Chapter 2 Summary
... • For the average velocity for a time interval, find the slope of the line connecting the two ...
... • For the average velocity for a time interval, find the slope of the line connecting the two ...
These problems - Tasker Milward Physics Website
... 1. A track star with a mass of 50kg is running with a velocity of 9m/s. Find the momentum of the runner. 2. How fast must a 58Kg football player run in order to have the same momentum as a 53kg player with a velocity of 6.2m/s? 3. An 85kg diver jumps from a diving board 3.0 m above the water and com ...
... 1. A track star with a mass of 50kg is running with a velocity of 9m/s. Find the momentum of the runner. 2. How fast must a 58Kg football player run in order to have the same momentum as a 53kg player with a velocity of 6.2m/s? 3. An 85kg diver jumps from a diving board 3.0 m above the water and com ...
2.0 Circular Motion An object moves in a straight line if the net force
... When r = 0, the oscillation continues with same amplitude indefinitely. x ...
... When r = 0, the oscillation continues with same amplitude indefinitely. x ...
Ch33 - Siena College
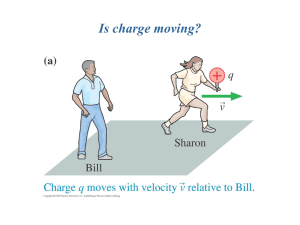
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
Types of Variation
... Distance is the separation between two positions. Displacement is the change in position of a body and it has both magnitude and direction. Velocity is the rate of change of position. An objects initial position, di, its constant average velocity, v, its position, d, and the time, t, since the objec ...
... Distance is the separation between two positions. Displacement is the change in position of a body and it has both magnitude and direction. Velocity is the rate of change of position. An objects initial position, di, its constant average velocity, v, its position, d, and the time, t, since the objec ...
Types of Variation
... Distance is the separation between two positions. Displacement is the change in position of a body and it has both magnitude and direction. Velocity is the rate of change of position. An objects initial position, di, its constant average velocity, v, its position, d, and the time, t, since the objec ...
... Distance is the separation between two positions. Displacement is the change in position of a body and it has both magnitude and direction. Velocity is the rate of change of position. An objects initial position, di, its constant average velocity, v, its position, d, and the time, t, since the objec ...
Physics, Force, Motion - Region 11 Math and Science Teacher
... (Forces are like shoes - they come in pairs!) ...
... (Forces are like shoes - they come in pairs!) ...
BT109 General Chemistry
... An object is held in place by friction on an inclined surface. The angle of inclination is increased until the object starts moving. If the surface is kept at this angle, the object ...
... An object is held in place by friction on an inclined surface. The angle of inclination is increased until the object starts moving. If the surface is kept at this angle, the object ...