PSC1121Chap2-4
... If you push with 25 N on an object, and somebody else pushes in the opposite direction with 15 N, the net force applied to the object is 10 N The object will accelerate as if a single 10-N force acts on it Direction of the object is always in the direction of the net force Acceleration also depends ...
... If you push with 25 N on an object, and somebody else pushes in the opposite direction with 15 N, the net force applied to the object is 10 N The object will accelerate as if a single 10-N force acts on it Direction of the object is always in the direction of the net force Acceleration also depends ...
Lab 7: Friction Multi-blocks
... where µs and µk are the coefficient of static and kinetic friction and n is the normal force which presses the two surfaces together. In general, µs > µk because it takes a larger force to start an object sliding (static friction) than to keep it sliding (kinetic friction). They depend only on the m ...
... where µs and µk are the coefficient of static and kinetic friction and n is the normal force which presses the two surfaces together. In general, µs > µk because it takes a larger force to start an object sliding (static friction) than to keep it sliding (kinetic friction). They depend only on the m ...
Chapter 15 - KFUPM Faculty List
... displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is ...
... displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is ...
Ch#15 - KFUPM Faculty List
... downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is m and t is ...
... downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position (y) in m from its equilibrium position as a function of time (t) is: ( Ans: y = 0.05 cos (10 * t)) Q13 A particle (m = 0.2 kg) is attached to a spring. The motion of the particle is described by x = 0.10 cos (10*t +PI/3) where x is m and t is ...
Physics 225 Relativity and Math Applications Unit 5 E = mc
... You can tell that light carries energy: if you sit in the sunlight for too long, your skin will turn a painful red, and it definitely takes energy to do that! Light also carries momentum: you need a very sensitive experiment to see it, but if you fire a laser beam at a thin suspended foil, the foil ...
... You can tell that light carries energy: if you sit in the sunlight for too long, your skin will turn a painful red, and it definitely takes energy to do that! Light also carries momentum: you need a very sensitive experiment to see it, but if you fire a laser beam at a thin suspended foil, the foil ...
Wednesday, July 14, 2004
... A one piece cylinder is shaped as in the figure with core section protruding from the larger drum. The cylinder is free to rotate around the central axis shown in the picture. A rope wrapped around the drum whose radius is R1 exerts force F1 to the right on the cylinder, and another force exerts F2 ...
... A one piece cylinder is shaped as in the figure with core section protruding from the larger drum. The cylinder is free to rotate around the central axis shown in the picture. A rope wrapped around the drum whose radius is R1 exerts force F1 to the right on the cylinder, and another force exerts F2 ...
PHYSICS 110 Laboratory
... we want to include them. So, in this case, we can think of two forces acting on the object. The first is gravity, which always acts downward. We know that we can identify the force of gravity with the value mg, where m is the mass of the object and g is the acceleration do to gravity. The second for ...
... we want to include them. So, in this case, we can think of two forces acting on the object. The first is gravity, which always acts downward. We know that we can identify the force of gravity with the value mg, where m is the mass of the object and g is the acceleration do to gravity. The second for ...
Lecture 16 - Circular Motion
... The acceleration of the moon towards earth is given by our equation for centripetal acceleration. So Newton was able to evaluate the ratio of the moon’s centripetal acceleration to g. Now the question is, does this acceleration decrease as the square of the distance? He found that the ratio of dista ...
... The acceleration of the moon towards earth is given by our equation for centripetal acceleration. So Newton was able to evaluate the ratio of the moon’s centripetal acceleration to g. Now the question is, does this acceleration decrease as the square of the distance? He found that the ratio of dista ...
HW7
... vcom , values for the initial velocities were used. Since the system is isolated with no ...
... vcom , values for the initial velocities were used. Since the system is isolated with no ...
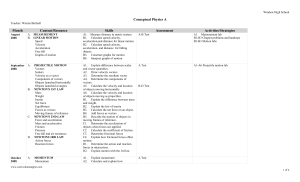
Curriculum Map - Weld RE
... A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of inertia B3. Calculate the net force on an object. B4. Add forces as vectors B5. ...
... A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of inertia B3. Calculate the net force on an object. B4. Add forces as vectors B5. ...
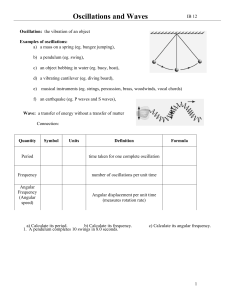
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.


![Physics for SciEngrs [3rd]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015834502_1-903d7f9c800dd53147166e2caa63cce8-300x300.png)