Slide 1
... Forces represent interactions between one piece of matter and another. Therefore, forces come in pairs. For each force exerted on one body, there is an equal, but oppositely directed, force on some other body interacting with it. “You cannot touch without being touched.” Paul Hewitt This is often ca ...
... Forces represent interactions between one piece of matter and another. Therefore, forces come in pairs. For each force exerted on one body, there is an equal, but oppositely directed, force on some other body interacting with it. “You cannot touch without being touched.” Paul Hewitt This is often ca ...
Homework for the week of November 3. 6th week of... Ch. 27: 6, 8, 16, 20, 23, 33, 35, 36
... potential energy of the particle becomes kinetic energy as it is accelerated. Then, since the particle is moving perpendicularly to the magnetic field, the magnetic force will be a maximum. That force will cause the ion to move in a circular path, and the radius can be determined in terms of the mas ...
... potential energy of the particle becomes kinetic energy as it is accelerated. Then, since the particle is moving perpendicularly to the magnetic field, the magnetic force will be a maximum. That force will cause the ion to move in a circular path, and the radius can be determined in terms of the mas ...
Forces
... Resistive Force on a Falling Object Air resistance creates a resistive force opposite to the force of gravity. The faster an object falls, the bigger the resistive force. Eventually the upwards resistive force becomes as big as the downwards gravitational force. The two forces are equal and opposite ...
... Resistive Force on a Falling Object Air resistance creates a resistive force opposite to the force of gravity. The faster an object falls, the bigger the resistive force. Eventually the upwards resistive force becomes as big as the downwards gravitational force. The two forces are equal and opposite ...
chapter 4 - forces and newton`s laws of motion
... The Normal Force is found by adding vectorially the normal components of all the other forces acting on the object. (1) If an object is resting on a horizontal surface, Fn = Mg (2) If an object on a horizontal surface is being partly lifted by another force, Fa, then Fn = Mg - Fa. (3) If an object o ...
... The Normal Force is found by adding vectorially the normal components of all the other forces acting on the object. (1) If an object is resting on a horizontal surface, Fn = Mg (2) If an object on a horizontal surface is being partly lifted by another force, Fa, then Fn = Mg - Fa. (3) If an object o ...
Lecture04
... Kinematics described motion only – no real Physics. Why does a particle have a certain acceleration? New concepts (in 17th century): • Forces - pushes or pulls - cause acceleration • Inertia (mass) measures how much matter is being accelerated – resistance to acceleration Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion: ...
... Kinematics described motion only – no real Physics. Why does a particle have a certain acceleration? New concepts (in 17th century): • Forces - pushes or pulls - cause acceleration • Inertia (mass) measures how much matter is being accelerated – resistance to acceleration Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion: ...
Sept 2012 101 Lecture 5 1
... When objects made of different materials are rubbed together, they become charged with equal but opposite charges. Charged objects either repel one another (for like charges, a or b) or attract one another (for unlike charges, c). ...
... When objects made of different materials are rubbed together, they become charged with equal but opposite charges. Charged objects either repel one another (for like charges, a or b) or attract one another (for unlike charges, c). ...
PERFORMANCE STANDARDS IS 3
... 7. Understand that matter is made of atoms and that atoms are made of subatomic particles. 8. Understand atomic structure, including: most space occupied by electrons nucleus made of protons and neutrons isotopes of an element masses of proton and neutron 2000 times greater than mass of elec ...
... 7. Understand that matter is made of atoms and that atoms are made of subatomic particles. 8. Understand atomic structure, including: most space occupied by electrons nucleus made of protons and neutrons isotopes of an element masses of proton and neutron 2000 times greater than mass of elec ...
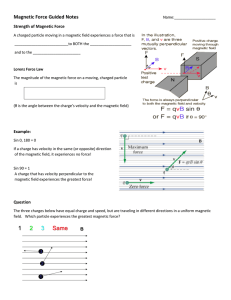
Magnetic Force Guided Notes
... A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experiences a force that is __________________________to BOTH the ____________________ and to the _______________________ ...
... A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experiences a force that is __________________________to BOTH the ____________________ and to the _______________________ ...
3.4 Newton`s Law of Inertia - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 1. Objects do not change motion without unbalanced force. 2. Objects in motion do not always require a force to keep them moving. 3. Objects have two “natural” states of motion, at rest (static equilibrium) and moving at a constant speed and direction (dynamic equilibrium). ...
... 1. Objects do not change motion without unbalanced force. 2. Objects in motion do not always require a force to keep them moving. 3. Objects have two “natural” states of motion, at rest (static equilibrium) and moving at a constant speed and direction (dynamic equilibrium). ...
Fundamental interaction
Fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions in physical systems that don't appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four conventionally accepted fundamental interactions—gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear. Each one is understood as the dynamics of a field. The gravitational force is modeled as a continuous classical field. The other three are each modeled as discrete quantum fields, and exhibit a measurable unit or elementary particle.Gravitation and electromagnetism act over a potentially infinite distance across the universe. They mediate macroscopic phenomena every day. The other two fields act over minuscule, subatomic distances. The strong nuclear interaction is responsible for the binding of atomic nuclei. The weak nuclear interaction also acts on the nucleus, mediating radioactive decay.Theoretical physicists working beyond the Standard Model seek to quantize the gravitational field toward predictions that particle physicists can experimentally confirm, thus yielding acceptance to a theory of quantum gravity (QG). (Phenomena suitable to model as a fifth force—perhaps an added gravitational effect—remain widely disputed). Other theorists seek to unite the electroweak and strong fields within a Grand Unified Theory (GUT). While all four fundamental interactions are widely thought to align at an extremely minuscule scale, particle accelerators cannot produce the massive energy levels required to experimentally probe at that Planck scale (which would experimentally confirm such theories). Yet some theories, such as the string theory, seek both QG and GUT within one framework, unifying all four fundamental interactions along with mass generation within a theory of everything (ToE).