Millikan Oil-Drop Experiment
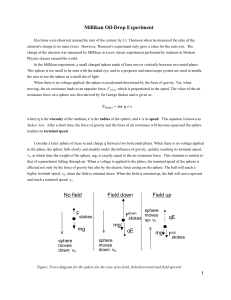
... where η is the viscosity of the medium, r is the radius of the sphere, and v is its speed. This equation is known as Stokes' law. After a short time, the force of gravity and the force of air resistance will become equal and the sphere reaches its terminal speed. Consider a latex sphere of mass m an ...
... where η is the viscosity of the medium, r is the radius of the sphere, and v is its speed. This equation is known as Stokes' law. After a short time, the force of gravity and the force of air resistance will become equal and the sphere reaches its terminal speed. Consider a latex sphere of mass m an ...
ELEC 3105 Lecture 1
... Given a group of charges we find the net electric field at any point in space by using the principle of superposition. This is a general principle that says a net effect is the sum of the individual effects. Here, the principle means that we first compute the electric field at the point in space due ...
... Given a group of charges we find the net electric field at any point in space by using the principle of superposition. This is a general principle that says a net effect is the sum of the individual effects. Here, the principle means that we first compute the electric field at the point in space due ...
Deducing the Dielectric Strength of Air from Van de
... by placing image charges within the conductor. The size and location of the charges are chosen to replicate the electric potential boundary conditions at the conductors. The solution to Laplace’s equation depends on the boundary conditions. Since the charges reproduce the boundary conditions, they w ...
... by placing image charges within the conductor. The size and location of the charges are chosen to replicate the electric potential boundary conditions at the conductors. The solution to Laplace’s equation depends on the boundary conditions. Since the charges reproduce the boundary conditions, they w ...
Force and Motion II 1.1
... The magnitude of the force F on the cart increases in direct proportion to the distance x that the cart is displaced from the equilibrium point (x=0). If you double x , then you double F. The constant k is the proportionality constant between F and x. The minus sign in F = kx indicates that the for ...
... The magnitude of the force F on the cart increases in direct proportion to the distance x that the cart is displaced from the equilibrium point (x=0). If you double x , then you double F. The constant k is the proportionality constant between F and x. The minus sign in F = kx indicates that the for ...
The frequency dependence of polarization
... A permanent dipole moment is caused by unbalanced sharing of electrons by atoms of a molecule. In an absence of an external electric field, these moments are oriented in a random order such that no net polarization is present. Under an external electric field, the dipoles rotate to align with the el ...
... A permanent dipole moment is caused by unbalanced sharing of electrons by atoms of a molecule. In an absence of an external electric field, these moments are oriented in a random order such that no net polarization is present. Under an external electric field, the dipoles rotate to align with the el ...
Newton`s Third Law - Center Grove Schools
... While you are pushing the ball, this downward force adds to the downward force of gravity. According to Newton’s second law, the acceleration of the ball increases. So while you are pushing, the acceleration of the ball is greater than the acceleration of both you and the elevator. This causes the b ...
... While you are pushing the ball, this downward force adds to the downward force of gravity. According to Newton’s second law, the acceleration of the ball increases. So while you are pushing, the acceleration of the ball is greater than the acceleration of both you and the elevator. This causes the b ...
MS Word - Doane College Physics Web Server
... horseshoe magnet (labeled N and S). With these two magnets you will investigate the force exerted on a current in a wire. GE 4: Force from a Magnetic Field 1. Place the horseshoe magnet around the wire with the current flowing downward as shown in the figure below. The magnetic field from the magnet ...
... horseshoe magnet (labeled N and S). With these two magnets you will investigate the force exerted on a current in a wire. GE 4: Force from a Magnetic Field 1. Place the horseshoe magnet around the wire with the current flowing downward as shown in the figure below. The magnetic field from the magnet ...
File
... Again there is an important difference between gravitational fields and electric fields due to the fact that… We therefore define the direction of an electric field as… ...
... Again there is an important difference between gravitational fields and electric fields due to the fact that… We therefore define the direction of an electric field as… ...
Fundamental interaction
Fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions in physical systems that don't appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four conventionally accepted fundamental interactions—gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear. Each one is understood as the dynamics of a field. The gravitational force is modeled as a continuous classical field. The other three are each modeled as discrete quantum fields, and exhibit a measurable unit or elementary particle.Gravitation and electromagnetism act over a potentially infinite distance across the universe. They mediate macroscopic phenomena every day. The other two fields act over minuscule, subatomic distances. The strong nuclear interaction is responsible for the binding of atomic nuclei. The weak nuclear interaction also acts on the nucleus, mediating radioactive decay.Theoretical physicists working beyond the Standard Model seek to quantize the gravitational field toward predictions that particle physicists can experimentally confirm, thus yielding acceptance to a theory of quantum gravity (QG). (Phenomena suitable to model as a fifth force—perhaps an added gravitational effect—remain widely disputed). Other theorists seek to unite the electroweak and strong fields within a Grand Unified Theory (GUT). While all four fundamental interactions are widely thought to align at an extremely minuscule scale, particle accelerators cannot produce the massive energy levels required to experimentally probe at that Planck scale (which would experimentally confirm such theories). Yet some theories, such as the string theory, seek both QG and GUT within one framework, unifying all four fundamental interactions along with mass generation within a theory of everything (ToE).























