ComCMePr2c
... The designations are given in the caption signature to Figure 2. For angles a and iEa in work [2] are also given formulas, which depend on the ecliptic angles of orbits: Ωa, iеа etc. As a result of approximation of observation data S. Newcomb [3] has presented ecliptic angles as polynomials of the ...
... The designations are given in the caption signature to Figure 2. For angles a and iEa in work [2] are also given formulas, which depend on the ecliptic angles of orbits: Ωa, iеа etc. As a result of approximation of observation data S. Newcomb [3] has presented ecliptic angles as polynomials of the ...
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... FP = Ffr = µ k FN = µ k mg = ( 0.30 )( 35 kg ) 9.8 m s 2 = 103 = 1.0 × 10 2 N If the coefficient of kinetic friction is zero, then the horizontal force required is 0 N, since there is no friction to counteract. Of course, it would take a force to START the crate moving, but once it was moving, no fu ...
... FP = Ffr = µ k FN = µ k mg = ( 0.30 )( 35 kg ) 9.8 m s 2 = 103 = 1.0 × 10 2 N If the coefficient of kinetic friction is zero, then the horizontal force required is 0 N, since there is no friction to counteract. Of course, it would take a force to START the crate moving, but once it was moving, no fu ...
Elastic Collision
... SE Derive formulas for impulse from Newton’s third law ( FAB FBA ) and Newton’s second law ( F ma ) and kinematics formulas for acceleration ...
... SE Derive formulas for impulse from Newton’s third law ( FAB FBA ) and Newton’s second law ( F ma ) and kinematics formulas for acceleration ...
Newton`s Laws - Ipod Physics
... Newton’s third law simply says that forces come in pairs. You push on a wall and the wall pushes on you. We call these action/reaction force pairs. One of the skills most people master is walking. We rarely think about the act of walking – you don’t have to concentrate on it, it’s just something tha ...
... Newton’s third law simply says that forces come in pairs. You push on a wall and the wall pushes on you. We call these action/reaction force pairs. One of the skills most people master is walking. We rarely think about the act of walking – you don’t have to concentrate on it, it’s just something tha ...
Document
... is accelerating or rotating. An inertial reference frame is one in which Newton’s first law is valid. This excludes rotating and accelerating frames. How can we tell if we are in an inertial reference frame? By checking to see if Newton’s first law holds! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... is accelerating or rotating. An inertial reference frame is one in which Newton’s first law is valid. This excludes rotating and accelerating frames. How can we tell if we are in an inertial reference frame? By checking to see if Newton’s first law holds! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Acceleration - Cloudfront.net
... • Displacement: is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point. • Average speed: is the total distance traveled divided by the total time of travel. • Speed: is the distance an object travels per unit of time. ...
... • Displacement: is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point. • Average speed: is the total distance traveled divided by the total time of travel. • Speed: is the distance an object travels per unit of time. ...
Rigid Body Dynamics
... So far we have formulated classical mechanics in inertial frames of reference, i.e., those vector bases in which Newton’s second law holds (we have also allowed general coordinates, in which the Euler-Lagrange equations hold). However, it is sometimes useful to use non-inertial frames, and particula ...
... So far we have formulated classical mechanics in inertial frames of reference, i.e., those vector bases in which Newton’s second law holds (we have also allowed general coordinates, in which the Euler-Lagrange equations hold). However, it is sometimes useful to use non-inertial frames, and particula ...
Collisions M2 - Teachnet UK-home
... A uniform sphere A of mass m is moving with speed u on a smooth horizontal table when it collides directly with another uniform sphere B of mass 2m which is at rest on the table. The spheres are of equal radius and the coefficient of restitution between them is e. The direction of motion of A is unc ...
... A uniform sphere A of mass m is moving with speed u on a smooth horizontal table when it collides directly with another uniform sphere B of mass 2m which is at rest on the table. The spheres are of equal radius and the coefficient of restitution between them is e. The direction of motion of A is unc ...
Chapter 3: Motion and Forces Goals of Period 3
... Newton’s Law, F = M a, tells us that the amount of acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it. From the equation, we might expect that giving an object a push with a force F would cause it to accelerate forever, since Newton’s Law does not specify the duration of the ac ...
... Newton’s Law, F = M a, tells us that the amount of acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it. From the equation, we might expect that giving an object a push with a force F would cause it to accelerate forever, since Newton’s Law does not specify the duration of the ac ...
Mechanics and Properties of Matter Revision Questions Multiple
... A bicycle pump has its barrel full of air at a pressure of 1.0 x l05 Pa. The pressure in the tyre which is to be inflated is 1.5 x l05 Pa. If the original volume of air in the barrel is 600 cm3 and there is no temperature change during the movement of the piston, what will be the new volume of air i ...
... A bicycle pump has its barrel full of air at a pressure of 1.0 x l05 Pa. The pressure in the tyre which is to be inflated is 1.5 x l05 Pa. If the original volume of air in the barrel is 600 cm3 and there is no temperature change during the movement of the piston, what will be the new volume of air i ...
Earth Orientation: - Binary Research Institute
... 31,556,925.97s relative to a fixed frame of reference, implying that the position of the vernal equinox remains fixed with respect to the orientation of Earth’s axis in local space. The total number of rotations of Earth in such a complete orbit is expressed by the equations: 1 ÷ (1- (86164.0905382 ...
... 31,556,925.97s relative to a fixed frame of reference, implying that the position of the vernal equinox remains fixed with respect to the orientation of Earth’s axis in local space. The total number of rotations of Earth in such a complete orbit is expressed by the equations: 1 ÷ (1- (86164.0905382 ...
Chapter 2
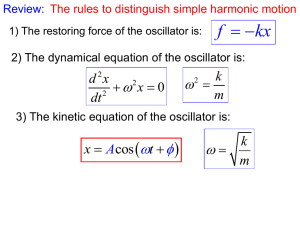
... 2) The state of the oscillator is determined by the parameters of amplitude A, angular frequency ωand phase angle φ. 3) ω is determined by the natural quantities of the system. A andφare determined by the system and the initial condition ...
... 2) The state of the oscillator is determined by the parameters of amplitude A, angular frequency ωand phase angle φ. 3) ω is determined by the natural quantities of the system. A andφare determined by the system and the initial condition ...