Net force
... • Net force: sum of ALL forces acting on the body. • An object at rest and an object moving with constant velocity both have no acceleration. ...
... • Net force: sum of ALL forces acting on the body. • An object at rest and an object moving with constant velocity both have no acceleration. ...
Chapter 5 PowerPoint
... 5-2 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Newton F=ma Object moving in a circle must be acted on by a force Fr=mar=mv2/r Net force must be directed toward the center of the circle. Centripetal force - force directed towards center of circle ...
... 5-2 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Newton F=ma Object moving in a circle must be acted on by a force Fr=mar=mv2/r Net force must be directed toward the center of the circle. Centripetal force - force directed towards center of circle ...
Forces - SCHOOLinSITES
... attractive force on each other, F = G (m1m2)/d2 G = 6.67 x 10-11 m3/kg.s2 Acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.8 m/s2 Mercury – 3.8 m/s2 Jupiter – 25.8 m/s2 Gravity is one of the four basic forces that also include the electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear forc ...
... attractive force on each other, F = G (m1m2)/d2 G = 6.67 x 10-11 m3/kg.s2 Acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.8 m/s2 Mercury – 3.8 m/s2 Jupiter – 25.8 m/s2 Gravity is one of the four basic forces that also include the electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear forc ...
Page 407-408 - Cloudfront.net
... • 8. the object’s masses and distance. • 9. the leaf has greater surface area. • 10. it moves based on its mass and velocity. • 11. The force the four children are exerting on the object balanced one another. • 12. Fluid friction usually less than sliding friction. By bathing the parts of the machi ...
... • 8. the object’s masses and distance. • 9. the leaf has greater surface area. • 10. it moves based on its mass and velocity. • 11. The force the four children are exerting on the object balanced one another. • 12. Fluid friction usually less than sliding friction. By bathing the parts of the machi ...
File
... weightlessness. They do have a gravitational force acting on them, though! The satellite and all its contents are in free fall, so there is no normal force. This is what leads to the experience of weightlessness. ...
... weightlessness. They do have a gravitational force acting on them, though! The satellite and all its contents are in free fall, so there is no normal force. This is what leads to the experience of weightlessness. ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 3
... C. Velocity- speed of the object and its direction 1. is a vector quantity 2. Size of objects velocity is speed 3. Object will have different velocities if have different speeds or move in different directions ...
... C. Velocity- speed of the object and its direction 1. is a vector quantity 2. Size of objects velocity is speed 3. Object will have different velocities if have different speeds or move in different directions ...
Lab 7 Work Energy
... Select two times in your data as the initial and final states. The initial time should be just after release and the final time should be before the hanging weight hits the ground. Record the following values at these two times. initial position (m) final position (m) initial speed (m/s) final speed ...
... Select two times in your data as the initial and final states. The initial time should be just after release and the final time should be before the hanging weight hits the ground. Record the following values at these two times. initial position (m) final position (m) initial speed (m/s) final speed ...
How do Newton`s Laws describe motion?
... What about the ladder on top of the truck? The ladder is in motion because the truck is in motion. When the truck stops, the ladder stays in motion. The truck is stopped by the force of the car, but the ladder is not. What force stops the ladder? ...
... What about the ladder on top of the truck? The ladder is in motion because the truck is in motion. When the truck stops, the ladder stays in motion. The truck is stopped by the force of the car, but the ladder is not. What force stops the ladder? ...
Honors Physics – 1st Semester Exam Review
... i. P = IV = I2R (unit: Watt) ii. Energy dissipated by a circuit element: E = Pt iii. Units of energy (J, kWh) ...
... i. P = IV = I2R (unit: Watt) ii. Energy dissipated by a circuit element: E = Pt iii. Units of energy (J, kWh) ...
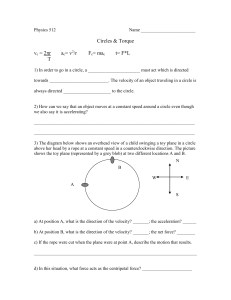
Physics 512 - Scarsdale Schools
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
Name:______KEY_ Quiz Study Guide Topics included on this quiz
... **Make sure you KNOW this equation. It is one of Newton’s Laws and may not be given to you on the quiz. ...
... **Make sure you KNOW this equation. It is one of Newton’s Laws and may not be given to you on the quiz. ...