F g - mrbernabo
... it can be placed further or closer to the rotational axis. (If the skater starts at the left position. How will their rotational speed change) ...
... it can be placed further or closer to the rotational axis. (If the skater starts at the left position. How will their rotational speed change) ...
SPH4U: Forces
... Reason. Isaac says, “On the force diagram for moment 3 we should draw an upwards force due to the trampoline since he is still traveling upwards. We should make it smaller than gravity since that force is running out.” Do you agree or disagree with Isaac? Use an interaction diagram to help explain. ...
... Reason. Isaac says, “On the force diagram for moment 3 we should draw an upwards force due to the trampoline since he is still traveling upwards. We should make it smaller than gravity since that force is running out.” Do you agree or disagree with Isaac? Use an interaction diagram to help explain. ...
Forces and Motion Scripted - UTeach Outreach
... (3) Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses critical thinking, scientific reasoning, and problem solving to make informed decisions and knows the contributions of relevant scientists. The student is expected to: (D) relate the impact of research on scientific thought and society, in ...
... (3) Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses critical thinking, scientific reasoning, and problem solving to make informed decisions and knows the contributions of relevant scientists. The student is expected to: (D) relate the impact of research on scientific thought and society, in ...
(Tentative) Physics Curriculum-2015-2016
... --Isaac Newton The above statement reflects that even someone like Newton works in mechanics and calculus would have been impossible without the solid foundation established by both his colleagues and predecessors. This is why, this curriculum is design to create a community inside the classroom so ...
... --Isaac Newton The above statement reflects that even someone like Newton works in mechanics and calculus would have been impossible without the solid foundation established by both his colleagues and predecessors. This is why, this curriculum is design to create a community inside the classroom so ...
Seesaws 9 Balanced Seesaw
... Ang. Position – an object’s orientation Ang. Velocity – change in ang. position w/ time Torque – a twist or spin Ang. Accel. – change in ang. velocity with time Rotational Mass – measure of rotational inertia ...
... Ang. Position – an object’s orientation Ang. Velocity – change in ang. position w/ time Torque – a twist or spin Ang. Accel. – change in ang. velocity with time Rotational Mass – measure of rotational inertia ...
Motion, Forces, and Simple Machines
... Instantaneous Speed Average speed is useful if you don’t care about the details of the motion. For example, suppose you went on a long road trip and traveled 640 km in 8 h. Your average speed was 80 km/h, even though you might have been stuck in a traffic jam for some of the time. When your motion i ...
... Instantaneous Speed Average speed is useful if you don’t care about the details of the motion. For example, suppose you went on a long road trip and traveled 640 km in 8 h. Your average speed was 80 km/h, even though you might have been stuck in a traffic jam for some of the time. When your motion i ...
Motion, Forces, and Simple Machines
... Instantaneous Speed Average speed is useful if you don’t care about the details of the motion. For example, suppose you went on a long road trip and traveled 640 km in 8 h. Your average speed was 80 km/h, even though you might have been stuck in a traffic jam for some of the time. When your motion i ...
... Instantaneous Speed Average speed is useful if you don’t care about the details of the motion. For example, suppose you went on a long road trip and traveled 640 km in 8 h. Your average speed was 80 km/h, even though you might have been stuck in a traffic jam for some of the time. When your motion i ...
Chapter 8 Oscillations
... the right as shown above right and released from rest so that it swings as a simple pendulum with small amplitude. Assume that both spheres undergo simple harmonic motion 11. Which of the following is true for both spheres? (A) The maximum kinetic energy is attained as the sphere passes through its ...
... the right as shown above right and released from rest so that it swings as a simple pendulum with small amplitude. Assume that both spheres undergo simple harmonic motion 11. Which of the following is true for both spheres? (A) The maximum kinetic energy is attained as the sphere passes through its ...
Lecture Notes 02: Conservation Laws (Continued): Conservation of Linear Momentum, Maxwell's Stress Tensor
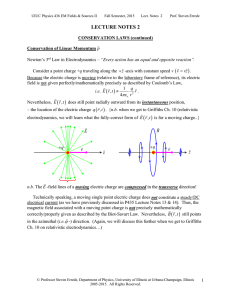
... n.b. In electrostatics and in magnetostatics, Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion always holds. In electrodynamics, Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion does not hold for the apparent relative motion of two electric charges! (n.b. Isaac Newton could not have forseen this {from an apple falling on his head} because gra ...
... n.b. In electrostatics and in magnetostatics, Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion always holds. In electrodynamics, Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion does not hold for the apparent relative motion of two electric charges! (n.b. Isaac Newton could not have forseen this {from an apple falling on his head} because gra ...
PREPARING FOR THE AP PHYSICS EXAM
... five potential answers in a familiar standardized testing format. As in 2004, the free-response section of the Physics B exam in 2005 will be slightly shorter than in the past, containing a total of 80 instead of 90 points. It will consist of two 15-point questions and five 10-point questions. Howev ...
... five potential answers in a familiar standardized testing format. As in 2004, the free-response section of the Physics B exam in 2005 will be slightly shorter than in the past, containing a total of 80 instead of 90 points. It will consist of two 15-point questions and five 10-point questions. Howev ...
Systems of Linear Equations - Kirkwood Community College
... space, as well as the concepts of energy and force. Within physics, scientists often use polynomials to define the rules that govern nature and all its effects. Consider the formula for force, F = ma (force equals mass times acceleration). This formula defines why a basketball bounces higher when sl ...
... space, as well as the concepts of energy and force. Within physics, scientists often use polynomials to define the rules that govern nature and all its effects. Consider the formula for force, F = ma (force equals mass times acceleration). This formula defines why a basketball bounces higher when sl ...