Applying Newton`s 2nd Law to
... Ex 1) Two blocks of identical material are connected by a light rope on a level surface. An applied force of 55 N [right] causes the blocks to ● Since the boxes are attached by a wire, they accelerate. While in motion, the magnitude of the force of friction on the accelerate at the same rate. We blo ...
... Ex 1) Two blocks of identical material are connected by a light rope on a level surface. An applied force of 55 N [right] causes the blocks to ● Since the boxes are attached by a wire, they accelerate. While in motion, the magnitude of the force of friction on the accelerate at the same rate. We blo ...
Classical Dynamics for a System of Particles (Chapter 9)
... In everyday life life, we normally think of a collision as an event in which two objects hit each other. In physics the word is used in a more general way. A collision is an event in which: Two objects move together, experience equal but opposite f forces, and d accelerate l in response to those h ...
... In everyday life life, we normally think of a collision as an event in which two objects hit each other. In physics the word is used in a more general way. A collision is an event in which: Two objects move together, experience equal but opposite f forces, and d accelerate l in response to those h ...
impulse - sportscoachinghigher
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
physics: semester 1 final review
... What would be its vertical acceleration? 17. (Complete): Impulse equals change of ________________. 18. (Complete): Impulse equal force times _____________ 19. A tennis player applies an average 10N force to a 0.05 Kg ball that flies off at 40 m/s. For what time was the racket in contact with the b ...
... What would be its vertical acceleration? 17. (Complete): Impulse equals change of ________________. 18. (Complete): Impulse equal force times _____________ 19. A tennis player applies an average 10N force to a 0.05 Kg ball that flies off at 40 m/s. For what time was the racket in contact with the b ...
Sports Mechanics Principles
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
Document
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of al ...
Lab3PreLab
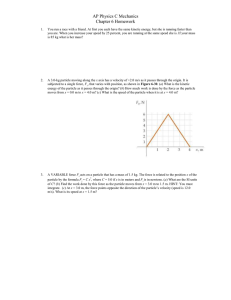
... Assume that m1 m2 sum to a total mass of 0.300 kg. The mass m2 varies over the range 0.010 kg ≤ m 2 ≤ 0.070 kg . Both masses will begin at rest, and then be subject to a force equal to m2 g , where g is the acceleration of gravity, 9.80 m s-2. That force will be applied to the 0.300 kg total mass ...
... Assume that m1 m2 sum to a total mass of 0.300 kg. The mass m2 varies over the range 0.010 kg ≤ m 2 ≤ 0.070 kg . Both masses will begin at rest, and then be subject to a force equal to m2 g , where g is the acceleration of gravity, 9.80 m s-2. That force will be applied to the 0.300 kg total mass ...
PHYS 102 Midterm Exam 2 (09.04.2016) Solutions
... perpendicular to the current. This results in a force with only radial and vertical components. By symmetry, we find that the radial force components from segments on opposite sides of the loop cancel. The net force then is purely vertical and upward. Symmetry also shows us that each current element ...
... perpendicular to the current. This results in a force with only radial and vertical components. By symmetry, we find that the radial force components from segments on opposite sides of the loop cancel. The net force then is purely vertical and upward. Symmetry also shows us that each current element ...
Forces and Motion - sheffield.k12.oh.us
... seconds. How fast was the rock going when it left the boy’s hand? ...
... seconds. How fast was the rock going when it left the boy’s hand? ...
Slide 1 - Particle and Astroparticle Physics
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
How much force is required to inflate a high pressure
... During your travels through deep space you discover a new solar system. You land on the outermost planet and determine that the acceleration due to gravity is 2.7 m/s^2. If your mass back on Earth is 72 kg, what force would you exert on a scale in pounds while standing on the planet's surface? The ...
... During your travels through deep space you discover a new solar system. You land on the outermost planet and determine that the acceleration due to gravity is 2.7 m/s^2. If your mass back on Earth is 72 kg, what force would you exert on a scale in pounds while standing on the planet's surface? The ...
An introduction to the Lorentz
... The potential and field at x are naturally expressed in terms of u, the particle’s proper time when it encounters x’s past light cone, and r, the distance between x and the particle, as measured at that time in the MCLF. This motivates the introduction of a (noninertial) coordinate system for flat s ...
... The potential and field at x are naturally expressed in terms of u, the particle’s proper time when it encounters x’s past light cone, and r, the distance between x and the particle, as measured at that time in the MCLF. This motivates the introduction of a (noninertial) coordinate system for flat s ...
Linear and Rotational Kinematics
... A wheel has eight spokes and a radius of 30 cm. It is mounted on a fixed axle and is spinning at 2.5 rev/s. You want to shoot a 24cm arrow parallel to this axle and through the wheel without hitting any of the spokes. spokes Assume that the arrow and the spokes are very thin. (a) What minimum speed ...
... A wheel has eight spokes and a radius of 30 cm. It is mounted on a fixed axle and is spinning at 2.5 rev/s. You want to shoot a 24cm arrow parallel to this axle and through the wheel without hitting any of the spokes. spokes Assume that the arrow and the spokes are very thin. (a) What minimum speed ...
Circular Motion Web Lab
... familiarity with the control of the animation. The object speed, radius of the circle, and object mass can be varied by using the sliders or the buttons. The vector nature of velocity and acceleration can be depicted on the screen. A trace of the objects motion can be turned on, turned off and erase ...
... familiarity with the control of the animation. The object speed, radius of the circle, and object mass can be varied by using the sliders or the buttons. The vector nature of velocity and acceleration can be depicted on the screen. A trace of the objects motion can be turned on, turned off and erase ...
Ch15
... In many real systems, non-conservative forces are present. This is no longer an ideal system (the type we have dealt with so far). Friction and air resistance are common non-conservative forces. In this case, the mechanical energy of the system diminishes in time, the motion is said to be damped ...
... In many real systems, non-conservative forces are present. This is no longer an ideal system (the type we have dealt with so far). Friction and air resistance are common non-conservative forces. In this case, the mechanical energy of the system diminishes in time, the motion is said to be damped ...
Physics 880.06: Problem Set 6
... Note: please turn these problems into the mailbox of the grader, Wissam AlSaidi, by 5PM on Friday, May 23, 2003. Remember that you will be graded only on the best 5 out of the 7 problem sets. 1. Consider a single Abrikosov vortex parallel to the z axis. Assume that this vortex experiences three forc ...
... Note: please turn these problems into the mailbox of the grader, Wissam AlSaidi, by 5PM on Friday, May 23, 2003. Remember that you will be graded only on the best 5 out of the 7 problem sets. 1. Consider a single Abrikosov vortex parallel to the z axis. Assume that this vortex experiences three forc ...
Satellite Motion
... By measuring a and T one can use this relation to determine the mass M. It is in this way that we determine relatively easily the mass of the sun and the masses of those planets (such as earth) having moons. Actually, if we had taken into account the neglected motion of M around the CM of the syste ...
... By measuring a and T one can use this relation to determine the mass M. It is in this way that we determine relatively easily the mass of the sun and the masses of those planets (such as earth) having moons. Actually, if we had taken into account the neglected motion of M around the CM of the syste ...