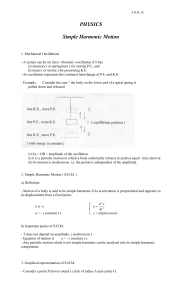
PHYSICS
... (i) A body is said to be forced vibration (oscillation )if there is an external periodic driving force acting on it. (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving ...
... (i) A body is said to be forced vibration (oscillation )if there is an external periodic driving force acting on it. (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving ...
Lecture 04.v2.9-6-12..
... W = Fd cos. Work is a scalar. We can determine work two ways: Work is the 1) component of force in the direction of displacement times the magnitude of displacement. 2) component of displacement in the direction of the force times the magnitude of the force. ...
... W = Fd cos. Work is a scalar. We can determine work two ways: Work is the 1) component of force in the direction of displacement times the magnitude of displacement. 2) component of displacement in the direction of the force times the magnitude of the force. ...
Tutorial_07_HW_Sol - UMD Physics
... Work depends on both force and distance: Wprof on cart = Fprof on cart∆x. Along path 1, the professor pushes the cart for less distance (as noted in part A), but he exerts a greater force, since he’s fighting gravity head-on (as noted in part B). By contrast, along path 2, the professor pushes with ...
... Work depends on both force and distance: Wprof on cart = Fprof on cart∆x. Along path 1, the professor pushes the cart for less distance (as noted in part A), but he exerts a greater force, since he’s fighting gravity head-on (as noted in part B). By contrast, along path 2, the professor pushes with ...
Physics B AP Review Packet: Mechanics Name
... L = p x r L = (mv) x r Where momentum (mv) is perpendicular to the distance r Angular momentum, like linear momentum is conserved and when objects move in a circle, the angular momentum stays the same unless outside force acts. For an elliptical orbit, as the velocity changes, the radius changes as ...
... L = p x r L = (mv) x r Where momentum (mv) is perpendicular to the distance r Angular momentum, like linear momentum is conserved and when objects move in a circle, the angular momentum stays the same unless outside force acts. For an elliptical orbit, as the velocity changes, the radius changes as ...
force
... – Acceleration is a change in velocity [speed or direction] – Mass is the amount of matter in an object ...
... – Acceleration is a change in velocity [speed or direction] – Mass is the amount of matter in an object ...
Definitions
... Newton’s Second Law applies to an inertial reference frame, meaning a reference system for measuring position and time that is not accelerating. If we wish to use Newton’s Second Law in an accelerating reference frame, we need to add extra terms to the equation that can be considered as forces opera ...
... Newton’s Second Law applies to an inertial reference frame, meaning a reference system for measuring position and time that is not accelerating. If we wish to use Newton’s Second Law in an accelerating reference frame, we need to add extra terms to the equation that can be considered as forces opera ...
Plan of Lectures - The Budker Group
... A story about how Richard Feynman became a physicist (balls in a Radio Flyer) Subtleties of inertial vs. non-inertial frames. We defined an inertial frame as such a frame where a body does not accelerate in the absence of forces. Also, in an inertial frame, we have the Second Newton’s Law. Does a fr ...
... A story about how Richard Feynman became a physicist (balls in a Radio Flyer) Subtleties of inertial vs. non-inertial frames. We defined an inertial frame as such a frame where a body does not accelerate in the absence of forces. Also, in an inertial frame, we have the Second Newton’s Law. Does a fr ...
Unit 1: Motion
... Big Ideas Mechanical waves are vibrations in a medium that move from source to receiver, conveying energy. Conceptual Understandings A demonstration spring or slinky is helpful to study the properties of waves. It is helpful to relate work done to produce the wave to the energy given to the wave. Fo ...
... Big Ideas Mechanical waves are vibrations in a medium that move from source to receiver, conveying energy. Conceptual Understandings A demonstration spring or slinky is helpful to study the properties of waves. It is helpful to relate work done to produce the wave to the energy given to the wave. Fo ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.























