Response to Physics Draft by AIP
... understanding of electromagnetism which is in Unit 3. Suggest that this section is deleted) interactions between light and matter that involve the processes of reflection, refraction and absorption; (Comment: the phrase ‘Interactions between light and matter’ is commonly interpreted as referring t ...
... understanding of electromagnetism which is in Unit 3. Suggest that this section is deleted) interactions between light and matter that involve the processes of reflection, refraction and absorption; (Comment: the phrase ‘Interactions between light and matter’ is commonly interpreted as referring t ...
Chapter 20 - Solutions
... This formula indicates that the force and the electric field point in the same direction for a positively charged particle, and in opposite directions for a negatively charged particle. Hint C.2 Determining the direction of the electric field The acceleration of the particle can be determined from t ...
... This formula indicates that the force and the electric field point in the same direction for a positively charged particle, and in opposite directions for a negatively charged particle. Hint C.2 Determining the direction of the electric field The acceleration of the particle can be determined from t ...
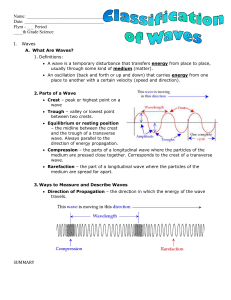
Waves What Are Waves? Definitions: A wave is a temporary
... James Clerk Maxwell and Heinrich Hertz are two scientists who studied how electromagnetic waves are formed and how fast they travel. Electromagnetic waves can be described by their wavelengths, energy, and frequency. All three of these things describe a different property of light, yet they are ...
... James Clerk Maxwell and Heinrich Hertz are two scientists who studied how electromagnetic waves are formed and how fast they travel. Electromagnetic waves can be described by their wavelengths, energy, and frequency. All three of these things describe a different property of light, yet they are ...
The Darwin Magnetic Interaction Energy and its Macroscopic
... The Coulomb potential energy is known to describe the interaction of charged particles with suÆcient accuracy for a wide range of applications, especially in atomic, molecular, and condensed matter physics. In cases where radiation is of importance the electrostatic Coulomb treatment does not suÆce ...
... The Coulomb potential energy is known to describe the interaction of charged particles with suÆcient accuracy for a wide range of applications, especially in atomic, molecular, and condensed matter physics. In cases where radiation is of importance the electrostatic Coulomb treatment does not suÆce ...
LAB X: Title
... motion, the velocity will neither increase nor decrease, but the force will change the direction of motion. It is very important to remember (even more to realize for the first time) that Centripetal Force is not a force in the same way that gravity, rope tension, the normal force, etc. are forces. ...
... motion, the velocity will neither increase nor decrease, but the force will change the direction of motion. It is very important to remember (even more to realize for the first time) that Centripetal Force is not a force in the same way that gravity, rope tension, the normal force, etc. are forces. ...
Whites and Wu - Keith W. Whites - South Dakota School of Mines
... The dielectric reduction afforded by interacting particle edges and corners reported in the last section is an intriguing phenomenon and one that, to our knowledge, has not been previously recorded in the literature. To provide additional evidence for this phenomenon, we have constructed the measure ...
... The dielectric reduction afforded by interacting particle edges and corners reported in the last section is an intriguing phenomenon and one that, to our knowledge, has not been previously recorded in the literature. To provide additional evidence for this phenomenon, we have constructed the measure ...
9 Dynamics of Single Aerosol Particles
... p = 1 atm is µxair = 1.8 x 1 0 - 5 k g m - 1 s - 1 . The air mean free path at T = 298 K and p = 1 atm is then found using (9.6) to be λair(298K, 1 atm) = 0.0651 µm ...
... p = 1 atm is µxair = 1.8 x 1 0 - 5 k g m - 1 s - 1 . The air mean free path at T = 298 K and p = 1 atm is then found using (9.6) to be λair(298K, 1 atm) = 0.0651 µm ...
PowerPoint
... Both lines have identical charge densities +l C/m. Point A is equidistant from both lines and Point B is located above the top line as shown. How does EA, the magnitude of the electric field at point A compare to EB, the magnitude of the electric field at point B? A. EA < EB B. EA = EB C. EA > EB “c ...
... Both lines have identical charge densities +l C/m. Point A is equidistant from both lines and Point B is located above the top line as shown. How does EA, the magnitude of the electric field at point A compare to EB, the magnitude of the electric field at point B? A. EA < EB B. EA = EB C. EA > EB “c ...
Coulomb and Spin-Orbit Interaction Effects in a
... Spintronics seeks to create devices where the spin degree of freedom is used alongside, or instead of, charge currents. These devices could have a large variety of applications, including information encoding, transmission, processing, etc. It is predicted that such devices would have lower power co ...
... Spintronics seeks to create devices where the spin degree of freedom is used alongside, or instead of, charge currents. These devices could have a large variety of applications, including information encoding, transmission, processing, etc. It is predicted that such devices would have lower power co ...
Phy213_CH22_worksheet
... FE= qeE = eE = -7.0x10-20 N ˆj{inward toward the line} What is the acceleration of the electron located at point P? ...
... FE= qeE = eE = -7.0x10-20 N ˆj{inward toward the line} What is the acceleration of the electron located at point P? ...
Fundamental interaction
Fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions in physical systems that don't appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four conventionally accepted fundamental interactions—gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear. Each one is understood as the dynamics of a field. The gravitational force is modeled as a continuous classical field. The other three are each modeled as discrete quantum fields, and exhibit a measurable unit or elementary particle.Gravitation and electromagnetism act over a potentially infinite distance across the universe. They mediate macroscopic phenomena every day. The other two fields act over minuscule, subatomic distances. The strong nuclear interaction is responsible for the binding of atomic nuclei. The weak nuclear interaction also acts on the nucleus, mediating radioactive decay.Theoretical physicists working beyond the Standard Model seek to quantize the gravitational field toward predictions that particle physicists can experimentally confirm, thus yielding acceptance to a theory of quantum gravity (QG). (Phenomena suitable to model as a fifth force—perhaps an added gravitational effect—remain widely disputed). Other theorists seek to unite the electroweak and strong fields within a Grand Unified Theory (GUT). While all four fundamental interactions are widely thought to align at an extremely minuscule scale, particle accelerators cannot produce the massive energy levels required to experimentally probe at that Planck scale (which would experimentally confirm such theories). Yet some theories, such as the string theory, seek both QG and GUT within one framework, unifying all four fundamental interactions along with mass generation within a theory of everything (ToE).