Chapter 9. Center of Mass and Linear Momentum
... ball, what value of m results in the larger ball stopping when it collides with the small ball? (b) What height does the small ball then reach (Fig. 970b)? ...
... ball, what value of m results in the larger ball stopping when it collides with the small ball? (b) What height does the small ball then reach (Fig. 970b)? ...
Physics Honors v. 2016
... Students will utilize the International System of Units to evaluate the size and scale of various objects and measurements, including distance, time, mass, Students will explain how the behavior of matter and energy follow predictable patterns that are ...
... Students will utilize the International System of Units to evaluate the size and scale of various objects and measurements, including distance, time, mass, Students will explain how the behavior of matter and energy follow predictable patterns that are ...
File
... Q 17 At what distance from the mean position is the kinetic energy in simple harmonic oscillaton equal to P.E ? Marks (3) View Answer Q 18 A simple pendulum of length l and having a bob of mass m is suspended in a car. The car is moving on a circular track of radius r with a uniform speed v. If the ...
... Q 17 At what distance from the mean position is the kinetic energy in simple harmonic oscillaton equal to P.E ? Marks (3) View Answer Q 18 A simple pendulum of length l and having a bob of mass m is suspended in a car. The car is moving on a circular track of radius r with a uniform speed v. If the ...
Vacuum friction in rotating particles - AUXILIARY
... is the partition function at temperature T . The first term in Eq. (1) reduces to hm|p̂(t)|mi = hm|p̂S |mi, and from here, we can recast (1) as Z ...
... is the partition function at temperature T . The first term in Eq. (1) reduces to hm|p̂(t)|mi = hm|p̂S |mi, and from here, we can recast (1) as Z ...
day 2 newtons laws review - Appoquinimink High School
... 5) The coefficient of static friction between a box and aramp is 0.5. The ramp’s incline angle is 30o. If the box is placed at rest on the ramp, the box will do which of the following? (A) accelerate down the ramp (B) accelerate briefly down the ramp, but then slow down and stop (C) move with const ...
... 5) The coefficient of static friction between a box and aramp is 0.5. The ramp’s incline angle is 30o. If the box is placed at rest on the ramp, the box will do which of the following? (A) accelerate down the ramp (B) accelerate briefly down the ramp, but then slow down and stop (C) move with const ...
PWE 8-12: A Simple Pulley I
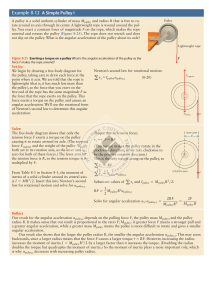
... We begin by drawing a free-body diagram for the pulley, taking care to draw each force at the point where it acts. We are told that the rope is lightweight (that is, it has much less mass than the pulley), so the force that you exert on the free end of the rope has the same magnitude F as the force ...
... We begin by drawing a free-body diagram for the pulley, taking care to draw each force at the point where it acts. We are told that the rope is lightweight (that is, it has much less mass than the pulley), so the force that you exert on the free end of the rope has the same magnitude F as the force ...
Ch3 - Momentum and Conservation of Momentum
... Conservation of mass states: The total mass of an isolated system is constant. To apply these, we must define a “system.” ...
... Conservation of mass states: The total mass of an isolated system is constant. To apply these, we must define a “system.” ...
Solve using elimination. When we are using the elimination method
... our first equation. Check in our second equation we substitute one for x plus our one for y and check to see if it is equal to two. Obviously two does equal two so it does check out. Our answer as an ordered pair would be one comma one. Solve using elimination. Here we have two equations and none of ...
... our first equation. Check in our second equation we substitute one for x plus our one for y and check to see if it is equal to two. Obviously two does equal two so it does check out. Our answer as an ordered pair would be one comma one. Solve using elimination. Here we have two equations and none of ...
Cons of Momentum, Gravity, Torque Study Guide
... ____ 13. In an inelastic collision between two objects with unequal masses, a. the total momentum of the system will increase. b. the total momentum of the system will decrease. c. the kinetic energy of one object will increase by the amount that the kinetic energy of the other object decreases. d. ...
... ____ 13. In an inelastic collision between two objects with unequal masses, a. the total momentum of the system will increase. b. the total momentum of the system will decrease. c. the kinetic energy of one object will increase by the amount that the kinetic energy of the other object decreases. d. ...
Course 3
... Some problems produce equations that have variables on both sides of the equal sign. Solving an equation with variables on both sides is similar to solving an equation with a variable on only one side. You can add or subtract a term containing a variable on both sides of an equation. ...
... Some problems produce equations that have variables on both sides of the equal sign. Solving an equation with variables on both sides is similar to solving an equation with a variable on only one side. You can add or subtract a term containing a variable on both sides of an equation. ...
MAXWELL`S EQUATIONS IN A CURVED SPACE TIME K. Ghosh
... In this article we will discuss a few mathematical aspects of classical electrodynamics. In Section 2 we will discuss an alternate derivation of the Poisson’s equation of electrostatics for the static sources [1]. It may not be possible to apply the Gauss’ divergence theorem to a vector field when t ...
... In this article we will discuss a few mathematical aspects of classical electrodynamics. In Section 2 we will discuss an alternate derivation of the Poisson’s equation of electrostatics for the static sources [1]. It may not be possible to apply the Gauss’ divergence theorem to a vector field when t ...
Explanation - Fort Bend ISD
... Masses attract one another about their centers with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them (whew!). ...
... Masses attract one another about their centers with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them (whew!). ...
Physics I Lab Packet
... It is apparent that Newton‟s Second Law is predictive, but does not provide an exact fit of the experimental data. Certain problems have been ignored; among these are the rotational inertia of the pulley and the friction of the pulley with its axle, the friction of the cart‟s wheels on their axles, ...
... It is apparent that Newton‟s Second Law is predictive, but does not provide an exact fit of the experimental data. Certain problems have been ignored; among these are the rotational inertia of the pulley and the friction of the pulley with its axle, the friction of the cart‟s wheels on their axles, ...