Elastic Collisions Momentum is conserved m 1 ѵ 1i +
... Conservation of Momentum Momentum is always conserved in collisions (and also for objects pushing away from each other) ...
... Conservation of Momentum Momentum is always conserved in collisions (and also for objects pushing away from each other) ...
Class 7 in Electrodynamics
... What we have got here is that nothing is moving in the system, and yet it has a linear momentum. Something has to move, so what is actually moving in this system? It turns out that there is a mechanical momentum associated with the current flow, locating this momentum is not easy, and it is actually ...
... What we have got here is that nothing is moving in the system, and yet it has a linear momentum. Something has to move, so what is actually moving in this system? It turns out that there is a mechanical momentum associated with the current flow, locating this momentum is not easy, and it is actually ...
File - Mr. Catt`s Class
... Newton’s First Two Laws of Motion 1. The year Galileo died—1642—is the year Isaac Newton was born. Newton took the work of Galileo and Kepler and created a new theory of motion. 2. Newton’s First Law (Law of Inertia): Unless a net, outside force, acts upon an object, the object will maintain a cons ...
... Newton’s First Two Laws of Motion 1. The year Galileo died—1642—is the year Isaac Newton was born. Newton took the work of Galileo and Kepler and created a new theory of motion. 2. Newton’s First Law (Law of Inertia): Unless a net, outside force, acts upon an object, the object will maintain a cons ...
Newton`s 2nd
... A) __________________ __________________ __________________ __ B) __________________ __________________ __________________ __ C) __________________ __________________ __________________ __ D) __________________ __________________ __________________ __ ...
... A) __________________ __________________ __________________ __ B) __________________ __________________ __________________ __ C) __________________ __________________ __________________ __ D) __________________ __________________ __________________ __ ...
JPO 152 Additional physics 9 May 2013
... 2 and 3. In a closed and isolated system the centre of mass must be between the two object and must undergo no changes in its velocity. This means that middle graph must be the centre of mass and in order to be physically possible this line cannot have a change in gradient when the two objects colli ...
... 2 and 3. In a closed and isolated system the centre of mass must be between the two object and must undergo no changes in its velocity. This means that middle graph must be the centre of mass and in order to be physically possible this line cannot have a change in gradient when the two objects colli ...
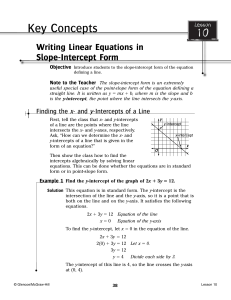
Algebra III 1.4 Guided Notes
... Often in mathematics you are taught the long way of solving a problem first. Then, the longer method is used to develop shorter techniques. The long way stresses understanding and the short way stresses efficiency. For instance, you can think of completing the square as a “long way” of solving a qua ...
... Often in mathematics you are taught the long way of solving a problem first. Then, the longer method is used to develop shorter techniques. The long way stresses understanding and the short way stresses efficiency. For instance, you can think of completing the square as a “long way” of solving a qua ...
Document
... A second order homogeneous equation with constant coefficients is written as: ay by cy 0 a 0 where a, b and c are constant The steps to follow in order to find the general solution is as follows: (1) Write down the characteristic equation a 0 a2 b c 0 ...
... A second order homogeneous equation with constant coefficients is written as: ay by cy 0 a 0 where a, b and c are constant The steps to follow in order to find the general solution is as follows: (1) Write down the characteristic equation a 0 a2 b c 0 ...
Newton`s Laws Study Guide
... “An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line, unless acted on by an unbalanced force.” In other words, if an object is still (not moving), an unbalanced force is necessary to make it move. Once an object is moving, it will go ...
... “An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line, unless acted on by an unbalanced force.” In other words, if an object is still (not moving), an unbalanced force is necessary to make it move. Once an object is moving, it will go ...
PowerPoints
... – Example: if the acceleration is along the direction of motion, the speed grows by the same amount in each time interval (e.g., second) – if the speed changes by 1 meter per second each second, the acceleration is (1 meter per second) per second, or 1 m/s2. if v = 15 m/s at time t = 0, and a = 1 m/ ...
... – Example: if the acceleration is along the direction of motion, the speed grows by the same amount in each time interval (e.g., second) – if the speed changes by 1 meter per second each second, the acceleration is (1 meter per second) per second, or 1 m/s2. if v = 15 m/s at time t = 0, and a = 1 m/ ...
5.2 Newton`s First Law
... A. accelerates inversely proportional to its mass. B. remains at rest because it has zero acceleration. C. remains at rest unless acted upon by a net force. D. remains at rest due to the constant presence of ...
... A. accelerates inversely proportional to its mass. B. remains at rest because it has zero acceleration. C. remains at rest unless acted upon by a net force. D. remains at rest due to the constant presence of ...