Physics/Graphing Notes
... An object in motion will remain in motion or an object at rest will remain at rest, unless an unbalanced force acts upon it. Example: A car slamming into a telephone pole. The driver is thrown from the vehicle. This is because the person stays in motion because there is not an unbalanced force to st ...
... An object in motion will remain in motion or an object at rest will remain at rest, unless an unbalanced force acts upon it. Example: A car slamming into a telephone pole. The driver is thrown from the vehicle. This is because the person stays in motion because there is not an unbalanced force to st ...
8.3 Newton`s law of motion - Hope Christian College Parent and
... •The answer is that these forces are acting on different bodies (and there are other forces to consider). •It doesn’t matter to the lawn mower that there is a force on me… all that matters to the lawn mower is that there is a force on it, so it starts to move! •Another action-reaction pair you need ...
... •The answer is that these forces are acting on different bodies (and there are other forces to consider). •It doesn’t matter to the lawn mower that there is a force on me… all that matters to the lawn mower is that there is a force on it, so it starts to move! •Another action-reaction pair you need ...
Energy
... Describe the Cavendish experiment and explain why it was so important. What does and does not cause gravitational attraction between two objects? Do problems that show how the force of gravity between two objects changes if • one or both of their masses change • the distance between them changes • t ...
... Describe the Cavendish experiment and explain why it was so important. What does and does not cause gravitational attraction between two objects? Do problems that show how the force of gravity between two objects changes if • one or both of their masses change • the distance between them changes • t ...
Fall Semester Review
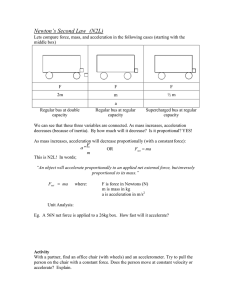
... Newton’s 1st Law: an object with no (net) force on it moves with constant velocity. Newton’s 2nd Law: F=ma Newton’s 3rd Law: When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. There are all kinds of Forces, ...
... Newton’s 1st Law: an object with no (net) force on it moves with constant velocity. Newton’s 2nd Law: F=ma Newton’s 3rd Law: When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. There are all kinds of Forces, ...
Homework No. 03 (Spring 2015) PHYS 520B: Electromagnetic Theory
... 2R π n where R is the distance from center to a corner of the polygon. (e) Show that the magnetic field at the center of a circular loop of radius R, B= ...
... 2R π n where R is the distance from center to a corner of the polygon. (e) Show that the magnetic field at the center of a circular loop of radius R, B= ...
Newton*s Laws - Lindbergh School District
... An object in motion tends to stay in motion with a constant velocity and an object at rest tends to stay at rest unless acted upon by a net force. So what does that mean?... ...
... An object in motion tends to stay in motion with a constant velocity and an object at rest tends to stay at rest unless acted upon by a net force. So what does that mean?... ...
CH 13
... *object moves through a fluid -all liquids and gases are fluids -usually opposes motion less than sliding friction *Lubricants: change sliding friction to fluid friction ...
... *object moves through a fluid -all liquids and gases are fluids -usually opposes motion less than sliding friction *Lubricants: change sliding friction to fluid friction ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... Born: England Dec. 25, 1643, the same year Galileo died Died in 1727, aged 85 years During Great Plague of 1665, while at home from college, developed 3 Laws of Motion Queen Anne knighted him in 1705, to become “Sir” ...
... Born: England Dec. 25, 1643, the same year Galileo died Died in 1727, aged 85 years During Great Plague of 1665, while at home from college, developed 3 Laws of Motion Queen Anne knighted him in 1705, to become “Sir” ...
Chapter 3 - Department Of Computer Science
... A force’s capability may be balanced or canceled by other force(s): the net effect is then zero More than one force acts on an object: ...
... A force’s capability may be balanced or canceled by other force(s): the net effect is then zero More than one force acts on an object: ...
Examples of Lagrange`s Equations
... is called the generalized force, while the right-hand side is the time derivative of the generalized momentum. For normal coordinates like x, y, z, the generalized force is really the force, and the generalized momentum is really the momentum. However, for angular coordinates we saw that the general ...
... is called the generalized force, while the right-hand side is the time derivative of the generalized momentum. For normal coordinates like x, y, z, the generalized force is really the force, and the generalized momentum is really the momentum. However, for angular coordinates we saw that the general ...
Derivation of the Navier-Stokes Equations - RIT
... The above three equations are collectively called the Navier's equations, named after their originator. Note that these equations have 4 independent variables (x, y, z, and t) but 12 dependent variables (u, v, w, and the stress components). We shall assume that the body force components (which is us ...
... The above three equations are collectively called the Navier's equations, named after their originator. Note that these equations have 4 independent variables (x, y, z, and t) but 12 dependent variables (u, v, w, and the stress components). We shall assume that the body force components (which is us ...
Lorenz Force
... the z axis. The distance between the plates is d. The upper plate is grounded and the lower one is connected to a potential V . ~ that as a result of the presence of the two fields B ~ and E, ...
... the z axis. The distance between the plates is d. The upper plate is grounded and the lower one is connected to a potential V . ~ that as a result of the presence of the two fields B ~ and E, ...