EOF11 L5 - WordPress.com
... 1. If a stretched slingshot has 100 J of potential energy, how fast will a 0.5 kg softball be moving right after the launcher fires it? Specify the system, its initial and final states, and any assumptions you made. Explain how these assumptions affect your answer. (20 m/s) 2. A crane lifts a 50 g c ...
... 1. If a stretched slingshot has 100 J of potential energy, how fast will a 0.5 kg softball be moving right after the launcher fires it? Specify the system, its initial and final states, and any assumptions you made. Explain how these assumptions affect your answer. (20 m/s) 2. A crane lifts a 50 g c ...
Pull It, Push It
... won’t move. The tendency for objects to stay at rest or to keep moving is called inertia. Throw a ball and it soars to the basket. Your push overcomes the ball’s inertia so the ball moves. Objects need a push or pull to stop moving, too. The ball’s inertia would keep it moving. When you catch a ball ...
... won’t move. The tendency for objects to stay at rest or to keep moving is called inertia. Throw a ball and it soars to the basket. Your push overcomes the ball’s inertia so the ball moves. Objects need a push or pull to stop moving, too. The ball’s inertia would keep it moving. When you catch a ball ...
Question paper - Edexcel
... A For work to be done a force must always be applied. B When work is done energy is transferred. C Work done is the product of force and distance moved perpendicular to the force. D Work done is a scalar quantity. (Total for Question 2 = 1 mark) 3 Concrete pillars may be used to support ...
... A For work to be done a force must always be applied. B When work is done energy is transferred. C Work done is the product of force and distance moved perpendicular to the force. D Work done is a scalar quantity. (Total for Question 2 = 1 mark) 3 Concrete pillars may be used to support ...
Work
... The work-energy relationship is the most important relationship of the unit. The work done by external forces (Wext) is related to the total mechanical energy of the initial (TMEi) and of the total energy of the final state (TMEf) of a system as follows: TMEi + Wext = TMEf Your goal should be to com ...
... The work-energy relationship is the most important relationship of the unit. The work done by external forces (Wext) is related to the total mechanical energy of the initial (TMEi) and of the total energy of the final state (TMEf) of a system as follows: TMEi + Wext = TMEf Your goal should be to com ...
Rotational Kinematics (Part I from chapter 10)
... techniques are much like those with constant linear acceleration ...
... techniques are much like those with constant linear acceleration ...
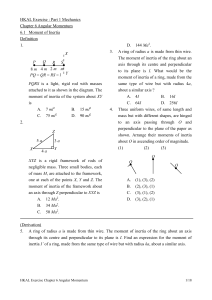
13.11. Visualize: Solve: Torque by a force is defined as τ = Frsinφ
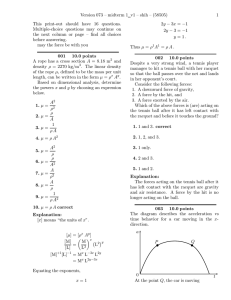
... 13.33. Model: The can is a rigid body rolling across the floor. Assume that the can has uniform mass distribution. Solve: The rolling motion of the can is a translation of its center of mass plus a rotation about the center of mass. The moment of inertia of the can about the center of mass is 12 MR ...
... 13.33. Model: The can is a rigid body rolling across the floor. Assume that the can has uniform mass distribution. Solve: The rolling motion of the can is a translation of its center of mass plus a rotation about the center of mass. The moment of inertia of the can about the center of mass is 12 MR ...
First--Inertia (see above for this law in detail)
... When the net force is zero, there are balanced forces and there is no change in motion. To achieve a net force of zero means that an applied force balances the force of friction so that the combined force acting on the object is zero. (Ex. Tug-of-War, when there is a deadlock and no one is able to m ...
... When the net force is zero, there are balanced forces and there is no change in motion. To achieve a net force of zero means that an applied force balances the force of friction so that the combined force acting on the object is zero. (Ex. Tug-of-War, when there is a deadlock and no one is able to m ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.