90°, so the slope is a vertical cliff. Then the skier falls freely with acceleration g, as expected. In this case n = 0 because there’s no contact between skier and slope. At in ...
... showing that a horizontal surface exerts a force that just balances the skier’s weight. At the other extreme, consider u = 90°, so the slope is a vertical cliff. Then the skier falls freely with acceleration g, as expected. In this case n = 0 because there’s no contact between skier and slope. At in ...
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations
... point of the rigid body is replaced by a force F9 of the same magnitude and same direction, but acting at a different point, provided that the two forces have the same line of action. But since F and F9 have the same moment about any given point, it is clear that they form two equipollent systems of ...
... point of the rigid body is replaced by a force F9 of the same magnitude and same direction, but acting at a different point, provided that the two forces have the same line of action. But since F and F9 have the same moment about any given point, it is clear that they form two equipollent systems of ...
Chapter I
... to measure the distance covered by the bullet at the instant, they don't need any speedometer to find its speed at any instant t, nor they need any clock to see the time required to cover the definite distance. In fact, they need not have to do any such experiment. What they need to describe the mot ...
... to measure the distance covered by the bullet at the instant, they don't need any speedometer to find its speed at any instant t, nor they need any clock to see the time required to cover the definite distance. In fact, they need not have to do any such experiment. What they need to describe the mot ...
College Physics, 2e (Knight)
... provided by gravitational attraction. The net force experienced by an astronaut is 0, thus the astronaut is weightless. (The astronaut is in a continual state of free fall while in orbit.) Var: 1 10) Can a satellite be in an elliptical orbit under uniform circular motion? Answer: No. A satellite in ...
... provided by gravitational attraction. The net force experienced by an astronaut is 0, thus the astronaut is weightless. (The astronaut is in a continual state of free fall while in orbit.) Var: 1 10) Can a satellite be in an elliptical orbit under uniform circular motion? Answer: No. A satellite in ...
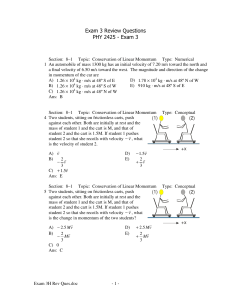
Exam 3 Review Questions PHY 2425 - Exam 3
... Section: 8–2 Topic: Kinetic Energy of a System Type: Conceptual 12 A golf ball and a Ping-Pong ball are dropped in a vacuum chamber. When they have fallen halfway to the floor, they have the same A) speed. B) potential energy. C) kinetic energy. D) momentum. E) speed, potential energy, kinetic ener ...
... Section: 8–2 Topic: Kinetic Energy of a System Type: Conceptual 12 A golf ball and a Ping-Pong ball are dropped in a vacuum chamber. When they have fallen halfway to the floor, they have the same A) speed. B) potential energy. C) kinetic energy. D) momentum. E) speed, potential energy, kinetic ener ...
rev1 - UConn Physics
... A fighter pilot flying in a circular turn will pass out if the centripetal acceleration he experiences is more than about 9 times the acceleration of gravity g. If his F18 is moving with a speed of 300 m/s, what is the approximate diameter of the tightest turn this pilot can make and survive to tell ...
... A fighter pilot flying in a circular turn will pass out if the centripetal acceleration he experiences is more than about 9 times the acceleration of gravity g. If his F18 is moving with a speed of 300 m/s, what is the approximate diameter of the tightest turn this pilot can make and survive to tell ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.