Dynamics of spherical particles on a surface: Collision
... and the interaction with the substrate introduce an additional set of parameters ~e.g., the coefficients of rolling and sliding friction!, which have not been included in the theoretical descriptions of the system. Our goal is to bridge this gap between experiment and theory, and formulate a model t ...
... and the interaction with the substrate introduce an additional set of parameters ~e.g., the coefficients of rolling and sliding friction!, which have not been included in the theoretical descriptions of the system. Our goal is to bridge this gap between experiment and theory, and formulate a model t ...
Classical electrodynamics - University of Guelph Physics
... Here, ǫ0 and µ0 are constants, and ∇ = (∇x , ∇y , ∇z ) is the gradient operator of vector calculus (with the obvious notation ∇x f = ∂f /∂x for any function f ). The Maxwell equations state that the electric field is produced by charges and time-varying magnetic fields, while the magnetic field is p ...
... Here, ǫ0 and µ0 are constants, and ∇ = (∇x , ∇y , ∇z ) is the gradient operator of vector calculus (with the obvious notation ∇x f = ∂f /∂x for any function f ). The Maxwell equations state that the electric field is produced by charges and time-varying magnetic fields, while the magnetic field is p ...
Chapter 8
... incompressible steady flow over a semi-infinite flat plate with an uniform incoming flow of velocity U in parallel to the plate. The flow is two dimensional. The coordinates are chosen such that x is in the incoming flow direction with x=0 being located the leading edge and y is normal to the plate ...
... incompressible steady flow over a semi-infinite flat plate with an uniform incoming flow of velocity U in parallel to the plate. The flow is two dimensional. The coordinates are chosen such that x is in the incoming flow direction with x=0 being located the leading edge and y is normal to the plate ...
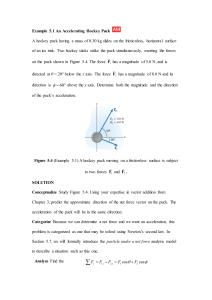
Chapter 8 Applications of Newton`s Second Law
... Example 8.10: Capstan ........................................................................................... 44 ...
... Example 8.10: Capstan ........................................................................................... 44 ...
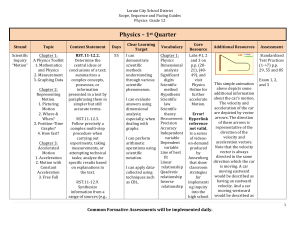
Physics – 1st Quarter
... In earlier grades, Newton’s laws of motion were introduced; gravitational forces and fields were described conceptually; the gravitational force (weight) acting on objects near Earth’s surface was calculated; fricti ...
... In earlier grades, Newton’s laws of motion were introduced; gravitational forces and fields were described conceptually; the gravitational force (weight) acting on objects near Earth’s surface was calculated; fricti ...
Chapter 1 notes
... due to their masses. Gravity can change the motion of an object by changing its speed, direction, or both. • All matter has mass, and gravity is a result of mass. Therefore, all matter is affected by gravity and all objects experience an attraction toward all other objects. • The mass of most object ...
... due to their masses. Gravity can change the motion of an object by changing its speed, direction, or both. • All matter has mass, and gravity is a result of mass. Therefore, all matter is affected by gravity and all objects experience an attraction toward all other objects. • The mass of most object ...
Engineering Principles - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... and then in small groups discuss why you think these areas are considered important enough to be studied by everyone taking a BTEC National Engineering course. Pick one or more topics and discuss how they might be relevant to a product, activity or industry you are familiar with. ...
... and then in small groups discuss why you think these areas are considered important enough to be studied by everyone taking a BTEC National Engineering course. Pick one or more topics and discuss how they might be relevant to a product, activity or industry you are familiar with. ...
Ch 08 B1 QFD.cwk (WP)
... (d) increase his weight (e) increase the height of his center of mass Explain your reasoning. 25. The net torque on a rotating wheel is τ and the wheel turns at angular speed ω . What power is developed by the torque? Hint: Start with a power formula from linear motion and substitute the analogous r ...
... (d) increase his weight (e) increase the height of his center of mass Explain your reasoning. 25. The net torque on a rotating wheel is τ and the wheel turns at angular speed ω . What power is developed by the torque? Hint: Start with a power formula from linear motion and substitute the analogous r ...
Lab 9 - Suffolk County Community College
... Choose two carts. Attach enough small masses to one to ensure equal masses for the two carts. Leave one at rest in the middle of the air track and set the other into motion. Measure the velocity and consequently the momentum for both carts BEFORE and AFTER the collision. The velocity measurements ar ...
... Choose two carts. Attach enough small masses to one to ensure equal masses for the two carts. Leave one at rest in the middle of the air track and set the other into motion. Measure the velocity and consequently the momentum for both carts BEFORE and AFTER the collision. The velocity measurements ar ...