Forces act everywhere. They cause changes in motion and also act
... When an apple falls from a tree it accelerates towards the ground. Why? In response to this question most people reply 'gravity'. The idea of an apple falling to the ground is often associated with Newton. Newton's genius was to find a single model which explained not only the motion of an apple fal ...
... When an apple falls from a tree it accelerates towards the ground. Why? In response to this question most people reply 'gravity'. The idea of an apple falling to the ground is often associated with Newton. Newton's genius was to find a single model which explained not only the motion of an apple fal ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... there are other isotopes which can be induced to fission by neutron bombardment. Plutonium-239 is also fissionable by bombardment with slow neutrons, and both it and uranium-235 have been used to make nuclear fission bombs. Plutonium-239 can be produced by "breeding" it from uranium-238. Uranium238, ...
... there are other isotopes which can be induced to fission by neutron bombardment. Plutonium-239 is also fissionable by bombardment with slow neutrons, and both it and uranium-235 have been used to make nuclear fission bombs. Plutonium-239 can be produced by "breeding" it from uranium-238. Uranium238, ...
Unit 3- Forces Topic Objectives Assignments Newton`s Second Law
... 10. What is the formula to calculate gravitational force? _____________________________________ 11. If you increase the distance between two planets, the gravitational force between those planets will [ increase / decrease / stay the same ] 12. If you increase the size of a planet, the gravitationa ...
... 10. What is the formula to calculate gravitational force? _____________________________________ 11. If you increase the distance between two planets, the gravitational force between those planets will [ increase / decrease / stay the same ] 12. If you increase the size of a planet, the gravitationa ...
Name: Period: Newton`s 2nd Law: Find the missing force 1. A 5 kg
... In a Physics lab, Ernesto and Amanda apply a 34.5 N rightward force to a 4.52-kg cart to accelerate it across a horizontal surface at a rate of 1.28 m/s/s. Determine the friction force acting upon the cart. ...
... In a Physics lab, Ernesto and Amanda apply a 34.5 N rightward force to a 4.52-kg cart to accelerate it across a horizontal surface at a rate of 1.28 m/s/s. Determine the friction force acting upon the cart. ...
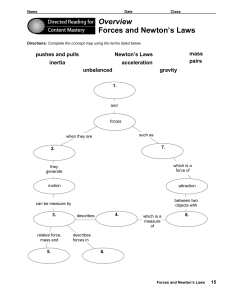
Overview Forces and Newton`s Laws
... Directions: Complete the paragraphs by using the words listed below to fill in the blanks. ...
... Directions: Complete the paragraphs by using the words listed below to fill in the blanks. ...
Page 1 Problem An electron is released from rest in a uniform
... ) in the hydrogen nucleus with the gravitational force between the same electron and proton. What is the ratio of these two forces? Solution The magnitude of the electric force is given by Coulomb’s law ...
... ) in the hydrogen nucleus with the gravitational force between the same electron and proton. What is the ratio of these two forces? Solution The magnitude of the electric force is given by Coulomb’s law ...
Intermolecular Forces
... dielectric constant of the sphere, i.e., εi > 1. Indeed, for a sphere of high dielectric (εi » 1), in vacuo, the polarizability is αi ≈ 4πε0ai3 = 3ε0vi. This is readily derivable for a simple oneelectron Bohr atom. However, if ε > εi, as might occur in a condensed medium (readily in water, where ε = ...
... dielectric constant of the sphere, i.e., εi > 1. Indeed, for a sphere of high dielectric (εi » 1), in vacuo, the polarizability is αi ≈ 4πε0ai3 = 3ε0vi. This is readily derivable for a simple oneelectron Bohr atom. However, if ε > εi, as might occur in a condensed medium (readily in water, where ε = ...
∑ ∑
... all particles move with the same speed. Many applications, however, require a beam in which all the particle speeds are the same. Using crossed fields particles of a specific speed can be selected as follows: We can use the magnetic force in conjunction with the electric force to filter out particle ...
... all particles move with the same speed. Many applications, however, require a beam in which all the particle speeds are the same. Using crossed fields particles of a specific speed can be selected as follows: We can use the magnetic force in conjunction with the electric force to filter out particle ...
16-3 Coulomb`s Law
... Comparing Coulomb’s law to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, which gives the force between two objects with mass, we see that they have the same form: (Equation 8.1: Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation) where ...
... Comparing Coulomb’s law to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, which gives the force between two objects with mass, we see that they have the same form: (Equation 8.1: Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation) where ...
Fundamental interaction
Fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions in physical systems that don't appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four conventionally accepted fundamental interactions—gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear. Each one is understood as the dynamics of a field. The gravitational force is modeled as a continuous classical field. The other three are each modeled as discrete quantum fields, and exhibit a measurable unit or elementary particle.Gravitation and electromagnetism act over a potentially infinite distance across the universe. They mediate macroscopic phenomena every day. The other two fields act over minuscule, subatomic distances. The strong nuclear interaction is responsible for the binding of atomic nuclei. The weak nuclear interaction also acts on the nucleus, mediating radioactive decay.Theoretical physicists working beyond the Standard Model seek to quantize the gravitational field toward predictions that particle physicists can experimentally confirm, thus yielding acceptance to a theory of quantum gravity (QG). (Phenomena suitable to model as a fifth force—perhaps an added gravitational effect—remain widely disputed). Other theorists seek to unite the electroweak and strong fields within a Grand Unified Theory (GUT). While all four fundamental interactions are widely thought to align at an extremely minuscule scale, particle accelerators cannot produce the massive energy levels required to experimentally probe at that Planck scale (which would experimentally confirm such theories). Yet some theories, such as the string theory, seek both QG and GUT within one framework, unifying all four fundamental interactions along with mass generation within a theory of everything (ToE).