CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS
... If the gravitational acceleration on the moon is 1.6 ms-2, compare the time taken for the object to fall from the same height on the Moon. A Same as t s B Less than t s C Longer than t s ...
... If the gravitational acceleration on the moon is 1.6 ms-2, compare the time taken for the object to fall from the same height on the Moon. A Same as t s B Less than t s C Longer than t s ...
APRotMotionHW2010.29.. - Jaclyn Kuspiel Murray
... A spinning wheel on a fireworks display is initially rotating in a counterclockwise direction. The wheel has an angular acceleration of -4.60 rad/s2. Because of this acceleration, the angular velocity of the wheel changes from its initial value to a final value of -24.0 rad/s. While this change occu ...
... A spinning wheel on a fireworks display is initially rotating in a counterclockwise direction. The wheel has an angular acceleration of -4.60 rad/s2. Because of this acceleration, the angular velocity of the wheel changes from its initial value to a final value of -24.0 rad/s. While this change occu ...
Course Title: Physical Science 9 A – Physics Highly Qualified
... they interact with matter. Waves can have different wavelengths, frequencies, and amplitudes, and travel at different speeds. PS3E (9-12) Electromagnetic waves differ from physical waves because they do not require a medium and they all travel at the same speed in a vacuum. This is the maximum spe ...
... they interact with matter. Waves can have different wavelengths, frequencies, and amplitudes, and travel at different speeds. PS3E (9-12) Electromagnetic waves differ from physical waves because they do not require a medium and they all travel at the same speed in a vacuum. This is the maximum spe ...
Course Title: Physical Science 9 A – Physics Highly Qualified
... they interact with matter. Waves can have different wavelengths, frequencies, and amplitudes, and travel at different speeds. PS3E (9-12) Electromagnetic waves differ from physical waves because they do not require a medium and they all travel at the same speed in a vacuum. This is the maximum spe ...
... they interact with matter. Waves can have different wavelengths, frequencies, and amplitudes, and travel at different speeds. PS3E (9-12) Electromagnetic waves differ from physical waves because they do not require a medium and they all travel at the same speed in a vacuum. This is the maximum spe ...
Chapter 13 ppt
... life in weightless conditions. In your Science Journal, write one or two paragraphs explaining how you would carry out daily activities while weightless. Describe eating, sleeping, going to school, working in class, and any other activity you would like to include. ...
... life in weightless conditions. In your Science Journal, write one or two paragraphs explaining how you would carry out daily activities while weightless. Describe eating, sleeping, going to school, working in class, and any other activity you would like to include. ...
Newton`s Laws Review Key
... things together, like your hands, sometimes they squish into each other and get in each other's way. But even completely smooth, hard things have some friction. This friction is the result of the molecules in both objects being attracted to each other. 2. Explain how inertia and momentum are related ...
... things together, like your hands, sometimes they squish into each other and get in each other's way. But even completely smooth, hard things have some friction. This friction is the result of the molecules in both objects being attracted to each other. 2. Explain how inertia and momentum are related ...
Rotational Motion Test Review
... 13. A comet orbiting the Sun can be considered an isolated system with no outside forces or torques acting on it. As the comet moves in its highly elliptical orbit, what remains constant? A. Its distant from the Sun B. Its angular speed C. Its linear speed D. Its angular momentum E. The gravitationa ...
... 13. A comet orbiting the Sun can be considered an isolated system with no outside forces or torques acting on it. As the comet moves in its highly elliptical orbit, what remains constant? A. Its distant from the Sun B. Its angular speed C. Its linear speed D. Its angular momentum E. The gravitationa ...
Force = Mass x Acceleration - GZ @ Science Class Online
... When sky divers reach terminal velocity they are traveling at a constant speed. The forces of gravity accelerating the skydiver towards earth are matched exactly by the force of friction from the air particles pushing against the skydiver. If the person wears a more aerodynamic suit or points their ...
... When sky divers reach terminal velocity they are traveling at a constant speed. The forces of gravity accelerating the skydiver towards earth are matched exactly by the force of friction from the air particles pushing against the skydiver. If the person wears a more aerodynamic suit or points their ...
to full article
... This may be somewhat boring to the gung ho members but they do apply to our everyday lives. ...
... This may be somewhat boring to the gung ho members but they do apply to our everyday lives. ...
CP-S-HW-ch-8-detailed
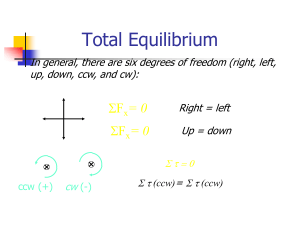
... object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forces act at the same point on the object. (d) The object is in equilibrium if the net force and ...
... object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forces act at the same point on the object. (d) The object is in equilibrium if the net force and ...
Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields
... ALWAYS found in pairs (N,S) while single electric charges (positive or negative) can be isolated. For example, if you cut a bar magnet in half each piece will have a N and S pole! 2) The forces between magnets are similar to those between electric charges in that the magnitude of the force varies in ...
... ALWAYS found in pairs (N,S) while single electric charges (positive or negative) can be isolated. For example, if you cut a bar magnet in half each piece will have a N and S pole! 2) The forces between magnets are similar to those between electric charges in that the magnitude of the force varies in ...
Chapter 5 - Mr. Theby
... Lever: a simple machine that consists of a bar that pivots at a fixed point called a fulcrum ◦ First Class Lever: The fulcrum is between the input force and the load, always change the direction of the input force. Ex: push down = load goes up ◦ Second Class Lever: The load is between the fulcrum an ...
... Lever: a simple machine that consists of a bar that pivots at a fixed point called a fulcrum ◦ First Class Lever: The fulcrum is between the input force and the load, always change the direction of the input force. Ex: push down = load goes up ◦ Second Class Lever: The load is between the fulcrum an ...