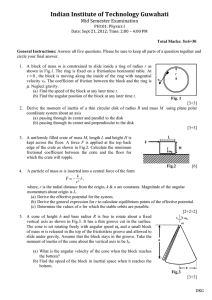
For an object travelling with “uniform circular motion,”
... by a student who is holding the other end of the string. Which one of the following statements is false? a) The tension in the string will increase with the speed of rotation. b) The rock will fly off along a tangent to the circle if the string breaks. c) The circle described by the rock could be ab ...
... by a student who is holding the other end of the string. Which one of the following statements is false? a) The tension in the string will increase with the speed of rotation. b) The rock will fly off along a tangent to the circle if the string breaks. c) The circle described by the rock could be ab ...
Forces
... in the direction toward the center of motion – centripetal acceleration then, is the acceleration of an object toward the center of a curved or circular path – acceleration occurs during a curve because the direction is changing therefore making velocity change – example: centripetal force (friction ...
... in the direction toward the center of motion – centripetal acceleration then, is the acceleration of an object toward the center of a curved or circular path – acceleration occurs during a curve because the direction is changing therefore making velocity change – example: centripetal force (friction ...
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR PHYS 2425
... Satisfactory completion of this course earns the student four semester hours credit in University Physics required by most colleges of students who plan to major in physics, chemistry, certain fields of engineering and other majors which require a calculus-based physics. The student should have take ...
... Satisfactory completion of this course earns the student four semester hours credit in University Physics required by most colleges of students who plan to major in physics, chemistry, certain fields of engineering and other majors which require a calculus-based physics. The student should have take ...
13.1 - Newton`s Law of Motion
... Tangential and Normal Forces. • Determination of the resultant force components ΣFr, ΣFθ, ΣFz causing a particle to move with a known acceleration. • If acceleration is not specified at given instant, directions or magnitudes of the forces acting on the particle must be known or computed to solve. • ...
... Tangential and Normal Forces. • Determination of the resultant force components ΣFr, ΣFθ, ΣFz causing a particle to move with a known acceleration. • If acceleration is not specified at given instant, directions or magnitudes of the forces acting on the particle must be known or computed to solve. • ...
Acceleration - Solon City Schools
... movement of two surfaces that are in contact and are sliding over each other ...
... movement of two surfaces that are in contact and are sliding over each other ...
Physics 11 Chapter 6.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... While it is true that no work is being done on the wall by you, there is work being done inside your arm muscles. Exerting a force via a muscle causes small continual motions in your muscles, which is work, and which causes you to tire. An example of this is holding a heavy load at arm’s length. Whi ...
... While it is true that no work is being done on the wall by you, there is work being done inside your arm muscles. Exerting a force via a muscle causes small continual motions in your muscles, which is work, and which causes you to tire. An example of this is holding a heavy load at arm’s length. Whi ...
force - My CCSD
... Newton’s 1st Law of Motion Inertia Galileo came up with the definitions of FORCE and FRICTION. Force is any push or pull. Friction is the name given to the force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Galileo was concerned with how things move rather than why they ...
... Newton’s 1st Law of Motion Inertia Galileo came up with the definitions of FORCE and FRICTION. Force is any push or pull. Friction is the name given to the force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Galileo was concerned with how things move rather than why they ...
The Toolbox of Science
... – The energy possessed by a body because of its motion, equal to one half the mass of the body times the square of its speed. ...
... – The energy possessed by a body because of its motion, equal to one half the mass of the body times the square of its speed. ...
Chapter 10: Dynamics of rotational motion
... • Torque: Is it a force? • torques rotational motion (just as forces linear accelerations) • combination of translation and rotation: rolling objects • Calculation of work done by a torque • Angular momentum conservation • rotational dynamics and angular momentum: they are related ...
... • Torque: Is it a force? • torques rotational motion (just as forces linear accelerations) • combination of translation and rotation: rolling objects • Calculation of work done by a torque • Angular momentum conservation • rotational dynamics and angular momentum: they are related ...
Chapter 9 PPT
... Requirement: The angular speed must be expressed in rad/s. SI Unit of Rotational Kinetic Energy: joule (J) ...
... Requirement: The angular speed must be expressed in rad/s. SI Unit of Rotational Kinetic Energy: joule (J) ...
projectile
... If shot at any angle greater than 0 degrees, the projectile will travel up for a while, then down. The time up is equal to the time down. The closer the launch angle is to 90 degrees, the more time the projectile will spend in the air (assuming that the initial velocity is constant). ...
... If shot at any angle greater than 0 degrees, the projectile will travel up for a while, then down. The time up is equal to the time down. The closer the launch angle is to 90 degrees, the more time the projectile will spend in the air (assuming that the initial velocity is constant). ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.