II. Acceleration
... 4. Explain why Venus, which is slightly less massive than Earth, experiences a stronger gravitational pull from the sun than Earth does. ...
... 4. Explain why Venus, which is slightly less massive than Earth, experiences a stronger gravitational pull from the sun than Earth does. ...
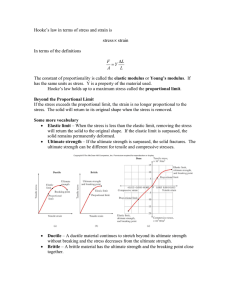
forces & energy
... gravity is the only force. 2. The force of gravity does not change in size at all. 3. The force of air resistance starts to increase. 4. When the forces are balanced the object reaches constant maximum speed, called Terminal Velocity. ...
... gravity is the only force. 2. The force of gravity does not change in size at all. 3. The force of air resistance starts to increase. 4. When the forces are balanced the object reaches constant maximum speed, called Terminal Velocity. ...
Objective:
... A toy car which is moving at a constant velocity accelerates when it is pulled using an elastic string. c) Slows down a moving object. When a vehicle moves from a smooth surface to a rough surface, the force of friction retards the motion of the vehicle. d) Stops the motion of an object. When a car ...
... A toy car which is moving at a constant velocity accelerates when it is pulled using an elastic string. c) Slows down a moving object. When a vehicle moves from a smooth surface to a rough surface, the force of friction retards the motion of the vehicle. d) Stops the motion of an object. When a car ...
Forces and Motion
... Direction is measured with a compass. The points on a compass are N for North, S for South, E for East, and W for West. To describe an object’s velocity, you must include both its speed and the direction it is moving. You must use a stopwatch, a meter stick, and a compass to measure velocity. ...
... Direction is measured with a compass. The points on a compass are N for North, S for South, E for East, and W for West. To describe an object’s velocity, you must include both its speed and the direction it is moving. You must use a stopwatch, a meter stick, and a compass to measure velocity. ...
Conceptual Quiz on Work, energy and Power
... So in the first case, we have: 1/2 m (302 - 02) = 1/2 m (900) In the second case, we have: 1/2 m (602 - 302) = 1/2 m (2700) Thus, the bigger energy change occurs in the second case. ...
... So in the first case, we have: 1/2 m (302 - 02) = 1/2 m (900) In the second case, we have: 1/2 m (602 - 302) = 1/2 m (2700) Thus, the bigger energy change occurs in the second case. ...
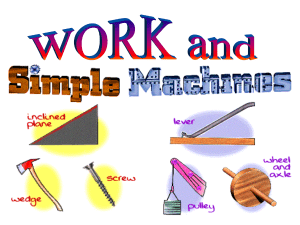
machines. S8P3c: Demonstrate the effect of simple
... When a plane is inclined, or slanted, it can help you move objects across distances. A common inclined plane is a ramp. Lifting a heavy box onto a loading dock is much easier if you slide the box up a ramp (an ...
... When a plane is inclined, or slanted, it can help you move objects across distances. A common inclined plane is a ramp. Lifting a heavy box onto a loading dock is much easier if you slide the box up a ramp (an ...
Worksheet 1
... 41. A snowboarder at the top of Terry Peak has more potential energy than a snowboarder at the top of Lookout Mountain. 42. Mechanical energy is equal to the total kinetic energy in a system. 43. Energy stored in chemical bonds is called gravitational potential energy. ...
... 41. A snowboarder at the top of Terry Peak has more potential energy than a snowboarder at the top of Lookout Mountain. 42. Mechanical energy is equal to the total kinetic energy in a system. 43. Energy stored in chemical bonds is called gravitational potential energy. ...
Work - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... point in an ISOLATED system is equal to the total mechanical energy at any later point (in the absence of friction) Energy can be transformed from one type to another Example: A falling book starts with potential energy. As it falls, the potential energy gets transformed into kinetic energy ...
... point in an ISOLATED system is equal to the total mechanical energy at any later point (in the absence of friction) Energy can be transformed from one type to another Example: A falling book starts with potential energy. As it falls, the potential energy gets transformed into kinetic energy ...
Chapter 8
... wrapped around the cylinder. If the bucket starts from rest at the top of the well and falls for 3.0 s before hitting the water, how far does it fall? ...
... wrapped around the cylinder. If the bucket starts from rest at the top of the well and falls for 3.0 s before hitting the water, how far does it fall? ...
rotary motion - GEOCITIES.ws
... A tangential force of 5.0 N is applied for 10.0 s to the rim of a 1.5 Kg bicycle wheel having a radius of 25 cm. If the wheel starts from rest, find : (a) The rotational inertia of the wheel, (b) Its angular acceleration, (c) Its angular velocity at 10.0 s, (d) The distance traveled by a point on th ...
... A tangential force of 5.0 N is applied for 10.0 s to the rim of a 1.5 Kg bicycle wheel having a radius of 25 cm. If the wheel starts from rest, find : (a) The rotational inertia of the wheel, (b) Its angular acceleration, (c) Its angular velocity at 10.0 s, (d) The distance traveled by a point on th ...
Conservation of Energy
... Review the solution steps Conservation of energy problems might include elastic potential energy—in addition to gravitational potential and kinetic energy. Some terms will be zero if you choose the before and after states wisely! ...
... Review the solution steps Conservation of energy problems might include elastic potential energy—in addition to gravitational potential and kinetic energy. Some terms will be zero if you choose the before and after states wisely! ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.