Force and Motion I 4.0
... force F. Make sure that the spring scale reads “zero” when it is held in the horizontal position and nothing is attached to the small hook. Attach the small hook of the spring scale to the cart. Pull the cart along the track with a constant force of 0.10 N. It may be a bit tricky to keep the force c ...
... force F. Make sure that the spring scale reads “zero” when it is held in the horizontal position and nothing is attached to the small hook. Attach the small hook of the spring scale to the cart. Pull the cart along the track with a constant force of 0.10 N. It may be a bit tricky to keep the force c ...
Advanced Placement Physics – B
... body on which the reaction force acts and state the magnitude and direction of this reaction. 13. Apply Newton’s Third Law in analyzing the force of contact between two bodies that accelerate together along a horizontal or vertical line, or between two surfaces that slide across one another. 14. Kno ...
... body on which the reaction force acts and state the magnitude and direction of this reaction. 13. Apply Newton’s Third Law in analyzing the force of contact between two bodies that accelerate together along a horizontal or vertical line, or between two surfaces that slide across one another. 14. Kno ...
Some Computational Science Algorithms
... – most differential equations cannot be solved exactly – must use numerical methods that compute approximate solutions • convert calculus problem to linear algebra problem ...
... – most differential equations cannot be solved exactly – must use numerical methods that compute approximate solutions • convert calculus problem to linear algebra problem ...
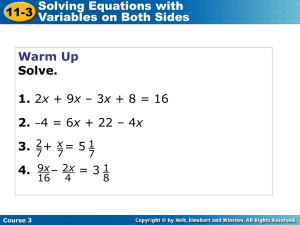
Course 3
... Some problems produce equations that have variables on both sides of the equal sign. Solving an equation with variables on both sides is similar to solving an equation with a variable on only one side. You can add or subtract a term containing a variable on both sides of an equation. ...
... Some problems produce equations that have variables on both sides of the equal sign. Solving an equation with variables on both sides is similar to solving an equation with a variable on only one side. You can add or subtract a term containing a variable on both sides of an equation. ...
Newton`s Laws and Friction
... Acceleration and Force are vectors; they contain both direction and magnitude. If an unbalanced or net force acts upon an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force at a rate proportional to the net force. F= ma describes an important relationship between an object’s mass ...
... Acceleration and Force are vectors; they contain both direction and magnitude. If an unbalanced or net force acts upon an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force at a rate proportional to the net force. F= ma describes an important relationship between an object’s mass ...
Kindergarten CPSD Science Curriculum Guide
... and conceptual, but not quantitative addition of forces are used at this level.) The patterns of an object’s motion in various situations can be observed and measured; when past motion exhibits a regular pattern, future motion can be predicted from it. (Boundary: Technical terms, such as magnitude, ...
... and conceptual, but not quantitative addition of forces are used at this level.) The patterns of an object’s motion in various situations can be observed and measured; when past motion exhibits a regular pattern, future motion can be predicted from it. (Boundary: Technical terms, such as magnitude, ...
Part B: Force, Acceleration and Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... 7. Consider Newton's second law of motion to determine which of the following statements are true? List all that apply. a. If an object is accelerating to the right, the net force on the object must be directed towards the right. b. If an object is moving to the right and slowing down, then the net ...
... 7. Consider Newton's second law of motion to determine which of the following statements are true? List all that apply. a. If an object is accelerating to the right, the net force on the object must be directed towards the right. b. If an object is moving to the right and slowing down, then the net ...
Molecular coefficient of friction concerns the force
... Acceleration and Force are vectors; they contain both direction and magnitude. If an unbalanced or net force acts upon an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force at a rate proportional to the net force. F= ma describes an important relationship between an object’s mass ...
... Acceleration and Force are vectors; they contain both direction and magnitude. If an unbalanced or net force acts upon an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force at a rate proportional to the net force. F= ma describes an important relationship between an object’s mass ...
Sample Questions for the AP Physics 1 Exam
... frictionless surface. A force F is exerted individually on each block, as shown above. The graph shows how F varies with time t. Which block has the greatest average power provided to it between t 5 0 s and t 5 3 s? (A) The block of mass m (B) The block of mass 2m (C) Both blocks have the same po ...
... frictionless surface. A force F is exerted individually on each block, as shown above. The graph shows how F varies with time t. Which block has the greatest average power provided to it between t 5 0 s and t 5 3 s? (A) The block of mass m (B) The block of mass 2m (C) Both blocks have the same po ...
Lab M5: Hooke`s Law
... Simple harmonic motion occurs whenever there is a restoring force which is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium, as is the case here. Assuming no frictional forces and assuming that the spring is massless, the equation of motion of a mass on a spring is ...
... Simple harmonic motion occurs whenever there is a restoring force which is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium, as is the case here. Assuming no frictional forces and assuming that the spring is massless, the equation of motion of a mass on a spring is ...
momentum class notes
... Collisions commonly occur in contact sports (such as football) and racket and bat sports (such as baseball, golf, tennis, etc.). Consider a collision in football between a fullback and a linebacker during a goal-line stand. The fullback plunges across the goal line and collides in midair with lineb ...
... Collisions commonly occur in contact sports (such as football) and racket and bat sports (such as baseball, golf, tennis, etc.). Consider a collision in football between a fullback and a linebacker during a goal-line stand. The fullback plunges across the goal line and collides in midair with lineb ...
Chapter 5
... 29. We choose up as the +y direction, so a ( 3.00 m/s 2 )ˆj (which, without the unitvector, we denote as a since this is a 1-dimensional problem in which Table 2-1 applies). From Eq. 5-12, we obtain the firefighter’s mass: m = W/g = 72.7 kg. (a) We denote the force exerted by the pole on the fire ...
... 29. We choose up as the +y direction, so a ( 3.00 m/s 2 )ˆj (which, without the unitvector, we denote as a since this is a 1-dimensional problem in which Table 2-1 applies). From Eq. 5-12, we obtain the firefighter’s mass: m = W/g = 72.7 kg. (a) We denote the force exerted by the pole on the fire ...
Lab 1500-5 - Otterbein University
... the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. However, according to Newton, the force merely changes the velocity. It is the acceleration, not the velocity, that is proportional to the force. Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a mu ...
... the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. However, according to Newton, the force merely changes the velocity. It is the acceleration, not the velocity, that is proportional to the force. Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a mu ...
CHAPTER 1 Forces in action
... It also provides information about the displacement between any two instants. The instantaneous acceleration of an object at an instant of time can be obtained from a velocity–time graph, by determining the gradient of the line or curve at the point representing that instant. This method is a direct ...
... It also provides information about the displacement between any two instants. The instantaneous acceleration of an object at an instant of time can be obtained from a velocity–time graph, by determining the gradient of the line or curve at the point representing that instant. This method is a direct ...