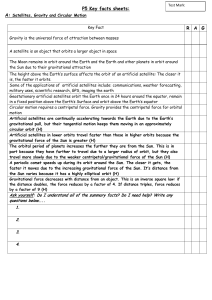
02mc
... can undergo circular motion, i.e. it can be deflected by more than 90 while in electric field the electron can be almost deflected by 90. B. False. In both the electric and magnetic field, the force depends on the magnitude of the charge; they are qE and qvB. C. False. If the region of the uniform ...
... can undergo circular motion, i.e. it can be deflected by more than 90 while in electric field the electron can be almost deflected by 90. B. False. In both the electric and magnetic field, the force depends on the magnitude of the charge; they are qE and qvB. C. False. If the region of the uniform ...
The Force
... acceleration due to gravity, but rather the gravitational field strength, with units of newtons/kilogram. Inertial and gravitational masses have been tested and are believed to always be equal in amount. This is why all objects freefall at the same rate of acceleration. ...
... acceleration due to gravity, but rather the gravitational field strength, with units of newtons/kilogram. Inertial and gravitational masses have been tested and are believed to always be equal in amount. This is why all objects freefall at the same rate of acceleration. ...
Chapter 4 - AstroStop
... Force only changes the state of motion. Zero acceleration does not imply ...
... Force only changes the state of motion. Zero acceleration does not imply ...
Newton`s Third Law and Momentum
... Review First and Second Laws 1. An object will remain at rest or in motion at constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. 2. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to the mass ...
... Review First and Second Laws 1. An object will remain at rest or in motion at constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. 2. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to the mass ...
Chapter 4: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... N1L: An object at rest will remain at rest unless it is acted upon by a net external force. An object in motion with constant velocity will continue to move with constant velocity unless it is acted upon by a net external force. ...
... N1L: An object at rest will remain at rest unless it is acted upon by a net external force. An object in motion with constant velocity will continue to move with constant velocity unless it is acted upon by a net external force. ...
Inverted Pendulum
... • Stability – pendulum returns to upward orientation • measurements of boundary conditions: frequency vs. amplitude length vs. amplitude angle in time (two cases); • inverted pendulum • “inverted” inverted pendulum – for drag determination ...
... • Stability – pendulum returns to upward orientation • measurements of boundary conditions: frequency vs. amplitude length vs. amplitude angle in time (two cases); • inverted pendulum • “inverted” inverted pendulum – for drag determination ...
The Vorticity Equation and Conservation of Angular Momentum Alex
... orbital and spin angular momentums are essentially uncoupled and independent. Angular momentum is a vector quantity, and the spin angular momentum is oriented along the axis of rotation of the column. Since the fluid column remains at a fixed point on Earth and is at all times oriented to the local ...
... orbital and spin angular momentums are essentially uncoupled and independent. Angular momentum is a vector quantity, and the spin angular momentum is oriented along the axis of rotation of the column. Since the fluid column remains at a fixed point on Earth and is at all times oriented to the local ...
Monday, April 14, 2008
... To simplify the problem, we will only deal with forces acting on x-y plane, giving torque only along z-axis. What do you think the conditions for equilibrium be in this case? The six possible equations from the two vector equations turns to three equations. ...
... To simplify the problem, we will only deal with forces acting on x-y plane, giving torque only along z-axis. What do you think the conditions for equilibrium be in this case? The six possible equations from the two vector equations turns to three equations. ...
Ch. 12 Notes - leavellphysicalscience
... Weight-the force of gravity acting on an object An object’s weight is the product of the objects mass and acceleration due to gravity acting on it. Weight=Mass x Acceleration due to gravity, or W=mg; g=9.8 m/s2 (F)orce or (W)eight is expressed in Newtons; Acceleration due to grativty (a or g) is exp ...
... Weight-the force of gravity acting on an object An object’s weight is the product of the objects mass and acceleration due to gravity acting on it. Weight=Mass x Acceleration due to gravity, or W=mg; g=9.8 m/s2 (F)orce or (W)eight is expressed in Newtons; Acceleration due to grativty (a or g) is exp ...
Chapter 3-
... Momentum is the property of a moving object. The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity. Momentum is represented by the symbol (p) and can be calculated as follows: Momentum (p) = mass (m) x velocity (v) The SI unit for momentum is kg x m/s ...
... Momentum is the property of a moving object. The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity. Momentum is represented by the symbol (p) and can be calculated as follows: Momentum (p) = mass (m) x velocity (v) The SI unit for momentum is kg x m/s ...
Ch. 4 Worksheet Forces in one dimensionx
... 6. When the net force equals zero the object is said to be at _________________________ and the forces are _____________________ and the object will not ________________________. 7. Calculate the apparent weight of a 86.0 Kg man riding on a elevator if the upward acceleration is 2.15m/s2? ...
... 6. When the net force equals zero the object is said to be at _________________________ and the forces are _____________________ and the object will not ________________________. 7. Calculate the apparent weight of a 86.0 Kg man riding on a elevator if the upward acceleration is 2.15m/s2? ...
Differential Equations
... can also be used to solve heat conduction problems with other boundary conditions than those given by previous two types. For example, the left end of the bar might be held at a fixed temperature T, while the other end is insulated. In this case the boundary conditions are ...
... can also be used to solve heat conduction problems with other boundary conditions than those given by previous two types. For example, the left end of the bar might be held at a fixed temperature T, while the other end is insulated. In this case the boundary conditions are ...
and S y
... • Projectile motion involves object that move up or down and right or left simultaneously. A ball thrown into the air at an angle is a common example as is water sprayed from a garden hose or a bullet fired at a target. • Any object once released from its accelerating force is accelerated downward b ...
... • Projectile motion involves object that move up or down and right or left simultaneously. A ball thrown into the air at an angle is a common example as is water sprayed from a garden hose or a bullet fired at a target. • Any object once released from its accelerating force is accelerated downward b ...