NNHS Introductory Physics: Midyear Review
... Which of the following types of energy is the source for D. A sky-diver falling to Earth with his parachute open. the initial energy gain of the water? A. electrical B. magnetic C. mechanical D. thermal Standard 2A4. Students will apply the concept of conservation of mechanical energy, and describe ...
... Which of the following types of energy is the source for D. A sky-diver falling to Earth with his parachute open. the initial energy gain of the water? A. electrical B. magnetic C. mechanical D. thermal Standard 2A4. Students will apply the concept of conservation of mechanical energy, and describe ...
Word document
... to analyze the motion of an object. (Be very familiar with the set up and attack of yo-yos !) 7. Use the conditions for static equilibrium to find the necessary force or necessary position that a force must be applied to keep an object at complete rest. (Be familiar with the “see-saw”.) 8. Use the L ...
... to analyze the motion of an object. (Be very familiar with the set up and attack of yo-yos !) 7. Use the conditions for static equilibrium to find the necessary force or necessary position that a force must be applied to keep an object at complete rest. (Be familiar with the “see-saw”.) 8. Use the L ...
Matching - Hauserphysics
... 5. Find the speed of a car that travels 500 miles in 10 hours. A) 729 mph B) 9 m/s C) 50 mph D) 0.11 mph 6. Find the time it takes to walk a distance of 15 meters at a speed of 3 m/s. A) 450 seconds B) 50 seconds C) 50 m/s ...
... 5. Find the speed of a car that travels 500 miles in 10 hours. A) 729 mph B) 9 m/s C) 50 mph D) 0.11 mph 6. Find the time it takes to walk a distance of 15 meters at a speed of 3 m/s. A) 450 seconds B) 50 seconds C) 50 m/s ...
CBSE Class 9 Work Energy and Power Solved test paper-05
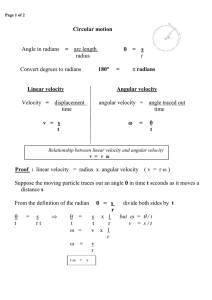
... When a satellite moves around the Earth in a circular path, then the force of gravity acts on it directed towards the centre. The motion of the satellite is in the horizontal plane. Therefore, the force of gravity of Earth on the satellite and the direction of motion of satellite are perpendicular t ...
... When a satellite moves around the Earth in a circular path, then the force of gravity acts on it directed towards the centre. The motion of the satellite is in the horizontal plane. Therefore, the force of gravity of Earth on the satellite and the direction of motion of satellite are perpendicular t ...
SHM Dynamics WS (honors)
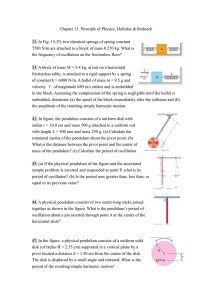
... The restoring force of the spring when it is deformed is responsible for the acceleration pattern of the mass. The magnitude of this force depends on the amount by which the spring is deformed. The further it is stretched or compressed from its rest length, the greater restoring force it exerts. ...
... The restoring force of the spring when it is deformed is responsible for the acceleration pattern of the mass. The magnitude of this force depends on the amount by which the spring is deformed. The further it is stretched or compressed from its rest length, the greater restoring force it exerts. ...
Newtons laws
... Mass is directly related to inertia. • The greater the mass the greater the tendency to resist change of an object’s motion. • objects will continue to do as they are doing with out friction. ...
... Mass is directly related to inertia. • The greater the mass the greater the tendency to resist change of an object’s motion. • objects will continue to do as they are doing with out friction. ...
kinetic energy - MrcsphysicsWiki
... or work is stored when a force does work “against” a force such as the gravitational force or a Hooke’s Law (spring) force. Forces that store or hide energy are ...
... or work is stored when a force does work “against” a force such as the gravitational force or a Hooke’s Law (spring) force. Forces that store or hide energy are ...
Solution
... the same velocity at the same time from ground level and feel no air resistance. Which statement about these stones is true? A) At its highest point, the heavier stone will have twice as much gravitational potential energy as the lighter one because it is twice as heavy. B) At their highest point, b ...
... the same velocity at the same time from ground level and feel no air resistance. Which statement about these stones is true? A) At its highest point, the heavier stone will have twice as much gravitational potential energy as the lighter one because it is twice as heavy. B) At their highest point, b ...
Physics 11 Final Exam Outline
... define normal force define coefficient of friction recognize the relationship between force due to friction and the strengths of normal force and coefficient of friction solve problems with objects sliding on horizontal surfaces, involving force of coefficient of normal friction fricti ...
... define normal force define coefficient of friction recognize the relationship between force due to friction and the strengths of normal force and coefficient of friction solve problems with objects sliding on horizontal surfaces, involving force of coefficient of normal friction fricti ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.