physics 150: test 1 study sheet
... 9. Find the impulse (change in momentum) experienced by an object when it is acted upon by an impulsive force. Find the average force given information about the impulse and time. 10. Use the Law of Conservation of Momentum to analyze a collision. Know what is meant by an elastic, inelastic, and per ...
... 9. Find the impulse (change in momentum) experienced by an object when it is acted upon by an impulsive force. Find the average force given information about the impulse and time. 10. Use the Law of Conservation of Momentum to analyze a collision. Know what is meant by an elastic, inelastic, and per ...
Motion of charged particles through magnetic and electric fields
... Consider the motion of a charged particle in uniform magnetic and electric fields. The magnetic field is directed in the +Z direction and the electric field is in the +Y direction. When a positively charged particle enters the electromagnetic field region so that it is travelling in an XY plane, the ...
... Consider the motion of a charged particle in uniform magnetic and electric fields. The magnetic field is directed in the +Z direction and the electric field is in the +Y direction. When a positively charged particle enters the electromagnetic field region so that it is travelling in an XY plane, the ...
Acceleration
... object moving only under the force of gravity is "g". The acceleration caused by gravity is 9.8 m/s2 If there was no air, all objects would fall at the same speed. Doesn’t depend on mass. After 1 second falling at 9.8 m/s After 2 seconds 19.6 m/s 3 seconds 29.4 m/s ...
... object moving only under the force of gravity is "g". The acceleration caused by gravity is 9.8 m/s2 If there was no air, all objects would fall at the same speed. Doesn’t depend on mass. After 1 second falling at 9.8 m/s After 2 seconds 19.6 m/s 3 seconds 29.4 m/s ...
Chapter 13
... developed in previous chapter for simple monoprotic weak acids. Thus, to maintain the initial pH (point A), we treat the system as if it contained a single monoprotic acid with a dissociation constant of Kal = 1.00 X 10-3. In region B have the equivalent of a simple buffer solution consisting of the ...
... developed in previous chapter for simple monoprotic weak acids. Thus, to maintain the initial pH (point A), we treat the system as if it contained a single monoprotic acid with a dissociation constant of Kal = 1.00 X 10-3. In region B have the equivalent of a simple buffer solution consisting of the ...
1 2 - Mrs. Williams` Class
... Solving Equations by 1-2 Adding or Subtracting An equation is a mathematical statement that two expressions are equal. A solution of an equation is a value of the variable that makes the equation true. To find solutions, isolate the variable. A variable is isolated when it appears by itself on one ...
... Solving Equations by 1-2 Adding or Subtracting An equation is a mathematical statement that two expressions are equal. A solution of an equation is a value of the variable that makes the equation true. To find solutions, isolate the variable. A variable is isolated when it appears by itself on one ...
Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
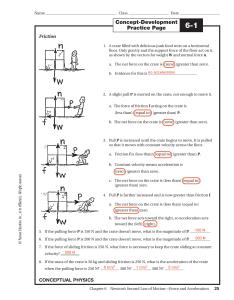
... 7. The net force is a vector sum which means that both the magnitude and direction of the forces must be considered. Fnet = ma. 8. FBDs or free body diagrams are diagrams that show the forces acting on an object, the direction of the forces and the magnitude/size of the forces. Use mathematical sym ...
... 7. The net force is a vector sum which means that both the magnitude and direction of the forces must be considered. Fnet = ma. 8. FBDs or free body diagrams are diagrams that show the forces acting on an object, the direction of the forces and the magnitude/size of the forces. Use mathematical sym ...
KEY Chapter 8 – Rotational Motion Chapter 6 – Work, Energy
... B. one-half as great C. twice as great D. four times as great 26. After the collision, the magnitude of the momentum of block A compared with that of block B is A. one-half as great B. twice as great C. four times as great D. the same 27. After the collision, the magnitude of the velocity of block A ...
... B. one-half as great C. twice as great D. four times as great 26. After the collision, the magnitude of the momentum of block A compared with that of block B is A. one-half as great B. twice as great C. four times as great D. the same 27. After the collision, the magnitude of the velocity of block A ...
Huang2000.pdf
... its parts on that side, where the motions conspire, must press and beat the contiguous air more violently than on the other, and there excite a reluctancy and reaction of the air proportionably greater.”. In 1686, Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica was published. Newton set up the first ma ...
... its parts on that side, where the motions conspire, must press and beat the contiguous air more violently than on the other, and there excite a reluctancy and reaction of the air proportionably greater.”. In 1686, Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica was published. Newton set up the first ma ...
[ Problem View ]
... Description: Student goes through right-hand rule questions and then looks at force on a charge moving at particular velocity through uniform magnetic field. Learning Goal: To understand the force on a charge moving in a magnetic field. Magnets exert forces on other magnets even though they are sepa ...
... Description: Student goes through right-hand rule questions and then looks at force on a charge moving at particular velocity through uniform magnetic field. Learning Goal: To understand the force on a charge moving in a magnetic field. Magnets exert forces on other magnets even though they are sepa ...
Basic Algebra
... force and is measured in Newtons (N), m equals mass measured in kilograms (kg), and a is acceleration and is measured in meters per seconds squared (m/s2). o Gravitational force is calculated using the equation F = mg, where F equals force and is measured in Newtons (N), m equals mass measured in ki ...
... force and is measured in Newtons (N), m equals mass measured in kilograms (kg), and a is acceleration and is measured in meters per seconds squared (m/s2). o Gravitational force is calculated using the equation F = mg, where F equals force and is measured in Newtons (N), m equals mass measured in ki ...
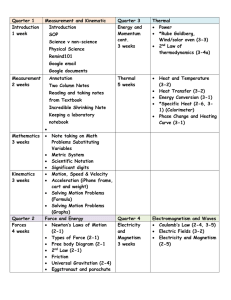
Instructor: Mike Maksimchuk Course/Grade Level: Physics A Week
... Practice Problems In-Class Demonstration Guided Notes Practice Problems ...
... Practice Problems In-Class Demonstration Guided Notes Practice Problems ...















![[ Problem View ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009194971_1-46a1d77561d5c03a41e4de32d5b76d8f-300x300.png)






