Chris Khan 2007 Physics Chapter 2 Distance is the total length of a
... o How long will it take a bird going 4 m/s to go 7 m? Avg Speed = Distance / Time Time = Distance / Avg Speed = 7 m / 4 m/s = 1.8 s. Average velocity = displacement / elapsed time. The unit for average velocity is also meters per second. vavg = ∆x / ∆t. Avg Velocity is more useful because it tells ...
... o How long will it take a bird going 4 m/s to go 7 m? Avg Speed = Distance / Time Time = Distance / Avg Speed = 7 m / 4 m/s = 1.8 s. Average velocity = displacement / elapsed time. The unit for average velocity is also meters per second. vavg = ∆x / ∆t. Avg Velocity is more useful because it tells ...
Examination Paper (Mechanics)
... (6) A rigid body is made of three identical thin rods, each with length L, fastened together in the form of a letter H, as shown in the diagram. The body is free to rotate about a horizontal axis that runs along the length of one of the legs of the H. The body is allowed to fall from rest from a pos ...
... (6) A rigid body is made of three identical thin rods, each with length L, fastened together in the form of a letter H, as shown in the diagram. The body is free to rotate about a horizontal axis that runs along the length of one of the legs of the H. The body is allowed to fall from rest from a pos ...
Learning Outcomes
... 13. Can I predict what will happen to the acceleration of an object if only the force changes? 14. Can I use the equation F=ma when only one force is acting? 15. Can I use the equation F=ma when more than one force is acting? 16. Can I use Newton’s laws to explain: a) the motion of an object during ...
... 13. Can I predict what will happen to the acceleration of an object if only the force changes? 14. Can I use the equation F=ma when only one force is acting? 15. Can I use the equation F=ma when more than one force is acting? 16. Can I use Newton’s laws to explain: a) the motion of an object during ...
doc - Seth Baum
... 20) The equation for magnification given image and object heights a. What is M = hi / ho 21) The energy of a photon a. What is E = hf or E = pc 22) The harmonic with wavelength three times longer than the third harmonic a. What is the first (fundamental) harmonic 23) An example of a longitudinal wav ...
... 20) The equation for magnification given image and object heights a. What is M = hi / ho 21) The energy of a photon a. What is E = hf or E = pc 22) The harmonic with wavelength three times longer than the third harmonic a. What is the first (fundamental) harmonic 23) An example of a longitudinal wav ...
Newton`s three laws of motion are…
... The force acting on a body is equal to the product of its mass times its acceleration, ...
... The force acting on a body is equal to the product of its mass times its acceleration, ...
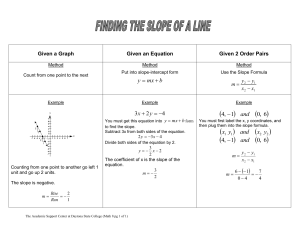
Finding the Slope of a Line
... 3 x 2 y 4 You must get this equation into y mx b form to find the slope. Subtract 3x from both sides of the equation. ...
... 3 x 2 y 4 You must get this equation into y mx b form to find the slope. Subtract 3x from both sides of the equation. ...
Sample PDF
... 23. A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity, = v î. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the fie ...
... 23. A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity, = v î. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the fie ...
Systems of Equations
... Once one variable is eliminated, the process to find the other variable is exactly the same as in the substitution method. ...
... Once one variable is eliminated, the process to find the other variable is exactly the same as in the substitution method. ...
Geometry Notes Name__________________ 3.5 Write and Graph
... have ______________ slopes, like 2 and _______________ ...
... have ______________ slopes, like 2 and _______________ ...
PH2011 - Physics 2A - University of St Andrews
... applicable to each problem and to correctly visualize and analyse the problem in order to allow a solution to be formulated. - Be confident in the use of vectors, their manipulation, their transformation to different coordinate systems, and to be clear about why vectors are necessary to properly und ...
... applicable to each problem and to correctly visualize and analyse the problem in order to allow a solution to be formulated. - Be confident in the use of vectors, their manipulation, their transformation to different coordinate systems, and to be clear about why vectors are necessary to properly und ...
mg - UF Physics
... Draw a FBD to show all the forces acting on the object Choose a coordinate system. If the direction of the net force is known, choose axes so that the net force (and acceleration) are along one of the axes Find the net force by adding the forces as vectors Use Newton’s second law to relate the net f ...
... Draw a FBD to show all the forces acting on the object Choose a coordinate system. If the direction of the net force is known, choose axes so that the net force (and acceleration) are along one of the axes Find the net force by adding the forces as vectors Use Newton’s second law to relate the net f ...
Circular motion and Centripetal Acceleration
... Something (a Force) must make an object move in a circle The Force causing circular motion can be one of many different forces, depends on the situation (orbit = gravitational force, car turning a corner = frictional force between tires and the road, ball on a string = tension force) ...
... Something (a Force) must make an object move in a circle The Force causing circular motion can be one of many different forces, depends on the situation (orbit = gravitational force, car turning a corner = frictional force between tires and the road, ball on a string = tension force) ...
1.2ppt
... expressions. In the previous example we saw a rational equation with constants in the denominators. That rational equation was a linear equation. The rational equation below is not a linear equation. The solution ...
... expressions. In the previous example we saw a rational equation with constants in the denominators. That rational equation was a linear equation. The rational equation below is not a linear equation. The solution ...
May 2002
... A small particle of mass m is constrained to slide, without friction, on the inside of a circular cone whose vertex is at the origin and whose axis is along the z-axis. The half angle at the apex of the cone is α and there is a uniform gravitational field g, directed downward and parallel to the axi ...
... A small particle of mass m is constrained to slide, without friction, on the inside of a circular cone whose vertex is at the origin and whose axis is along the z-axis. The half angle at the apex of the cone is α and there is a uniform gravitational field g, directed downward and parallel to the axi ...
1 Introduction - Mechanics - College of Engineering
... geometric properties of bodies (size, shape, etc.) Time – describes succession of events Mass – measures resistance of bodies to a change in velocity (=acceleration) Force – describes action of one body on another. It is a vector quantity. Distinguished as contact or volumetric ...
... geometric properties of bodies (size, shape, etc.) Time – describes succession of events Mass – measures resistance of bodies to a change in velocity (=acceleration) Force – describes action of one body on another. It is a vector quantity. Distinguished as contact or volumetric ...