Pre-Calculus 12A Section 7.3 Solving Exponential Equations
... Example 3: Solving Problems Involving Exponential Equations with the Same Base The half-life of radon-222 is 92 hours. If the initial amount of radon-222 was 48g, how long would it take for the radon to decay to 3 g? Solution: Find the equation of the function that describes the amount of radon pres ...
... Example 3: Solving Problems Involving Exponential Equations with the Same Base The half-life of radon-222 is 92 hours. If the initial amount of radon-222 was 48g, how long would it take for the radon to decay to 3 g? Solution: Find the equation of the function that describes the amount of radon pres ...
Name - westlake-science
... 5. Newton’s first law of motion is sometimes called the law of a. inertia b. conservation c. momentum d. resistance 6. A change in which of the following affects the weight of an object? a. momentum b. velocity c. acceleration due to gravity d. friction 7. Which represents Newton’s second law? a. v ...
... 5. Newton’s first law of motion is sometimes called the law of a. inertia b. conservation c. momentum d. resistance 6. A change in which of the following affects the weight of an object? a. momentum b. velocity c. acceleration due to gravity d. friction 7. Which represents Newton’s second law? a. v ...
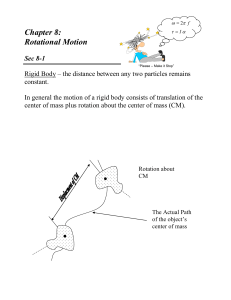
Chapter 8: Rotational Motion
... How to “think” about Torque 1. Torque must be specified about a pivot point 2. Torque is a product quantity made up of distance and force. 3. Torque causes angular acceleration, , in the same way that forces cause linear accelerations. 4. The Moment of Inertia, I, is a measure of resistance to rota ...
... How to “think” about Torque 1. Torque must be specified about a pivot point 2. Torque is a product quantity made up of distance and force. 3. Torque causes angular acceleration, , in the same way that forces cause linear accelerations. 4. The Moment of Inertia, I, is a measure of resistance to rota ...
LESSON PLAN 1.3 Newton`s
... http://www.hometrainingtools.com/a/newton-s-laws-of-motion-science-projects Use this formula (F = m x a) to measure force. Let’s do an experiment with this formula: http://www.racemath.info/forcesandpressure/what_is_f=ma.htm. Apply/Analyze: If the acceleration is larger, what will happen to the forc ...
... http://www.hometrainingtools.com/a/newton-s-laws-of-motion-science-projects Use this formula (F = m x a) to measure force. Let’s do an experiment with this formula: http://www.racemath.info/forcesandpressure/what_is_f=ma.htm. Apply/Analyze: If the acceleration is larger, what will happen to the forc ...
Chapter 7
... traveling in a circle, with what speed is it traveling linearly. Or a more practical use would be if the object were to break its circular motion, what path would it travel? Linear So what would the initial velocity be of the object as it breaks from the circle? ...
... traveling in a circle, with what speed is it traveling linearly. Or a more practical use would be if the object were to break its circular motion, what path would it travel? Linear So what would the initial velocity be of the object as it breaks from the circle? ...
Download Supplemental Information
... Where C is a dimensionless constant ~3, ζ denotes the zeta potentials of the nanoparticle (NP) and substrate, λD is the Debye length, R is the effective particle radius, and z is the distance from the substrate. For λD ~ R, we see that even one Debye length from the substrate, the EP force associate ...
... Where C is a dimensionless constant ~3, ζ denotes the zeta potentials of the nanoparticle (NP) and substrate, λD is the Debye length, R is the effective particle radius, and z is the distance from the substrate. For λD ~ R, we see that even one Debye length from the substrate, the EP force associate ...
香港考試局
... (iii) Unchanged. As the centripetal force is proportional to max FA as well as the weight, the minimum spinning speed (eqn(*)) does not depend on the mass. (b) The space station should rotate about an axis through its centre and normal to the plane containing the station with a constant angular spee ...
... (iii) Unchanged. As the centripetal force is proportional to max FA as well as the weight, the minimum spinning speed (eqn(*)) does not depend on the mass. (b) The space station should rotate about an axis through its centre and normal to the plane containing the station with a constant angular spee ...
Document
... yc (x) = C1 cos (4x) + C2 sin (4x) The method of variation of parameters tells us that the particular solution is of the form yp (x) = u1 (x) cos (4x) + u2 (x) sin (4x) where the functions u1 and u2 satisfy the conditions u01 cos (4x) + u02 sin (4x) = 0 −u01 4 sin (4x) + u02 4 cos (4x) = 2 sec (4x) ...
... yc (x) = C1 cos (4x) + C2 sin (4x) The method of variation of parameters tells us that the particular solution is of the form yp (x) = u1 (x) cos (4x) + u2 (x) sin (4x) where the functions u1 and u2 satisfy the conditions u01 cos (4x) + u02 sin (4x) = 0 −u01 4 sin (4x) + u02 4 cos (4x) = 2 sec (4x) ...
Section B: CHEMICAL ENGINEERING – Answer ALL questions
... A vacuum chamber which forms part of a linear accelerator contains both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field. When a charged particle is fired into the chamber it experiences an instantaneous force F1 (newtons) due to the electric field, and F2 (newtons) due to the magnetic field, a ...
... A vacuum chamber which forms part of a linear accelerator contains both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field. When a charged particle is fired into the chamber it experiences an instantaneous force F1 (newtons) due to the electric field, and F2 (newtons) due to the magnetic field, a ...
Slides - Nuffield Foundation
... • When can you use F = mR? • How does the friction model allow you to use F = ma and the constant acceleration equations to solve problems? • Can you think of other situations when friction ...
... • When can you use F = mR? • How does the friction model allow you to use F = ma and the constant acceleration equations to solve problems? • Can you think of other situations when friction ...
What is an elastic collision?
... objects colliding in an isolated system, the total momentum before and after the collision is equal. This is because the momentum lost by one object is equal to the momentum gained by the other Conservation of momentum is derived from Newton's laws of motion. Newton's third law states that every act ...
... objects colliding in an isolated system, the total momentum before and after the collision is equal. This is because the momentum lost by one object is equal to the momentum gained by the other Conservation of momentum is derived from Newton's laws of motion. Newton's third law states that every act ...