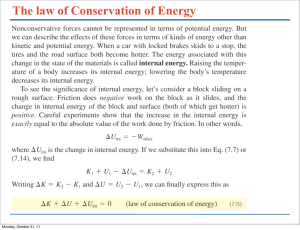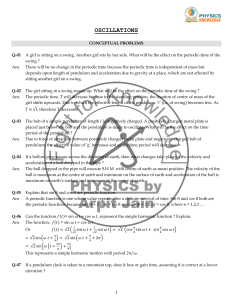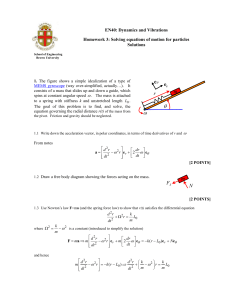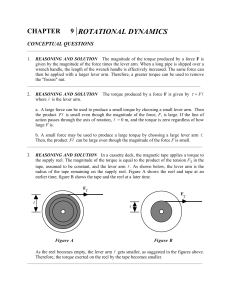
PRELAB: FORCES AND MOTION
... • To critically examine the inferences that can (and can’t) be drawn from observations Overview: In previous labs, you have used a motion detector to display position, velocity and acceleration graphs of various objects moving in one dimension. You were not concerned about how you got the objects to ...
... • To critically examine the inferences that can (and can’t) be drawn from observations Overview: In previous labs, you have used a motion detector to display position, velocity and acceleration graphs of various objects moving in one dimension. You were not concerned about how you got the objects to ...
lecture1437132938
... known as a higher pair. Example: – Wheel rolling on a surface, cam and follower pair, tooth gears, ball and roller bearings. ...
... known as a higher pair. Example: – Wheel rolling on a surface, cam and follower pair, tooth gears, ball and roller bearings. ...
apPhysics_lec_06
... Gravity or Weight (Gravitational force Earth pulling on objects around it): W ...
... Gravity or Weight (Gravitational force Earth pulling on objects around it): W ...
Module 2 UNDERSTANDING MOTION 2
... around. The speed (or the magnitude of the velocity) of the merry-go-round will be constant but the velocity will be changing because of the changing direction, so therefore there is an acceleration. (As long as one component is changing, be it the magnitude or the direction of the velocity.) Suppos ...
... around. The speed (or the magnitude of the velocity) of the merry-go-round will be constant but the velocity will be changing because of the changing direction, so therefore there is an acceleration. (As long as one component is changing, be it the magnitude or the direction of the velocity.) Suppos ...
Section Check
... will double the same object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acceleration. One unit of force causes a 1-kg mass to accelerate at 1 m/s2, so o ...
... will double the same object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acceleration. One unit of force causes a 1-kg mass to accelerate at 1 m/s2, so o ...
Gravity and Motion
... an unbalanced force. • An object in motion will remain in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... an unbalanced force. • An object in motion will remain in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
Chapter 9 Rotation
... Two points are on a disk that is turning about a fixed-axis through its center, perpendicular to the disk and through its center, at increasing angular velocity. One point on the rim and the other point is halfway between the rim and the center. (a) Which point moves the greater distance in a given ...
... Two points are on a disk that is turning about a fixed-axis through its center, perpendicular to the disk and through its center, at increasing angular velocity. One point on the rim and the other point is halfway between the rim and the center. (a) Which point moves the greater distance in a given ...
Chapter 11
... The angular momentum of the spacecraft about its center of mass is zero A gyroscope is set into rotation, giving it a nonzero angular momentum The spacecraft rotates in the direction opposite to that of the gyroscope So the total momentum of the system remains zero ...
... The angular momentum of the spacecraft about its center of mass is zero A gyroscope is set into rotation, giving it a nonzero angular momentum The spacecraft rotates in the direction opposite to that of the gyroscope So the total momentum of the system remains zero ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.